* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MGS43 Geometry 3 Fall Curriculum Map
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Conic section wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
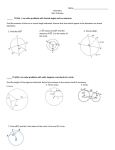
MGS43 MGS43 MGS43 GEOMETRY 3 CURRICULUM MAP Month Essential Content Questions September How do we find 1. Properties of Circles the measures of 2. Segments of Circles ‐ resulting angles, Tangent, Chords, Secants arcs, and 3. Properties of Tangents segments when 4. Central and Inscribed Angles lines intersect a circle, or within a circle? NYS Standard MGS43 Skill CCLS Standard G‐C 2 2. Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius intersects the circle. G‐C 3 3. Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle, and prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. G.G.50 Investigate, justify, and apply theorems about tangent lines to a circle: o o o 1. Identify parts of a circle 2. Identify special segments and lines 3. Use properties of tangents 4. Draw common tangent 5. Find measure of central and inscribed angles 6. Find the measure of an intercepted arc MGS43 Assessments Homework Chapter Test Quiz Project on circles about relationships of the following: ‐ Inscribed Angles ‐ Central Angles a perpendicular to the tangent at the point of tangency two tangents to a circle from the same external point common tangents of two non‐intersecting or tangent circles G.G.51 Investigate, justify, and apply theorems about the arcs determined by the rays of angles formed by two lines intersecting a circle when the vertex is: Ms. Lim o o October How do we use the properties and theorems involving circles to calculate the measures of angles and segments relating to circles? NYS Standard inside the circle (two chords) on the circle (tangent and chord) G‐C 2 Homework 2. Identify and describe Chapter Test Quiz relationships among inscribed Project on circles about angles, radii, and chords. Include relationships of the following: the relationship between central, ‐ Length of Segments of inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a a Circle diameter are right angles; the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius intersects the circle. G‐C 3 3. Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle, and prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. G.G.51 Investigate, justify, and apply theorems about the arcs determined by the rays of angles formed by two lines intersecting a circle when the vertex is: 1. Tangent Chord Angles 2. Angles formed inside a circle by intersecting chords 3. Angles formed outside a circle using secants and tangents 4. Lengths of Segments o o o 1. Find the measure of tangent chord angles 2. Find the measure of angles formed by intersecting chords 3. Find the measure of angles formed outside a circle using secants and tangents 4. Find the length of segments formed by intersecting chords 5. Find the length of segments formed by an intersecting tangent and secant 6. Find the length of segments formed by an intersecting secants inside the circle (two chords) on the circle (tangent and chord) outside the circle (two tangents, two secants, or tangent and secant) G.G.52 Investigate, justify, and apply theorems about arcs of a circle cut by two parallel lines Ms. Lim G.G.53 Investigate, justify, and apply theorems regarding segments intersected by a circle: o o o o November What are the basic tools used for a geometric construction? What is the difference between sketching a geometric figure and constructing a geometric figure? How do we write the equation of a circle in the coordinate plane? Ms. Lim along two tangents from the same external point along two secants from the same external point along a tangent and a secant from the same external point along two intersecting chords of a given circle 1. Geometric Constructions 2. Locus 3. Equation of a Circle 1. 2. 3. 4. Copy a Segment/Angle Bisect a Segment/Angle Construct Perpendicular Lines Construct perpendicular bisectors of segment. 5. Construct a line that is parallel to a given line through a given point 6. Construct an equilateral triangle using a given segment 7. Construct an isosceles triangle using given segments 8. Sketch on the same diagram the locus of points satisfying two given conditions and locate the point(s) of intersection of these loci 9. Write the equations of the locus of points at a given distance from a given line 10. Write the equation of the locus of points equidistant from two parallel lines 11. Write the equations of the locus of points equidistant from two G‐CO 12 Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. G‐GPE 1 Derive the equation of a circle of given center and radius using the Pythagorean Theorem Homework Chapter Test Quiz Project on Equation of a Circle NYS Standard December How can we change a figure’s position without changing its size and shape? How can we Ms. Lim intersecting lines 12. Write the equation of the locus of points equidistant from two given points 13. Write the equation of the locus of points at a given distance from a given point 14. Graph a circle given its equation 15. Find the radius of a circle given an equation 16. Write the equation of a circle given its graph G.G.17 Construct a bisector of a given angle, using a straightedge and compass, and justify the construction G.G.18 Construct the perpendicular bisector of a given segment, using a straightedge and compass, and justify the construction G.G.19 Construct lines parallel (or perpendicular) to a given line through a given point, using a straightedge and compass, and justify the construction G.G.20 Construct an equilateral triangle, using a straightedge and compass, and justify the construction G.G.71 Write the equation of a circle, given its center and radius or given the endpoints of a diameter G.G.72 Write the equation of a circle, given its center and radius or given the endpoints of a diameter Note: The center is an ordered pair of integers and the radius is an integer. G.G.73 Find the center and radius of a circle, given the equation of the circle in center‐radius form G.G.74 Graph circles of the form (x − h)2 + (y − k)2 = r2 1. Transformations 1. Identify and apply rules of G‐CO 2 Homework 2. Translations transformations Represent transformations in the Chapter Test 3. Reflections 2. Apply a composition of plane using, e.g., transparencies Quiz and geometry software; describe Project on transformations 4. Rotations transformations 5. Dilations 3. Using the slope, midpoint, and transformations as functions that 6. Composition of distance formulas take points in the plane as inputs Transformations and give other points as outputs. change a figure’s size without changing its shape? How can we represent a transformation in the coordinate plane? Ms. Lim 7. Midpoint 8. Distance 9. Slope Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch). G‐CO 4 Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments. G‐CO 5 Given a geometric figure and a rotation, reflection, or translation, draw the transformed figure using, e.g., graph paper, tracing paper, or geometry software. Specify a sequence of transformations that will carry a given figure onto another. G‐SRT 1 Verify experimentally the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor: A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center NYS Standard G.G.54 G.G.55 G.G.56 G.G.57 G.G.58 G.G.59 Ms. Lim unchanged. The dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio given by the scale factor. A – REI 3 Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters. G – GPE 5 Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and use them to solve geometric problems (e.g., find the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a given point). Define, investigate, justify, and apply isometries in the plane (rotations, reflections, translations, glide reflections) Note: Use proper function notation. Investigate, justify, and apply the properties that remain invariant under translations, rotations, reflections, and glide reflections Identify specific isometries by observing orientation, numbers of invariant points, and/or parallelism Justify geometric relationships (perpendicularity, parallelism, congruence) using transformational techniques (translations, rotations, reflections) Define, investigate, justify, and apply similarities (dilations and the composition of dilations and isometries) Investigate, justify, and apply the properties that remain invariant under similarities G.G.60 G.G.61 January Ms. Lim How do we calculate the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a 13‐ sided polygon? How do we calculate the measure of each interior angle of a regular polygon with 12 sides? What is the difference between the properties of the diagonals of a square and the properties of the diagonals of a rectangle? What is the difference between the properties of the 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identify specific similarities by observing orientation, numbers of invariant points, and/or parallelism Investigate, justify, and apply the analytical representations for translations, rotations about the origin of 90º and 180º, reflections over the lines x =0, y = 0, and y = x, and dilations centered at the origin Interior and Exterior Angles 1. Identify and apply properties of G‐GPE 4 Homework of Convex Polygons Quadrilaterals Use coordinates to prove simple Chapter Test Properties of Quadrilaterals geometric theorems algebraically. Quiz 2. Identify and apply properties of For example, prove or disprove Parallelograms Project on quadrilaterals Special Quadrilaterals Special Parallelograms that a figure defined by four given Trapezoids points in the coordinate plane is a 3. Organize and write two column rectangle; prove or disprove that and coordinate proofs the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2). G‐CO 11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include: opposite sides are congruent, opposite angles are congruent, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, and conversely, rectangles are parallelograms with congruent diagonals. diagonals of a parallelogram and the properties of the diagonals of a rhombus? Why is a trapezoid not considered a special parallelogram? NYS Standard G.G.36 G.G.37 G.G.38 G.G.39 G.G.40 G.G.41 Teacher Resources McDougal Littell Geometry Textbook Amsco Geometry Textbook Barrons Let’s Review Geometry Ms. Lim Investigate, justify, and apply theorems about the sum of the measures of the interior and exterior angles of polygons Investigate, justify, and apply theorems about each interior and exterior angle measure of regular polygons Investigate, justify, and apply theorems about parallelograms involving their angles, sides, and diagonals Investigate, justify, and apply theorems about special parallelograms (rectangles, rhombuses, squares) involving their angles, sides, and diagonals Investigate, justify, and apply theorems about trapezoids (including isosceles trapezoids) involving their angles, sides, medians, and diagonals Justify that some quadrilaterals are parallelograms, rhombuses, rectangles, squares, or trapezoids Media Resources McDougal Littell Classzone ‐ Online Textbook Geometer's Sketchpad Jefferson Math Project ‐ jmap.org Khan Academy ‐ khanacademy.org Regents Exam Prep Center ‐ regentsprep.org Ms. Lim