* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Light Energy - DiMaggio
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
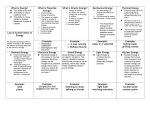
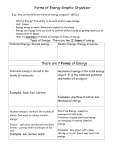
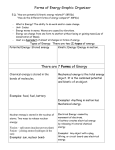
Mechanical Energy Mechanical energy is the energy of motion and position of an object. Also known as muscle or motor energy Both kinetic energy and potential energy are kinds of mechanical energy. Examples: Fan blades Turbines (big mechanical fans) Throwing a football Riding a bike Wind Bus driving Frog leaping Thermal Energy THERMAL ENERGY is the rapid movement of atoms and molecules. Also Known As: HEAT It is all of the kinetic energy (movement) of the atoms and molecules that make up substances. Everything has atoms, so everything has thermal energy (heat) Examples: Fire Heaters Sun Light bulbs People Electrical Energy • Electrical Energy is the energy stored in electrons(electricity) • Electrical energy can be thought of as potential energy that is waiting to be used. The potential energy is changed into kinetic energy when you plug in an electrical appliance and use it. Examples: Lightning Electricity TV Cell phones Batteries Radios Flashlights Chemical Energy CHEMICAL ENERGY is the energy stored in the bonds of chemical compounds When bonds break the energy is released Examples: Food Plants Oil and Gasoline Match tip Batteries Coal Nuclear Energy NUCLEAR ENERGY is the energy stored in the nucleus(center) of an atom • Nuclear energy can be produced when nuclei are joined in a fusion reaction or when a nucleus is split apart in a fission reaction. Examples: Uranium Nuclear power plants Nuclear bombs Sun Light Energy (aka electromagnetic) Light Energy is energy in the form of moving rays that produce light Examples: Light bulbs Sun Head lights Flashlights Candles Sound Energy Sound Energy is caused by an object’s vibrations to make noise The object’s vibrations transmit some kinetic energy to the air particles, which also vibrate. These vibrations cause sounds. Examples: Drums Talking Radio Engines Maracas Tuning fork