* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Neurological System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
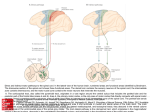
The Neurological System M. DuBois Fennal, PhD, RN, CNS, The Central Nervous System • Brain • Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System • Cranial Nerves • Spinal Nerves – Afferent (toward) – Efferent (away) Somatic Nervous System • Regulate voluntary motor control Autonomic Nervous System • Involve regulation of the body’s internal environment (viscera) through involuntary control or organ system Sympathetic Nervous System • Makes everything go faster – Heart rate – Respirations – Dilates pupils – Increase peristalses – Increase the urge to void – CAUSES ADNERGIC RESPONSE Parasympathetic • Slows everything down – Heart rate – Respirations – Peristalsis – CAUSES CHOLERNERGIC RESPONSES Neuron • Uses glucose as fuel to maintain homeostasis in the neurological environment • Sensory neurons (afferent) • Associational (from neuron to neuron sensory to motor) • Motor neurons (efferent) Neuroglia and Schwann Cells • Support the neurons Nerve Injury and Regeneration • Mature nerve cells do not generate • New research shows that if a damage nerve cell is near a neural tube it may somehow go back to into the tube, and produce movement that can be enhanced with rehabilitation. Synapses • Needed, a chemical, an electrical stimulus, a chemical and electrical stimulus • Nerve impulses have to jump from one area to the other because the neurons are not continuous. Neuro transmitters • Norepinephrine • Amino Acids The Cranium • Protects the brain • Is inflexible after a certain age • Can tolerate little expansion within the cavity. Meninges • Surround • Protect • Pia mater follows the contour of the brain and the spinal cord. Provide support for the blood vessels supplying the brain. • The choroid plexuses produces the spinal fluid Central Nervous System (Brain) • Weight 3 pounds • Utilizes 15% of the blood from each cardiac output • Necessary for vital functions, personality, intellect, and interaction with the environment • Control – Prefrontal area responsible for goal oriented behavior (concentration, short term memory, recall memory, reasoning and inhibition – Pre-motor are responsible for programming motor movement, including movement of the eyes • Primary motor area (specific motor movement) • Broca speech area is usually left hemisphere, responsible for motor part of speech (damage to the area causes aphasia (the inability to form words). • Parietal lobe • Involved in sensory association storage analysis interpretation • Occipital lobe – Vision • Temporal lobe – Auditory interpretation – Reception and interpretation of the spoken word (Wernicke area) – Long term memory – Balance – Taste – Smell • Limbic system – Primitive behavior emotion, feelings, biologic rhythms and sense of smell Diencephalon • The thalmus is a relay station • The hypothalmus maintains the environment and integrate behavior patterns, endocrine function, and regulate emotional function. Midbrain • Responsible for visual movement • Auditory movement • Communication with the spinal cord • Synthesization of dopamine a precursor of norepinephrine • Transports spinal fluid (aqueduct of Sylvius) Hindbrain • Responsible for reflexive and fine motor movement, balance, posture Myelencephalon • Responsible for – Respirations – Heart rate – Blood pressure – Sneezing, coughing, swallowing, vomiting – Sleep wake center Spinal Cord • Communication between the brain, the nerves, the muscles, the reflexes and the body. Cerebrospinal Fluid • Protects and bathe the brain and the spinal cord • Pressure 5 to 14 mmHg Vertebral Column • Thirty three verterbrae Blood Supply to the brain • Internal carotid arteries • Vertebral arteries – Anterior cerebral artery – Middle cerebral artery – Posterior cerebral artery – Circle of Willis Blood supply to the spinal cord • Vertebral arteries • Aorta (branches) • Posterior spinal arteries Peripheral Nervous system • The cranial and spinal nerves • Page 315 figure 12-22 and table 12-6