* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gause`s competitive exclusion principle and “the
Animal genetic resources for food and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Ecogovernmentality wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Natural resource economics wikipedia , lookup
Environmental resource management wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
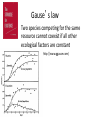
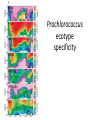
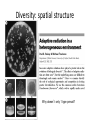
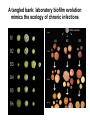
Gause’s competitive exclusion principle and “the paradox of the plankton” 713/813 Lecture 10 Gause’s law Two species competing for the same resource cannot coexist if all other ecological factors are constant (http://www.ggause.com) How do we define “niche” • Class: “A set of conditions (resource, environmental, biotic) that an organism exploits/inhabits best to avoid competition” • Hutchinson: “an N-dimensional hypervolume” But why are some ecosystems so diverse? The paradox of the plankton The problem that is presented by the phytoplankton is essentially how it is possible for a number of species to coexist in a relatively isotropic or unstructured environment all competing for the same sorts of materials The phytoplankton of which Hutchinson speaks Prochlorococcus, the most abundant photosynthetic organism on the planet How is diversity maintained? • How can a liter of seawater have at least 1,000,000 bacteria and 20,000 bacterial species? Prochlorococcus ecotype specificity Possible explanations • Predation and parasitism -related tradeoffs • Frequency-dependent selection (advantage when rare) • Resource partitioning and cross-feeding • Ecological subdivision (spatial structure, niche subdivision) • Dispersal creates environmental variability (could speed up evolution) • Symbioses and co-evolution Diversity resulting from predation/parasitism Diversity: parasitism With phage Without phage Diversity: frequency-dependence Diversity: resource partitioning (illustrating periodic selection) Diversity: spatial structure Why doesn’t only 1 type prevail? A tangled bank: laboratory biofilm evolution mimics the ecology of chronic infections t = 1000