* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AT 121 - Chapter 2 - Basic Electrical Principals
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
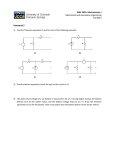
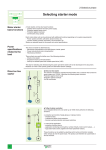
AT 121 - Chapter 12 Automotive Starters. Service, Diagnosis, and Inspection – PART B Name: _________________________________________ Date: __________________________________________ WARNING! This lab will have you working with live batteries. Batteries are dangerous devices and can explode if shorted. Fire and explosion can result from carelessness! Batteries also contain sulfuric acid. If skin or eyes come in contact with acid or corrosion on the battery surface flush with water and seek medical assistance! It is important to remember a few things about how a vehicle starts. Most vehicles made after 1990 have a “clutch interlock” switch. This switch prevents a manual transmission vehicle from being starter in gear. However, it is important to make sure that the vehicle is in neutral and the parking brake is set before any type of automotive inspection or service is preformed! To start the vehicle the clutch must be fully depressed. Other vehicles with an automatic transmission must be in either neutral or park in order for the vehicle to start. On most manual transmission vehicles equipped with a clutch interlock the interlock switch is located above the clutch pedal. On most automatics the “neutral safety switch” is located on the transmission housing and is controlled by the shifter cable or rod. On Car Starter Motor Inspection – Customer Complaint – “Poor Crank, or Intermittent Crank” If a starter does not run, and the battery checks out, this simple test may be preformed on any vehicle. The test is broken down to inspect the most basic parts of a starter circuit. Proper power and ground must be in the right place at the right time in order for the starter to function when the driver needs it. A Poor Crank means that the starter is functioning and it or the battery may be at fault, however a poor crank could indicate an area of high resistance in the starter circuit or battery wiring. For example, the vehicle may crank slowly, or intermittently. This test checks for areas of high resistance by measuring voltage drop between connections. Before performing this test the battery must be fully inspected and checked! WARNING: When servicing the starter motor or working underhood in the vicinity of the starter motor, note the heavy gauge input lead connected to the starter solenoid is hot at all times. Make sure the protective cap is installed over the terminal and is reinstalled after servicing. SECTION 4 Starter Component Tests - Voltage Drop Tests Tools you will need: Given Vehicle Tool Board Starter Bypass Switch DVOM 1 - Starter Motor—Motor Feed Circuit Make sure the battery is fully charged, and the ignition is OFF. Disconnect the inertia fuel shut off (IFS) switch. Connect a remote starter switch between the starter solenoid S-pin and the battery positive (+) pin. Connect the DVOM positive lead to the battery positive (+) post. Connect the negative lead to the starter solenoid M-pin. (Shown below) Descriptions 1 S-Pin 2 Remote Starter Switch – Bypasses Ignition Switch 3 Battery 4 DVOM 5 B-Pin 6 M-Pin 1 Engage the remote starter switch. Read and record the voltage. ________________ Volts (M pin test) The voltage reading should be 0.5 volt or less. If the voltage reading were 0.5 volts or less, you would go to the 2- Starter Motor-Ground Circuit Component Test. If the voltage reading is greater than 0.5 volt, this is an indication of excessive resistance at the connections of the positive battery cable or in the starter solenoid. These areas should be checked, cleaned and torqued to specification. Move the DVOM negative lead to the starter solenoid B-pin and repeat the test. If the voltage reading at the Bpin is lower than 0.5 volts, the concern is either in the connections at the starter solenoid or in the solenoid contacts. Read and record the voltage. ________________ Volts (B pin test) If there was a high voltage drop (greater than 0.5 volts), you should remove the cables from solenoid B-, S- and M-pins and then clean the cables and connections and reinstall the cables to the correct pins. The next step in the repair would be to retest the system if needed. If the voltage drop reading is still greater than 0.5 volts when checked at the M-pin or less than 0.5 volts when checked at the B-pin, the concern is in the solenoid contacts. Install a new starter motor. If the voltage reading taken at the solenoid B-pin is still greater than 0.5 volts after cleaning the cables and connections at the solenoid, the concern is either in the positive (+) battery cable connection or in the positive battery cable itself. Overall Results of Starter Feed Circuit Voltage Drop Test (Pass/Fail/Observations) __________________________________________________________________________________________ 2 - Starter Motor—Ground Circuit A slow cranking condition can be caused by resistance in the ground or return portion of the cranking circuit. Connect the DVOM positive lead to the starter motor housing (the connection must be clean and free of rust or grease). Connect the negative lead to the negative (-) battery pin. (Shown Below) Descriptions 1 DVOM 2 Battery 3 S-Pin 4 M-Pin 5 B-Pin 6 Remote Starter Switch – Bypasses Ignition Switch Engage the remote starter switch and crank the engine. Read and record the voltage reading. The reading should be 0.2 volts or less. Read and record the voltage. ________________ Volts (Starter Ground Test) If the voltage drop is more than 0.2 volts, clean the negative cable connections at the battery, the body ground connections and the starter ground connection. Retest the system. If the voltage drop is still greater than 0.2 volts, install a new cable. If the voltage reading is less than 0.2 volts and the engine still cranks slowly, install a new starter motor. 2 Overall Results of Ground Circuit Voltage Drop Test; (Pass/Fail/Observations) __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Q If at the starter motor feed test, your voltage was 3.4 volts when you tested the positive lead to the battery positive (+) post and the negative lead to the starter solenoid M-pin. What could be the cause? (M pin test) ______________________________________________________________________________________ If at the next test for starter motor feed, and the negative lead to the starter solenoid B-pin voltage was 2 volts, what could be the cause? (B pin test) ______________________________________________________________________________________ If after cleaning the cables and connections and reinstall the cables to the correct pins, the voltage drop was still 2 volts when checked at the M-pin, or less than 0.5 volts at the B-pin, what component would be replaced? ______________________________________________________________________________________ When testing the starter ground circuit, the positive lead to the starter motor and the negative lead to the negative (-) battery pin had a voltage drop of 0.5 volts, what could be the cause? __________________________________________________________________________________________ After finding a voltage drop of more than 0.2 volts, you cleaned the negative cable connections at the battery, the body ground connections and the starter ground connection. You then retest the system. If the voltage drop is still 0.5 volts. What component would you replace next? __________________________________________________________________________________________ After this test if the voltage drop is still .05 volts, the _________________________ should be replaced. Instructor’s Signature _________________________________________________________________ SECTION 5 Starter Motor Current Draw Test - On Car Starter Motor Inspection – Customer Complaint – “Slow Crank” Tools you will need: Given Vehicle ARBST Tester Conduct this test if the starter motor cranks slowly and also to compare starter motor electrical current to specifications. Remember, a slow crank could be caused hi high resistance. However high resistance will cause a low current draw in a starter circuit. A high current draw indicates an internally shorted starter winding. This short will still cause the starter to crank slow. Before performing this test the battery must be fully inspected and checked! Disconnect the low voltage wires at the coil pack connector. Disconnect inertia fuel switch power to the fuel pump to disable fuel flow on vehicles equipped with electronic fuel injection (EFI). This prevents the engine from starting. VERIFY the engine will CRANK but not START. NOTE: Make sure battery terminals and cable connections are clean. Turn ON the ARBST. It should indicate battery voltage, if not get the instructor. Clamp the black load lead of the ARBST to the battery negative terminal. 3 Clamp the red load lead of the ARBST to the battery positive terminal. Make sure both load leads are connected securely. Zero the ammeter of the ARBST by removing the gray amp probe from all wires and pressing the ZERO AMPS key. NOTE: Make sure the gray amp probe is around all wires connected to the negative battery terminal during this test. Clamp the gray amp probe of the ARBST around the battery ground cable so that the arrow on the probe points toward the battery. If not your AMPS reading will be (-) and ARBST will give a false answer. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Red Load Lead (Connect to Positive Battery Terminal) Black Load Lead (Connect to Negative Battery Terminal) Alternator, Regulator, Battery and Starter Tester (ARBST) Gray Amps Probe (Connect Around Negative Battery Cable with Arrow on Probe Pointing Toward Battery) Starter Motor Battery Press STARTING TEST. The display will read INPUT # CYLS = [[ENTER>>. Type in the vehicles number of cylinders 4, 5, 6, 8, 10 on the numeric keypad and press the ENTER key. Place the tester so you can see it from inside the vehicle. The display will then read DISABLE IGNITION AND CRANK ENGINE. Crank the engine. The display will read MAINTAIN CRANKING. Continue to crank the engine until the display reads either TEST COMPLETE or TEST INCOMPLETE. Then discontinue engine cranking. Press the CONTINUE key to display the cranking volts. Press the CONTINUE key once again to display the cranking amps. Press the CONTINUE key once again to display the starter motor diagnosis. The display will read either GOOD STARTER or BAD STARTER. Fill in the results below; Vehicle 1 Year _________________ Make _______________ Model _____________ Cranking Volts – Should not be below 9.6 ______________________________________ Cranking Amps – Should not be above 250 Amps _________________________________ Starter Motor Diagnosis ____________________________________ To view cranking volts again press the CONTINUE key. To display cranking amps again press the CONTINUE key a second time. Turn off the ARBST unit. 4 QNow, run the test again on another vehicle. Fill in the results below; Vehicle 2 Year _________________ Make _______________ Model _____________ Cranking Volts – Should not be below 9.6 ______________________________________ Cranking Amps – Should not be above 250 Amps _________________________________ Starter Motor Diagnosis ____________________________________ Instructor’s Signature _________________________________________________________________ SECTION 6 Off Vehicle Starter Inspection Tools you will need: Starter Componets DVOM After determining that a starter needs service. The starter would have to be removed from the vehicle and other tests may need to be preformed. Starter Drive Pinion Test This test would check the pinion drive unit (the Bendix). Problems that would take you to this test would be a starter that cranks, but does not engage the flywheel or a starter that does engage the flywheel but does not disengage. Turn the starter drive pinion by hand and hold the overrunning clutch. Replace the starter drive if the pinion turns in both directions or does not turn. Examine the pinion given to you. Pinion Drive Test Results: ______________________________________________________________ Armature Tests Open Circuit Test Slow cranking caused by high resistance, or an internal short in the starter could be caused by a damaged armature. An open circuit starter motor armature may sometimes be detected by examining the commutator for evidence of burning. A burn spot or damage on the commutator is caused by an arc formed every time the commutator segment, connected to the open circuit winding, passes under a brush. Visually examine the armatures given to you. Armature 1 Results ________________________________________________________________ Armature 2 Results ________________________________________________________________ Another test it to use the “Growler” – test the armatures given. Armature 1 Results ________________________________________________________________ Armature 2 Results ________________________________________________________________ 5 Grounded Circuit Test This test will determine if the winding insulation has been damaged, permitting a conductor to touch the starter frame and magnet or armature core. To determine if the armature windings are grounded, check with DVOM. Infinite resistance (OL) indicates a normal condition. Test the armatures by connecting one lead of the DVOM to the commutator, and then touch the other lead of the DVOM to the frame of the armature. Examine the armatures given to you. Armature 1 Results ________________________________________________________________ Armature 2 Results ________________________________________________________________ Starter Solenoid (Relay) This test would be done if the starter solenoid (relay) is found suspect. Make sure that the starter solenoid is isolated (removed) electrically from the starter motor. With the DVOM check for continuity and between S-terminal and ground (Case). If there is no continuity, there is an open wire; replace starter solenoid. S to Ground (Case) – Results: ___________________________________________ B to M should only have continuity when the plunger is depressed. All other points should be open. B to M – Results: ____________________________________ B to Case – Results: ____________________________________ Case to M – Results: ____________________________________ S should be open to the B wire, and the M wire, if not the starter solenoid is shorted. S to B – Results: ____________________________________ S to M – Results: ____________________________________ Solenoid S-Terminal Circuit Resistance Check the resistance of the entire S-terminal circuit, including all the switches, wires and connections. Resistance should be less than 0.6 ohms S Resistance: _______________________________ 6 Q Slow cranking caused by ______________, or an __________________ in the starter could be caused by a damaged armature. When testing a starter solenoid it should be _____________________ from the starter motor. S should be open to the B wire, and the M wire, if not the starter solenoid is _______________________. Fill in the blanks, you choices are; Battery (+), Ignition Switch, and Starter Motor B wire goes to the _____________________ S Wire goes to the _____________________ M wire goes to the _____________________ Instructor’s Signature _________________________________________________________________ SECTION 7 Starter Bench Testing Tools you will need: Starters Starter Tester Test the 5 starters using the bench tester. Check for; Bendix operation (apply and release) No-Load current draw (any current draw over 150 amps indicates a poor starter) Abnormal noise or vibration Starter 1 Current Draw :___________________________ Bendix (Ok/Not OK) _________________________ Starter 1 Results ______________________________________________________________________ Starter 2 Current Draw :___________________________ Bendix (Ok/Not OK) _________________________ Starter 2 Results ______________________________________________________________________ Starter 3 Current Draw :___________________________ Bendix (Ok/Not OK) _________________________ Starter 3 Results ______________________________________________________________________ Starter 4 Current Draw :___________________________ Bendix (Ok/Not OK) _________________________ Starter 4 Results ______________________________________________________________________ Starter 5 Current Draw :___________________________ Bendix (Ok/Not OK) _________________________ Starter 5 Results ______________________________________________________________________ Instructor's Signature _____________________________________________________ Things to remember from this lab: High Resistance Can Cause a Slow or no Crank Situation in a starter circuit An internal short in the starter windings can cause a Slow or no Crank Situation in a starter circuit There must be a good connection to all starter circuit components (B, M, and S) Starter bolts, and wires must be torqued to prevent poor connections 7 NATEF TASKS - VI. ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS C1. Perform starter current draw tests; determine necessary action. P-1 C2. Perform starter circuit voltage drop tests; determine necessary action. P-1 C3. Inspect and test starter relays and solenoids; determine necessary action. P-2 C5. Inspect and test switches, connectors, and wires of starter control circuits; perform necessary action. P-2 8