* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
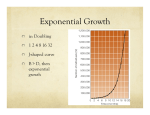
Population Dynamics Populations are studied by looking at changes in: 1) size 2) density 3) dispersion (clumping*,uniform,random) 4) age distribution ? How is population growth measured? (Births + Immigration) – (Deaths + Emigration) = growth ? What Affects Population Growth? - Carrying Capacity determines the # of individuals a habitat can support - carrying capacity is determined by: a) Biotic Potential - how quickly a species can reproduce b) Environmental Resistance - limits to a species growth ex.- space, food, mates, etc. ? What Ways Do Populations Grow? 2 Types of Growth 1) Exponential Growth - observed in quick reproducing species - can happen with unlimited resources 2) Logistic Growth - typical growth pattern for most species - environmental resistance causes growth to level off and fluctuate at carrying capacity ? What Affects the Density of Populations? 2 Types of Factors 1) Density-dependent - limits on growth that only affect very dense populations Examples- competition, disease, predation 2) Density-independent - affects a population regardless of size Examples- natural disasters, human disturbance Reproductive Methods - organisms can reproduce sexually/asexually - asexual reproduction- requires less energy - allows everyone to reproduce - doesn’t allow for diversity - sexual reproduction- requires more energy - only females can reproduce - allows for increased diversity - males can provide protection Reproductive Strategies 1) Opportunists (r-selected species) - put most of its energy into reproduction - reproduce at a young age - produce many offspring - no parental care - high growth rate 2) Competitors (K-selected species) - put most of its energy into survival - reproduce later - produce few offspring - provide parental care - low growth rate Life Expectancies for “r” & “K” species “r-selected” species show: - early loss survivorship curves - reproductive strategy leads to many deaths “K-selected” species show: - late loss survivorship curves - reproductive strategy leads to fewer deaths Species with intermediate strategies show: - constant loss survivorship curves - reproductive strategy leads to a constant rate of death Survivorship Curves ? How do we preserve species? Conservation Biology measures: 1) size of populations 2) possible changes in size 3) whether sizes are sustainable Conservation Biology believes: 1) biodiversity is important for survival 2) humans should not alter ecosystems 3) we should protect whole ecosystems ? How do we live more sustainably? We should understand that: 1) Our lives are dependent on the Earth & sun. 2) Everything on Earth is connected. 3) We should minimize damage & work with nature.