* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 15-3 Darwin presents his case
Survey
Document related concepts
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
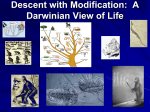
15-3 DARWIN PRESENTS HIS CASE PUBLICATION OF “ON THE ORIGIN OF THE SPECIES” 1859 ( 28 years after the Beagle) Darwin proposes a mechanism to explain the complexity of life. Theory: evolution has been going on for millions of years, and continues today. INHERITED VARIATION Members of every species vary from one another. This variation is important . With domesticated plants & animals, people have artificially selected desired traits. NATURAL SELECTION In nature, there is a struggle for existence. Those that are the best suited to their environment will survive and reproduce. Darwin called this ability fitness. SURVIVAL OF THE FITTEST Polar bear and walking stick Every generation, there will be some individuals that succeed better than others. They will live to reproduce, their traits going to their offspring. The less fit will die, or have fewer young. EVOLUTION Over time, natural selection results in changes in the inherited characteristics of a population. The changes increase a species’ fitness in their environment. Evolution of the horse DESCENT WITH MODIFICATION Each species alive today descended, with changes, from other species. • All species, living and extinct, were derived from common ancestors. • A single “tree of life” links us all together. • EVIDENCE: FOSSIL RECORD Fossils show that life has changed during earth’s history. Some species die out, others change and continue on. Fossil dinosaur, bat, early human HOMOLOGOUS BODY STRUCTURES Structures that develop from the same embryonic tissues, with different mature forms. All animals with backbones have similar body plans. The forelegs of birds, reptiles & mammals all have similar bones. The bones of birds closely resemble those of reptiles, where the bones of a bat’s wing resemble a mammalian pattern Vestigial organs Some organs in animals are greatly reduced in size- leaving only a trace, of the former structure. Examples: vestigial legs on skinks, vestigial pelvis in a humpback whale, human appendix. Embryos of species with a backbone are also very similar: cells develop in the same order, making similar tissues and organs in a wide variety of animals. SUMMARY OF DARWIN’S THEORY Inherited variation: all species have individuals that are slightly different from each other Over reproduction: species produce excess offspring Struggle for existence: there is competition to survive Natural selection: the weak will die off Survival of the fittest: the members best adapted to their environment will live to reproduce, and their traits will be passed on to their offspring. Satirical drawing of Darwin printed after publication of “On the Origin of Species”