* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
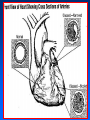
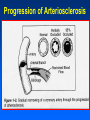
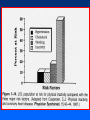
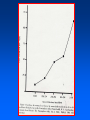
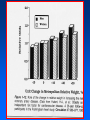
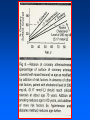
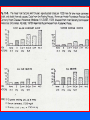
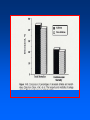
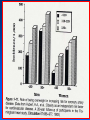
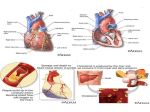
Arteriosclerosis and Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Arteriosclerosis Disease of the arteries characterized by thickening, loss of elasticity and calcification of arterial walls Resulting in decreased blood supply particularly to the cerebrum and lower extremities Often develops with: • aging • hypertension • diabetes Progression of Arteriosclerosis Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) • Seven million Americans effected • Caused by narrowing of the coronary arteries • No. 1 killer of men and women in U.S. >500,000 each year • > 60 million Americans have some form of coronary vascular disease (CVD) including high BP, CAD, CHD, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction and others • >2,600 Americans die each day of CVD, i.e., 1 death/33 sec • ~ $299 billion cost to the U.S. Risk factors • • • • • • • High blood pressure (hypertension) High blood cholesterol Smoking Obesity Physical inactivity Controllable Diabetes Stress (?) Risk Factors (cont’d) • Gender • Heredity • Age Uncontrollable Major Risk Factors: The Big Three • Hypertension • High cholesterol • Cigarette smoking AND…. we should add All three increase risk factor eight times LACK OF EXERCISE Hypertension • • • • Commonly called high blood pressure Systolic and diastolic measurements Normal systolic - 110-130 mmHg Normal diastolic - 70-90 mm Hg Symptoms of CHD • Chest pain (angina) • Shortness of breath • Heaviness, tightness, pain, burning, pressure or squeezing behind the breastbone or in the arms, neck, or jaws • Pain may vary • Perhaps no pain Cause & Consequencess of CHD • Lack of oxygen due to ischemia (lack of blood supply) • Narrowing of coronary arteries • Heart responds with angina • Finally, heart attack (myocardial infarction local ischemia usually due to thrombus (clot) or embolus (clot that has moved from another site and lodged in a smaller vessel) • Possible permanent damage Diagnosis of CHD • • • • Electrocardiogram (EKG) Stress test Nuclear scanning Coronary angiography Treatment for CHD • Lifestyle changes • Medication • Surgery Lifestyle Changes • • • • • Change of habits Low fat diet Lower weight Increase exercise Stop smoking Medications to Treat CHD • • • • • Beta blockers Nitroglycerine and other nitrates Calcium-channel blockers Aspirin Cholesterol-lowering drugs lovastatin, colestipol, cholestyramine, etc • Digitalis • ACE inhibitors • Diuretics Surgery to Treat CHD • • • • • Balloon angioplasty Atherectomy Laser angioplasty Stent insertion Coronary artery bypass operation (CABG) Gender Disparity • Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) more common in men • Women have higher mortality rates Older and sicker when first heart attack occurs Less aggressively treated than men Failure to recognize symptoms in timely fashion • MI in young, healthy women is rare Occurrence greater in those who use OC Age 30-39: 2.7X; 40-44: 5.7X; (complilcated by cigarette use) Effects of Smoking • For adult males, smoking has declined from 53 % to 38% • For women, remains at 30% • Has increased for younger and teenaged women • Heavy smoker = 20- 30 cigs/day Effects of Smoking (cont’d) • Cigs contain about 2000 compounds • Main harmful are tar, nicotine and CO Tar contains hydrocarbons and other carcinogenic substances Nicotine causes release of epinephrine and norepinephrine resulting in increased HR, BP, cardiac output, stroke volume, contractility, oxygen consumption, and coronary blood flow CO reduces oxygen carrying capacity of the blood; can precipitate angina Effects of Smoking (cont’d) • Contributes to development of atherosclerosis • Lowers levels of HDL causes deterioration of elasticity of vessels Responsible for 20% of all deaths from heart disease • Female smokers have a higher risk than male smokers STRESS • Sociocultural Mobility • Socioeconomic Status • Status Incongruity • Education Level • Anxiety and Neuroses • Life Dissatisfaction • Life Change • Behavior Pattern Signs of Preclinical CVD • Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) associated with increased CAD risk (Framingham Study) • Definite LVH-EKG increased CAD risk threefold Blood and Tissue Characteristics • Type O = lower cholesterol • Higher cholesterol contributes to higher rate of CAD • HDL:LDL (high density lipoproteins: low density lipoproteins) ratio may be more important than cholesterol level HDL • High density lipoproteins seem to have protective effect against development of atherosclerosis (a form or arteriosclerosis in which deposits of yellowish plaque containing cholesterol, lipoid substances and lipophages are formed within large and medium-sized arteries) • Women have higher concentrations than men • Most important of all lipid risk factors • Below 35 mg/dl----- 8X incidence of CAD compared to those with 65 mg/dl • Moderate alcohol intake may have + effect • Exercise has + effect • Greater weight has a negative effect DIET • • • • Reduce saturated fats Increase polyunsaturated fats Higher protein to fat ratio Count calories Effects of Exercise Additional Information