* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants pretest
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
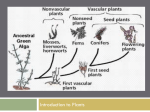
Plants Pretest 1. Meristematic tissues in plants are composed of cells specialized for cell division. These types of cells are most likely to be found in what part of the plant? A. B. C. D. E. Leaf epidermis Stem tips Vascular tissue Root tips Both b and d 2. This diagram shows an array (variety) of grass plants. You may notice that the majority of their plant body is underground with an abundance of root hairs. Which of the following would best explain the benefit of this particular adaptation? A. Improved ability to detect areas high in carbon dioxide B. More resistance to insecttransmitted disease C. Increased ability to maintain cooler leaf temperatures D. More surface area for absorption of water E. Increased photosynthetic ability 3. Stomata have the ability to open and close to aid the plant in its ability to survive in a terrestrial environment. Stomata open and close with the help of which of the following? A. Guard cells B. Accessory cells C. The cuticle D. Chloroplast E. None of the above 4. How do gymnosperms and angiosperms differ? A. Gymnosperms produce fruits while angiosperms produce pollen B. Gymnosperms produce pollen while angiosperms produce seeds C. Gymnosperms produce cones while angiosperms produce flowers D. Gymnosperms produce flowers while angiosperms produce cones E. Gymnosperms produce flowers while angiosperms produce pine needles 5. Which of the following has the name of an angiosperm’s male/female reproductive organ matched with the appropriate structures that form them. A. B. C. D. E. Stamen: Stigma, Style, Ovary Pistil: Filament, Anther Stamen: Sepals, Filament Pistil: Petals, Ovary Stamen: Filament, Anther Pistil: Stigma, Style, Ovary Stamen: Anther, Ovary Pistil: Ovule, Ovary, Filament Stamen: Seeds Pistil: Fruits 6. Which of these statements best explains the process of energy conversion that takes place in the mitochondria? C6H12O6 + 6 H2O 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ~36 ATP A. Energy is required for carbon dioxide molecules to form six-carbon sugar molecules. B. Water molecules and radiant energy are necessary for anaerobic respiration to take place. C. Oxygen molecules release energy in the form of heat during combustion reactions. D. The energy in the bonds of glucose molecules is transferred to the phosphate bonds in ATP. 7. A botanist has received a new species of plant from a rainforest in Central America. Which of the following represents an adaptation that this plant might possess? A. B. C. D. E. Needle-like leaves Broad leaves Narrow leaves All of the above None of the above 8. Which of the following is an example of plant structures showing an adaptation to their environment/biome? A. Waxy covering called a cuticle to prevent overexposure to sunlight B. Thick tree bark to protect from cold temperatures C. Lack of anthers to prevent reproduction D. Evergreen trees with needle-like leaves to prevent the picking of fruit E. Male pine cones growing low on the tree to ensure pollination 9. Many vegetables (ex. Carrots and beets) store glucose, made during photosynthesis. Since this type of storage unit is underground this portion of the plant is unable to photosynthesize. When glucose is transported to the site of storage by phloem, which two systems are working together? A. B. C. D. E. Root and reproductive Root and vascular Vascular and reproductive Muscular and vascular Reproductive and digestive 10. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs in the leaves of plants. The carbon dioxide is used to help harness energy from the sun. Plants use the energy for many functions. One of which is the production of flowers. When a plant’s phloem transports glucose to the site of flower production a flower’s the reproductive system is working primarily with A. B. C. D. E. The root system The vascular system The immune system The excretory system The integumentary system Plants Pretest 1. Meristematic tissues in plants are composed of cell specialized for cell division. These types of cells are most likely to be found in what part of the plant? A. B. C. D. E. Leaf epidermis Stem tips Vascular tissue Root tips Both b and d 2. This diagram shows an array (variety) of grass plants. You may notice that the majority of their plant body is underground with an abundance of root hairs. Which of the following would best explain the benefit of this particular adaptation? A. Improved ability to detect areas high in carbon dioxide B. More resistance to insecttransmitted disease C. Increased ability to maintain cooler leaf temperatures D. More surface area for absorption of water E. Increased photosynthetic ability 3. Stomata have the ability to open and close to aid the plant in its ability to survive in a terrestrial environment. Stomata open and close with the help of which of the following? A. Guard cells B. Accessory cells C. The cuticle D. Chloroplast E. None of the above 4. How do gymnosperms and angiosperms differ? A. Gymnosperms produce fruits while angiosperms produce pollen B. Gymnosperms produce pollen while angiosperms produce seeds C. Gymnosperms produce cones while angiosperms produce flowers D. Gymnosperms produce flowers while angiosperms produce cones E. Gymnosperms produce flowers while angiosperms produce pine needles 5. Which of the following has the name of an angiosperm’s male/female reproductive organ matched with the appropriate structures that form them. A. B. C. D. E. Stamen: Stigma, Style, Ovary Pistil: Filament, Anther Stamen: Sepals, Filament Pistil: Petals, Ovary Stamen: Filament, Anther Pistil: Stigma, Style, Ovary Stamen: Anther, Ovary Pistil: Ovule, Ovary, Filament Stamen: Seeds Pistil: Fruits 6. Which of these statements best explains the process of energy conversion that takes place in the mitochondria? C6H12O6 + 6 H2O 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ~36 ATP A. Energy is required for carbon dioxide molecules to form six-carbon sugar molecules. B. Water molecules and radiant energy are necessary for anaerobic respiration to take place. C. Oxygen molecules release energy in the form of heat during combustion reactions. D. The energy in the bonds of glucose molecules is transferred to the phosphate bonds in ATP. 7. A botanist has received a new species of plant from a rainforest in Central America. Which of the following represents an adaptation that this plant might possess? A. B. C. D. E. Needle-like leaves Broad leaves Narrow leaves All of the above None of the above 8. Which of the following is an example of plant structures showing an adaptation to their environment/biome? A. Waxy covering called a cuticle to prevent overexposure to sunlight B. Thick tree bark to protect from cold temperatures C. Lack of anthers to prevent reproduction D. Evergreen trees with needle-like leaves to prevent the picking of fruit E. Male pine cones growing low on the tree to ensure pollination 9. Many vegetables (ex. Carrots and beets) store glucose, made during photosynthesis. Since this type of storage unit is underground this portion of the plant is unable to photosynthesize. When glucose is transported to the site of storage by phloem, which two systems are working together? A. B. C. D. E. Root and reproductive Root and vascular Vascular and reproductive Muscular and vascular Reproductive and digestive 10. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs in the leaves of plants. The carbon dioxide is used to help harness energy from the sun. Plants use the energy for many functions. One of which is the production of flowers. When a plant’s phloem transports glucose to the site of flower production a flower’s the reproductive system is working primarily with A. B. C. D. E. The root system The vascular system The immune system The excretory system The integumentary system Grading Scale Number of Q’s Missed Grade 1 90 2 80 3 70 4 60 5 50 6 40 7 30 8 20 9 10 10 0