* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Systems Repair Worksheet
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
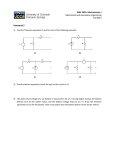
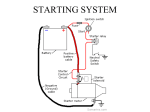
Systems Repair Worksheet Chapter 18 Starting & Traction Motor Systems Pages 537-570 Name 62 Points Due Date 1. Electric _________ are used to start the engine & in hybrids are used to move the vehicle. Motors are also used to operate many different accessories requiring either linear or rotary motion. 2. Starter motors & accessory motors use ___ voltage while traction or drive motors use ___voltage. 3. ____________ & ___________ are closely related because one can be used to create the other. 4. __________ flow through a wire creates a magnetic field & moving a _____ through a magnetic field creates current flow in the wire. Coils or loops of wire just intensify that effect. 5. A magnetic field called, called a ________ ________, exists around every magnet. 6. Temporary magnets (armatures) are made of _______ iron. Permanent magnets require hard iron. 7. The resistance that a material offers to passage of magnetic flux lines is called ______________. 8. Air has ________ reluctance. Soft iron cores & armatures have ________ reluctance. 9. An electric motor converts ____________ energy into ____________ energy. 10. Basic components of a motor are the stator or _______ windings, & the rotor or ____________. 11. Either the field windings or the armature can be made of _____________ magnets, but not both. 12. Starter motors are designed to operate under great ______________ for short periods of time. 13. The starter frame holds the stationary _______ coils (flat copper) & their _______ shoes (soft iron). 14. The ____________ is the rotating part of the starter, made up of windings and the commutator. 15. Starter ________ connect the armature & the field coils in either a series or parallel arrangement. 16. ____________ magnetic fields cause the motor armature to rotate. 17. _____________ magnet starter motors may have a planetary gear reduction to increase torque. 18. The slower the motor turns, the ______ current it will draw. Maximum current is drawn when it engaged, but the armature is not rotating. 19. The starting system has 2 distinct circuits: 1) the ________________ (motor feed-high amps) circuit, and 2) the ______________ (low amps-switching) circuit. 20. The motor feed circuit contains the battery & cables, the ______________, & the starter motor. 21. The control circuit contains the ___________ switch, starting ________ switch, a ________ or a solenoid (to use low amps to control higher amps), the battery, fuses, and normal-gauge wiring. 22. The __________ plunger is used to move the starter pinion gear & its contacts serve as a relay switch to energize the motor once the drive pinion engages the flywheel/flex plate ring gear. 23. A starter ______ is similar to a solenoid, switches high current using low current, but does not pull-in a plunger to actuate a starter drive. 24. A movable ______ ______ starter does not use a starter motor mounted solenoid. 25. To prevent the pinion gear from driving the armature at engine speed an _____________ clutch is built into the starter drive mechanism. 26. Starter drive-to-ring gear ratio is a gear reduction to provide a torque increase. True False 27. The starting safety switch allows the control circuit to be energized only if the automatic trans is in either the ________ or __________ position and only if the manual transmission has the clutch pedal fully pushed to the floor to disengage the transmission from the engine. 28. Perform a ______________ load test before performing any starting system tests. Note: Loose or dirty connections will cause excessive voltage drops in the motor feed circuit. 29. Battery volts should not drop below _____ volts during the 15 seconds of cranking voltage test. 30. Cranking current (amperage) should be between 100-250 amps for most gas engines. True False 31. A voltage drop test of both the ____________ side and the ground side (- to -) of the motor feed circuit should show between 0.2 to 0.6 volts if the battery/starter cables are in good condition. 32. Starter solenoids can be by-passed or jumped to verify their condition. 33. Ignition switches can be by-passed or jumped to verify their condition. True True False False 34. Even the low amps, control circuit can be __________ ______ (+ to +) tested during cranking to determine the condition (resistance) of the wiring. Good, low amps circuits should be under 0.2 VD. 35. A starter no-load or free speed bench test can be low on RPM’s if a pole ______ drags against the armature. This could be caused by either a loose shoe or by worn drive-end & brush-end bushings. 36. When testing an armature with a growler, a vibrating strap indicates a ___________ armature, continuity from commutator bars to the armature frame indicates a prematurely grounded motor, and no continuity from commutator bar to commutator bar indicates an ______ condition which will result in “dead spots” during cranking. 37. _________ should be of the proper length, commutator bars should be smooth, and the mica strips of insulation between the commutator bars should be properly undercut to a uniform depth. 38. Starter drive __________ on the armature shaft and both armature __________ should be lightly lubricated with high temperature grease during rebuilding procedures. 39. In the space below, wire-up a cranking circuit that uses a remotely mounted starter solenoid. (include: battery, grounds, fuse, P/N switch, ignition switch, solenoid, starter motor) 40. In the space below, wire-up a cranking circuit that uses both a starter relay and a starter solenoid. (include: battery, grounds, fuse, P/N switch, ignition switch, relay, solenoid, starter motor) 41. On the top circuit, draw in a DMM connected for a battery ground cable voltage drop test. 42. On the top circuit draw in a DMM connected for an open circuit voltage test of the battery. 43. On the bottom circuit, draw in a DMM connected for a battery positive cable voltage drop test. 44. On the bottom circuit draw in a DMM inductively connected for a cranking current draw test.