* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reading the Periodic Table
Carbon group wikipedia , lookup
Alkali metal wikipedia , lookup
Group 12 element wikipedia , lookup
Dmitri Mendeleev wikipedia , lookup
Boron group wikipedia , lookup
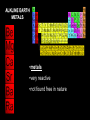
Alkaline earth metal wikipedia , lookup
Group 3 element wikipedia , lookup
Period 6 element wikipedia , lookup
Period 2 element wikipedia , lookup
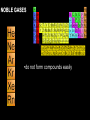
On the Outside—Write this! • Matter is made up of extremely small particles called ATOMS • Atoms are the smallest part of an element that has the chemical properties of the element. • Elements are composed of only one type of atom. • A single atom has mass and takes up space Reading the Periodic Table What is the Periodic Table? • The periodic table is the most useful tool to a chemist • A way of organizing & classifying elements • Arranged in columns and rows • Modern table created by Mendeleev Dmitri Columns • The vertical columns of elements are called groups or families – Usually numbered 1-18 – Elements in the same family have similar properties Rows • The horizontal rows of elements are called periods – Elements in a period are not alike in properties. – The first element in a period is usually an active solid – The last element in a period is always an inactive gas. Organization of the Elements • Elements are listed from left to right by atomic number • Atomic size increases from left to right across a period. • Atomic mass increases from left to right across a period. How do we read the PT? • Each element has its own square on the periodic table. • Atomic number • Element symbol • Element name – (common name) • Atomic mass Use the periodic table to find the following • • • • • Atomic number of oxygen Element symbol for krypton Element name for symbol W Atomic mass of calcium Common name and atomic mass for Md Classification of Elements • A zigzag line divides the periodic table into two sections • Metals are on the left • Non-metals are on the right Metals • Generally located on the left side of the zigzag line (blue boxes) • Have specific properties – Luster – Conduct electricity – Malleable – Ductile – React with acids • Examples: Sodium (Na), Calcium (Ca), Iron (Fe), Aluminum (Al) Nonmetals • Generally located on the right of the zigzag line (green boxes) • Have specific properties – Dull – Do not conduct electricity – Brittle • Examples: Chlorine (Cl), Oxygen (O), Sulfur (S), Iodine (I) Metalloids • Touch the zigzag line (purple boxes) • Have properties of both metals and nonmetals • Examples: Boron (B), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Arsenic (As)… Use your periodic table to identify each of the following elements as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids • • • • • Uranium (U) Mercury (Hg Radon (Rn) Tin (Sn) Zirconium (Zr) ALKALI METALS •very reactive metals that do not occur freely in nature •malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity. •softer than most other metals •can explode if they are exposed to water ALKLINE EARTH METALS •metals •very reactive •not found free in nature TRANSITION METALS •ductile and malleable, and conduct electricity and heat •iron, cobalt, and nickel, are the only elements known to produce a magnetic field. RARE EARTH ELEMENTS •many are man-made OTHER METALS •are ductile and malleable •are solid, have a relatively high density, and are opaque METALLOIDS •Have properties of both metals and nonmetals. •Some of the metalloids, such as silicon and germanium, are semi-conductors. This means that they can carry an electrical charge under special conditions. This property makes metalloids useful in computers and calculators NON-METALS •not able to conduct electricity or heat very well •very brittle, and cannot be rolled into wires or pounded into sheets •exist in two of the three states of matter at room temperature: gases (such as oxygen) and solids (such as carbon). •have no metallic luster, and do not reflect light. HALOGENS •"halogen" means "salt-former" and compounds containing halogens are called "salts" •exist in all three states of matter: •Solid- Iodine, Astatine •Liquid- Bromine •Gas- Fluorine, Chlorine NOBLE GASES •do not form compounds easily