* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NTI Day 9 - Russell County Schools
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
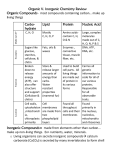
Russell County Schools Non-Traditional Instructional Expectations Day___9________ School: RCHS Course/Subject: Biology Teacher: Kelsey Learning Target: __Students will explain the differences between organic & inorganic compounds.______________ Lesson Expectations: Students will demonstrate their understanding of the differences that exist between organic & inorganic compounds by answering questions from reading passage. For Alternate Assignment Options: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QWf2jcznLsY Watch video and complete a ½ page summary For Supplemental Resources and Support: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QWf2jcznLsY For Teacher Support: [email protected] *Reminder: Assignments are due back to teachers within 2 school days. Day 9: Use the following reading passage as needed to answer questions 6-10. Biologically Important Molecules and Cellular Organization of Living Things Earth’s living environment is made up of millions and millions of diverse organisms, a wide range that includes towering redwood trees, sleek antelope, tiny bacteria, mushrooms that grow in huge circles, microscopic organisms that turn the tides red, and the students in your class. These living organisms are both similar to and different from each other. They also differ from the non-living parts of the environment. Although that difference may seem obvious, scientists have not been able to agree upon a simple definition of life. Most scientists agree that living things share certain characteristics that distinguish them from nonliving things, such as organized structures made of one or more cells, that carry out various chemical reactions (metabolism) able to maintain their cellular organization throughout life using energy to maintain life to grow and develop able to maintain a fairly stable internal environment (homeostasis) able to pass heredity information to new organisms of the same species in the process of reproduction Organization In unicellular (single-celled) organisms, the single cell performs all life functions. It functions independently. However, multicellular (many celled) organisms have various levels of organization within them. Individual cells may perform specific functions and also work together for the good of the entire organism. The cells become dependent on one another. Multicellular organisms have the following 5 levels of organization ranging from simplest to most complex: Chemical Compounds in Living Organisms There are two types of compounds (substances that contain more than one type of element): 1 Organic compounds – contain carbon, found in nature or organisms, may also contain H, O, or N and to a lesser extent P, S, Fe, Ca, Na, Cl, Mg, and K (relatively few elements compared to the number of elements on the periodic table). They are often very large and complex molecules. 2 Inorganic compounds – anything that is not organic is inorganic. As a rule, inorganic compounds do not contain C, but there are exceptions. Water Water is the most important inorganic compound! All organisms require water to survive. This is due to the fact that chemical reactions occur in water solutions. Without water, the cellular reactions cannot take place and the cell dies. Cohesion – cohesion is caused by the polarity of the water molecule, which as you know is caused by the covalent bond between O and each H. Because O is “stronger” than H, it pulls the shared electrons closer to it, making it “feel” negative. The H, on the other hand will “feel” positive and the molecule is called a polar molecule. The polarity of the water molecules causes an attractive force between them, resulting in cohesion. Adhesion – adhesion is defined as the attractive force between two different substances. Water is the best solvent because it adheres to many polar substances. Adhesion results in capillary action, which is the drawing up of water using very narrow glass tubing. Minerals Minerals are inorganic substances essential for cellular processes. Organic Molecules A organic molecule is one that typically consists of carbon atoms in rings or long chains, where other atoms (e.g. hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen) are attached. Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Most carbohydrates are made up of units of simple sugars called monosaccharides. Simple sugars bonded together create polysaccharides. Lipids Lipids unlike other carbohydrates are not soluble in water. Lipids include fats. Lipids are used in living systems to store energy. Proteins Proteins are macromolecules. They are constructed from one or more unbranched chains of amino acids; that is, they are polymers. A typical protein contains 200–300 amino acids but some are much smaller (the smallest are often called peptides) and some much larger (the largest to date is titin a protein found in skeletal and cardiac muscle; one version contains 34,350 amino acids in a single chain!). Every function in the living cell depends on proteins. Enzymes Enzymes are biological catalysts: this means that they speed up the chemical reactions in living things. Without enzymes, our guts would take weeks and weeks to digest our food, our muscles, nerves and bones would not work properly and so on -we would not be living! A catalyst is any substance which makes a chemical reaction goes faster, without itself being changed. A catalyst can be used over and over again in a chemical reaction: it does not get used up. Enzymes are very much the same except that they are easily denatured (destroyed: but do NOT use this word since the protein molecule is not broken down into amino-acids, it just loses it shape and will not work anymore) by heat. Our enzymes work best at body temperature. Our enzymes also have to have the correct pH. All enzymes are made of protein, whose building blocks are amino acids; that is why they are sensitive to heat, pH and heavy metal ions. Unlike ordinary catalysts, they are specific to one chemical reaction. An ordinary catalyst may be used for several different chemical reactions, but an enzyme only works for one specific reaction. Vitamins Vitamins are organic molecules with very important roles in the human body. Vitamin C D K Role in Humans Helps in healing wounds Growth of bones Clotting of blood Biologically Important Molecules 6. Some large insoluble food molecules are reduced to small, soluble food molecules by the process of: o A -digestion o B -excretion o C -response o D -growth 7. Which sequence is listed in order from simplest to most complex? o F – tissue -> cell -> organ system -> organ o G – cell -> tissue -> organ -> organ system o H – cell -> tissue -> organism -> organ o J – Organism -> tissue -> organ -> organ system 8. Living things are made mostly of these four main elements: o A – hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and protein o B – water, protein, carbohydrates, and fat o C – carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen o D – glucose, salt, mineral, and base 9. Enzyme molecules are synthesized primarily from: o A – amino acids o B -monosaccharides o C – fatty acids o D -phospholipids 10. The results of an experiment to determine the chemical composition of the cytoplasm of organism X are shown in the data table below: Substance Water Proteins Lipids Carbohydrates Minerals Percent by Mass in the Cytoplasm 77 15 5 2 1 What percentage of the cytoplasm is composed of organic material? o A -15 o B -20 o C -22 o D -92