* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Threads - IFSC-USP
Library (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Linux adoption wikipedia , lookup
Plan 9 from Bell Labs wikipedia , lookup
Berkeley Software Distribution wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Process management (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Copland (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed operating system wikipedia , lookup
Mobile operating system wikipedia , lookup
Spring (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
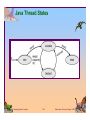
Chapter 5: Threads n Overview n Multithreading Models n Threading Issues n Pthreads n Solaris 2 Threads n Windows 2000 Threads n Linux Threads n Java Threads Operating System Concepts 5.1 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Single and Multithreaded Processes Operating System Concepts 5.2 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Benefits n Responsiveness n Resource Sharing n Economy n Utilization of MP Architectures Operating System Concepts 5.3 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 User Threads n Thread management done by user-level threads library n Examples - POSIX Pthreads - Mach C-threads - Solaris threads Operating System Concepts 5.4 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Kernel Threads n Supported by the Kernel n Examples - Windows 95/98/NT/2000 - Solaris - Tru64 UNIX - BeOS - Linux Operating System Concepts 5.5 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Multithreading Models n Many-to-One n One-to-One n Many-to-Many Operating System Concepts 5.6 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Many-to-One n Many user-level threads mapped to single kernel thread. n Used on systems that do not support kernel threads. Operating System Concepts 5.7 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Many-to-One Model Operating System Concepts 5.8 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 One-to-One n Each user-level thread maps to kernel thread. n Examples - Windows 95/98/NT/2000 - OS/2 Operating System Concepts 5.9 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 One-to-one Model Operating System Concepts 5.10 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Many-to-Many Model n Allows many user level threads to be mapped to many kernel threads. n Allows the operating system to create a sufficient number of kernel threads. n Solaris 2 n Windows NT/2000 with the ThreadFiber package Operating System Concepts 5.11 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Many-to-Many Model Operating System Concepts 5.12 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Threading Issues n Semantics of fork() and exec() system calls. n Thread cancellation. n Signal handling n Thread pools n Thread specific data Operating System Concepts 5.13 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Pthreads n a POSIX standard (IEEE 1003.1c) API for thread creation and synchronization. n API specifies behavior of the thread library, implementation is up to development of the library. n Common in UNIX operating systems. Operating System Concepts 5.14 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Solaris 2 Threads Operating System Concepts 5.15 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Solaris Process Operating System Concepts 5.16 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Windows 2000 Threads n Implements the one-to-one mapping. n Each thread contains - a thread id - register set - separate user and kernel stacks - private data storage area Operating System Concepts 5.17 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Linux Threads n Linux refers to them as tasks rather than threads. n Thread creation is done through clone() system call. n Clone() allows a child task to share the address space of the parent task (process) Operating System Concepts 5.18 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Java Threads n Java threads may be created by: F Extending Thread class F Implementing the Runnable interface n Java threads are managed by the JVM. Operating System Concepts 5.19 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002 Java Thread States Operating System Concepts 5.20 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2002