* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 10- The Cold War
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Mutual assured destruction wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Soviet atomic bomb project wikipedia , lookup
Canada in the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Single Integrated Operational Plan wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
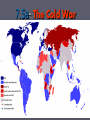
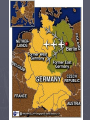
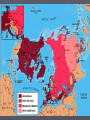
7.5a- The Cold War 7.5a Analyze the impact of the Cold War on national security and individual freedom, including the containment policy and the role of military alliances, the effects of the “Red Scare” and McCarthyism, the conflicts in Korea and the Middle East, the Iron Curtain and the Berlin Wall, the Cuban missile crisis, and the nuclear arms race. The Cold War The Cold War Begins ***After World War II tensions were high between the former allies. (US and Soviet Union) ► The United States and Great Britain were determined not occupy the conquered territories for very long. ► ***The Soviet Union on the other hand had suffered great losses and was determined not to be invaded again. ► ***Stalin decided to maintain control over Eastern Europe as a buffer zone. He went back on his promises to help rebuild a democratic Germany and for free elections in Poland. ► Stalin ruthlessly stomped out anti-communist opposition in the territories his army overran in World War II. ► ***Europe became divided between the western democracies, and the Soviet Satellite Nations. ► The Russians refused to allow much travel between the communist Europe and the Democratic Europe. ► Iron Curtain Speech- Winston Churchill gave a speech at Westminster college in Missouri and he said, “A shadow has fallen… and iron curtain has descended across the continent.” The result of this speech was that the dividing line between eastern and western Europe became known as the Iron Curtain. ► US Post-War Policies in Europe ► Many believed that eastern Europe could not be saved from Soviet domination without a major war and therefore the United States and the western democracies should concentrate on a strategy of *** containment- keeping communism in countries where it already existed. ► President Harry Truman reinforced this philosophy with the ***Truman Doctrine- which stated that the United States would not hesitate to intervene and aid nations overseas to resist communism. ► ***The Marshall Plan- as part of plan for implementing the Truman Doctrine Secretary of State George Marshall wanted to provide the war torn nations of Europe with financial support to rebuild their countries and economies. Western Europe prospered while the Soviet dominated countries struggled. The plan went a long way towards preventing the spread of communism in Europe. Increased Tensions ► ***The Marshall Plan did not offer aid to the devastated Soviet Union. ► ***Furthermore, the US used the threat of the atomic bomb in diplomatic talks with the USSR. ► Additionally, the US gave aid to the French who were fighting Soviet supported communist rebels in Indochina ► ***Stalin decided to force the west out of Berlin and instituted a blockade of the city not allowing needed supplies to come in by rail or road. The Berlin Airlift ► President Truman was firmly against Stalin, but did not want war. ► He authorized the Berlin Airlift where supplies were flown into West Berlin over a fifteen month period. The Soviets finally gave up in May of 1949, but this action helped fan the flames of the Cold War. International Alliances of the Cold War ► ***The Cold War divided the world into two camps. U.S. supporters and U.S.S.R supporters. ► In hopes of avoiding conflict the United Nations was formed. ► Within the organization was the Security Council which consisted of the United States, Great Britain, France, U.S.S.R, and China. Each of these countries had the power to veto any action taken by the United Nations and they must all agree before military action could be taken. International Alliances of the Cold War ► NATO vs. The Warsaw Pact- because most nations did not have nuclear weapons they allied themselves to those nations that did for collective security. ***NATO- North Atlantic Treaty Organization was an alliance between several European Nations and the United States to come to the others defense if attacked. NATO would provide a combined military force. ***The Warsaw Pact- The counterpart to NATO for the U.S.S.R and its allies. NATO logo Headquartered in Brussels, Belgium Flag of NATO (28 member nations) The Nuclear Threat ► World War II changed peoples lives and what they thought of the world, because quickly after the war the Soviet Union detonated its first fission bomb. Quickly followed the massive and deadly Hydrogen Bombs. ► The Nuclear Arms Race- Both the U.S. and U.S.S.R. in which both sides continually built updated weapons aimed at one another that provided for the possibility of massive retaliation sometimes called MAD (mutually assured destruction)