* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Matching: Joints - Moore Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
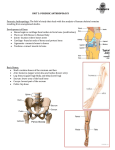
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. a) b) c) d) e) 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is: ____________________. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called _____________________. 4. In ossification, at around the time of birth, the center of each epiphysis begins to calcify. These areas are known as _________________ ossification centers. 5. What vitamin plays an important role in normal calcium absorption by bones? 6. Give TWO examples of flat bones. a) b) 7. When the calcium ion concentration of the blood rises above normal, the thyroid gland secretes ___________________________, which stimulates osteoblast activity. 8. Extension is defined as movement that ________________ the angle at a joint. 9. The outer covering of the bones that functions to nourish the bone are provide a surface upon which the tendons attach is the ________________________. 10. Twiddling your thumbs demonstrates the movement possible at the _______________ joint. 11. A pregnant woman does not receive enough calcium in her diet to satisfy the needs of the growing fetus. To compensate for the low levels of calcium in her blood, her body will secrete ___________________ hormone, which will stimulate _______________________ cells to begin breaking the calcium salts out of her bones. 12. What percentage of the bones in the body comprises the appendicular skeleton? 13. Of the following selections, the one that includes bones found exclusively in the axial skeleton is a) mandible, scapula, clavicle, sternum, ethmoid b) vertebrae, ischium, ilium, sphenoid, ribs c) frontal, cervical vertebrae, true ribs, sternum d) sacrum, occipital, scapula, ilium 14. What TWO (2) of the cranium are paired bones (they have a right & left bone)? a) b) 15. The suture that separates the frontal and parietal bones is the ___________________ suture. 16. The basic functional histological unit of the bone is the ______________________ system. 17. The opening on the skull that is a passageway for the brainstem and spinal cord to exit the skull is __________________________. 18. The large mass of ligaments that connects the two pubis bones and limits their movements is the ________________________. 19. The TWO (2) bones of the pectoral girdle include a) b) 20. The most massive and least mobile of the vertebrae are the ____________________. 21. What is the total number of bones in one foot? 22. Small fluid filled sacs found in and around synovial joints which function to pad and aid in smooth articulation are the _________________. 23. The wearing away of the articular cartilage due to age is called ____________________. 24. Ribs that have no connection to the sternum are called _______________ ribs. 25. The zygomatic arch is formed by the union of processes from what TWO (2) bones? a) b) 26. Bowed legs and weak bones are indicative of a person suffering from _________________. 27. Name TWO joints that are hinge joints? a) b) 28. The name given to C1 is ________________, while C2 is _____________________. 29. Red bone marrow is found in what type of bone in adults? 30. The three parts of the sternum are a) b) c) 31. The correct sequence of vertebrae from superior to inferior is a) b) c) d) e) 32. There are 85 named openings (foramen, canals, fissures, etc.) in the skull. What is their purpose? (p 132) 33. The first seven pairs of ribs are called true ribs, while the lower 5 pairs are called false ribs (the last two are specifically called floating). Why are they called false ribs? (p 153) 34. Name the three fused bones of the coxa. a) b) c) 35. The large posterior process on the scapula is the __________________ process. 36. The process of the humerus that articulates with the scapula is simply called the _______________. 37. What joint that permits the greatest range of motion of any joint in the body? 38. What four modifications for child bearing does the female pelvis exhibit? a) b) c) d) 39. Excessive growth hormone secretion before closure of the epiphyseal plates causes the disease known as _________________________. Matching 40. ____ Layers of calcified matrix 41. ____ “Residences” of osteocytes 42. ____ Longitudinal canal, carrying blood vessels and nerves 43. ____ Nonliving structural part of bone 44. ____ Tiny canals connecting lacunae a. b. c. d. e. Haversian (central) canal concentric lamellae lacunae canaliculi bony matrix 45. Classify each of the following terms as a projection (P), a depression (D), or an opening (O). (p134) _____ condyle _____ foramen _____ ramus _____ fossa _____ crest _____ head _____ spine _____ facet _____ fissure _____ meatus _____ tuberosity _____ sinus 46. A deficiency in calcium in the diet would lead to an increase in the hormone _________________ to be secreted into the blood. 47. An immovable joint is technically called __________________. 48. The organs protected by the thoracic cage include the ___________________ & the _____________. Ribs 1 – 7 are commonly called _________ ribs, whereas ribs 8 – 12 are called _______________ ribs. Ribs 11 & 12 are called ________________ ribs. All ribs articulate posteriorly with the __________________ and most connect anteriorly to the _________________, either directly by _________________ cartilage or indirectly. (p152) 49. An autoimmune disease resulting in inflammation and eventual fusion of a diarthritic joint is __________________________. 50. The special joint that is only found in the thumb of primates is the __________________. 51. Classify each of the following types of fractures. (p137 & notes) Matcing - Pelvic girdle (some will be used more than once) a) Acetabulum g) Iliac crest b) Anterior crest h) Ilium c) Calcaneus i) Ishium d) Femur j) Lateral malleolus e) Fibula k) Medial malleolus f) Greater & lesser l) Metatarsals trochanters m) Patella n) o) p) q) r) s) Pubic symphysis Pubis Sacroiliac joint Tarsals Tibia Tibial tuberosity 52. ____, ____, ____ 3 bones that fuse to form the hip 53. ____, ____, ____ 3 bones forming the knee joint 54. ____ Sites of muscle attachment on the proximal end of the femur 55. ____ Receives the weight of the body when sitting 56. ____ Bones forming the instep of the foot 57. ____ Point where the coxal bones join anteriorly 58. ____ Bones of the ankle 59. ____ Upper margin of the iliac bones 60. ____ Deep socket in the coxal bone that receives the head of the thigh bone 61. ____ Heel bone 62. ____ Process forming the outer ankle 63. ____ Longest bone of the body 64. ____ Lateral bone of the lower leg 65. ____ Point where the patellar ligament attaches 66. ____ The shin 67. ____ The kneecap 68. ____ Distal process on the medial tibial surface 69. ____ Lower leg bone that supports most of your body weight Matching – Pectoral girdle (some will be used more than once) a) Acromium g) Glenoid b) Capitulum h) Humerus c) Carpals i) Metacarpals d) Clavicle j) Olecranon e) Coracoid k) Phalanges f) Coronoid l) Radial tuberosity m) Radius n) Scapula o) Styloid p) Trochlea q) Ulna 70. ____, ____ 2 bones of the shoulder 71. ____, ____ 2 bones of the forearm 72. ____ Point on the scapula where the clavicle connects 73. ____ Socket in the scapula for the upper arm bone 74. ____ Process on the glenoid fossa that permits muscle attachment 75. ____ The collarbone 76. ____ Form the palm of the hand 77. ____ Upper arm bone 78. ____ Rounded knob of the humerus that articulates with the radius 79. ____ Bones of the wrist 80. ____ Distal medial process on the humerus that articulates with the ulna 81. ____ The fingers have three of these bones, but the thumb only has two 82. ____ Depression on the anterior side of the humerus that receives part of the forearm when flexed Matching – Skull (some will be used more than once) a) Coronal h) Mandible b) Ethmoid i) Mastoid c) Foramen magnum j) Maxilla d) Frontal k) Mental e) Infraorbital l) Nasal f) Lacrimal m) Occipital g) Lambdoid n) Palatine o) p) q) r) s) t) Parietal Sagittal Sphenoid Temporal Vomer Zygomatic 83. ____, ____ 2 bones that form the zygomatic arch (Hint: zygomatic bone is one of them) 84. ____, ____ 2 bones separated by the lambdoid suture 85. ____, ____ 2 paired bones of the cranium 86. ____ Bones of the roof of your mouth 87. ____ Forehead bone 88. ____ Jaw bone 89. ____ Hole at the base of the skull though which the spinal column passes 90. ____ Openings below the eye sockets 91. ____ Openings on the jaw bone 92. ____ Joint between the two parietal bones Matching: Axial skeleton (some will be used more than once) a) Cervical e) Lumbar b) Coccyx f) Manubrium c) False g) Sacrum d) Floating h) Thorasic i) j) True Xiphoid 93. ____ Ribs with no attachment to the sternum 94. ____ Inferior most part of the sternum 95. ____ Neck bones 96. ____ Lower back bones 97. ____ These 7 pairs of ribs each have their own cartilage attachment to the sternum 98. ____ Bones that were once a “pre-evolutionary” tail 99. ____ Part of the sternum that articulates with the clavical Matching: Joints a) Ball & socket b) Hinge c) Pivot 100. 101. 102. 103. 104. 105. 106. ____ C-1 / C-2 ____ Thumb ____ Knee ____ Coronal suture ____ Carpals ____ Hip ____ Pubic symphysis d) Amphiarthrosis e) Gliding f) Condyloid g) Synarthrosis h) Saddle