* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Surface anatomy of lower limb
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
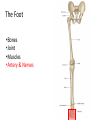
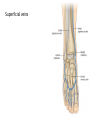
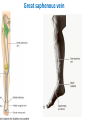
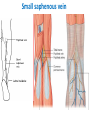
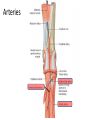
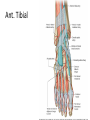
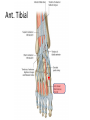
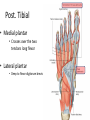
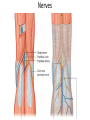
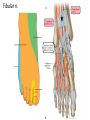
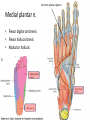
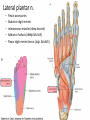
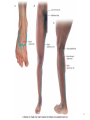
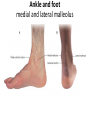
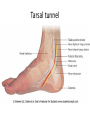
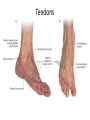
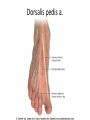
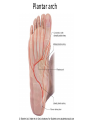
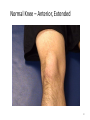
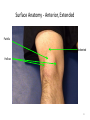
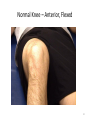
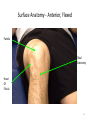
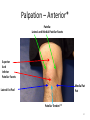
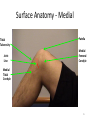
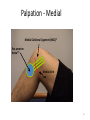
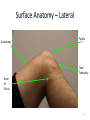
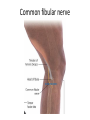
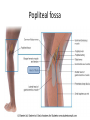
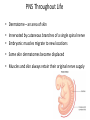
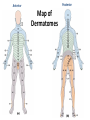
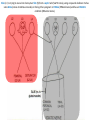
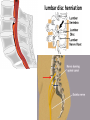
The Foot •Bones •Joint •Muscles •Artery & Nerves Superficial veins Great saphenous vein Small saphenous vein Arteries Ant. Tibial Dorsalis pedis artery Ant. Tibial Post. Tibial • Medial plantar • Crosses over the two tendons long flexor • Lateral plantar • Deep to flexor digitorum brevis Nerves Fibular n. Common plantar digital n. Medial plantar n. • Flexor digitorum brevis • Flexor hallucis brevis • Abductor hallucis Lateral plantar n. – – – – – Flexor accessories Abductor digiti minimi Interosseous muscles (deep brunch) Adductor hallucis (deep brunch) Flexor digiti minimi brevis (sup. brunch) Surface anatomy of lower limb 14 Ankle and foot medial and lateral malleolus Tarsal tunnel Tendons Dorsalis pedis a. Plantar arch Normal Knee – Anterior, Extended 20 Surface Anatomy - Anterior, Extended Patella Indented Hollow 21 Normal Knee – Anterior, Flexed 22 Surface Anatomy - Anterior, Flexed Patella Tibial Tuberosity Head Of Fibula 23 Palpation – Anterior* Patella: Lateral and Medial Patellar Facets Superior And Inferior Patellar Facets Medial Fat Pat Lateral Fat Pad Patellar Tendon** 24 Surface Anatomy - Medial Tibial Tuberosity Joint Line Patella Medial Femoral Condyle Medial Tibial Condyle 25 Palpation - Medial Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)* Pes anserine bursa** Medial joint line 26 Surface Anatomy – Lateral Quadriceps Patella Tibial Tuberosity Head Of Fibula 27 Common fibular nerve Injury to the common peroneal nerve • The common fibular nerve may be severed during fracture of the fibula neck. • Results in paralysis of all muscles in the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg. • The loss of eversion of the foot and dorsiflexion of the ankle causes footdrop. • Foot-drop: the foot drops and the toes drag of the floor when walking. Popliteal fossa PNS Throughout Life • Dermatome – an area of skin • Innervated by cutaneous branches of a single spinal nerve • Embryonic muscles migrate to new locations • Some skin dermatomes become displaced • Muscles and skin always retain their original nerve supply Posterior Anterior Map of Dermatomes Innervation of the Skin: Dermatomes • Upper limb – skin is supplied by nerves of the brachial plexus • Lower limb: Lumbar nerves – anterior surface Sacral nerves – posterior surface Elsie (L.3 ) is trying to rescue her clumsy man Slim (SI) from a septic tank (SciaTIC nerve), using a rope and a balloon. He has some GLUe (nerves to GLUteus muscles) on his leg. She is pregnant· is FEMale (FEMoral nerve) and has an OBstetric condition (OBturator nerve). lumbar disc herniation lumbar disc herniation Disc Level Root Comp. Weakness Reflex Involvement Sensory Loss Pain Distribution L3-L4 L4 quadriceps, tibialis anterior knee jerk medial knee and shin anterior thigh L4-L5 L5 extension of big toe no significant big toe back of thigh, lateral calf S1 gastrocnemius (ankle plantar flexion) Achilles lateral foot and heel back of thigh and calf L5-S1 Lower limb dermatomes • • • • • • • • • L1 Dermatome: over trochanter and groin L2 Dermatome: front of thigh to knee L3 Dermatome: upper buttock, anterior thigh and knee, medial lower leg L4 Dermatome: lateral Buttock, lateral thigh, medial leg, dorsum of foot, big toe L5 Dermatome: Buttock, posterior and lateral thigh, lateral aspect of leg, dorsum of foot, medial half of sole, first, second, and third toes S1 Dermatome: Buttock, thigh, and posterior leg S2 Dermatome: Buttock, thigh, and posterior leg S3 Dermatome: Groin, medial thigh to knee S4 Dermatome: Perineum, genitals, lower sacrum