* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Liver - The Practical Educator
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
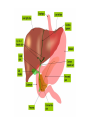
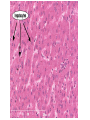
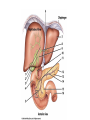
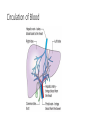
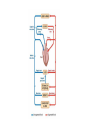
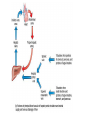
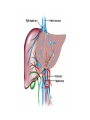
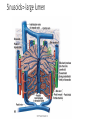
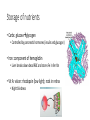
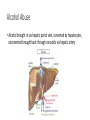
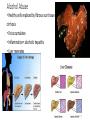
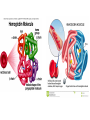
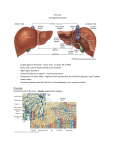
The Liver HL IB Bio Mrs. Whitman and Mr. Everhart Circulation of Blood Sinusoids=-large lumen Lobule: Sinusoids Kupffer=phagocytes Nutrient Storage • Homeostasis • Sugar+salt=osmolarity (osmolues/ liter) • Extra amino acids • No matter meal, liver maintains and regulates nutrients • Ex: sugar 90mg/100mL • Extra glucose=glycogen in hepatocytes; if in need turn into glucose Nutrient Storage • Ex: extra amino acids=ammoniaurea Storage of nutrients • Carbs: glucoseglycogen • Controlled by pancreatic hormones (insulin and glucagon) • Iron: component of hemoglobin • Liver breaks down dead RBC and stores Fe in ferritin • Vit A: vision: rhodopsin (low light); rods in retina • Night blindness Storage of Nutrients cont • Vit D: uptakes Ca; prevents rickets • B12: helps nerve and blood cells • Prevents anemia Liver synthesizes plasma proteins & cholesterol • Plasma proteins • Albumin- osmotic pressure (tendency to uptake water) • Fibrinogen- precursor for fibrin (clots blood) Detox • Hepatocytes have enzymes that break down toxins • • • • Alcohol Preservatives Herbicides Nicotine Alcohol Abuse • Alcohol brought in via hepatic portal vein, converted by hepatocytes, unconverted brought back through sinusoids via hepatic artery Alcohol Abuse • Healthy cells replaced by fibrous scar tissue cirrhosis • Fat accumulates • Inflammation= alcoholic hepatitis • Liver regerates Erythrocyte and hemoglobin break down • RBS rupture after 120 days • Kupffer cells break down hemoglobin into globin and heme • Globin is broken down into amino acids and returned into the blood to later be used in protein synthesis • Heme broken down into Iron and bilirubin (bile pigment) • Iron is either stored or sent to bone marrow to contribute to new RBC • Bilirubin is absorbed by hepatocytes and used to synthesize bile