* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3 HORMONES from SMALL INTESTINE
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Adjustable gastric band wikipedia , lookup
Ulcerative colitis wikipedia , lookup
Colonoscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ascending cholangitis wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Bariatric surgery wikipedia , lookup
Fecal incontinence wikipedia , lookup
Surgical management of fecal incontinence wikipedia , lookup
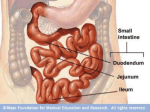
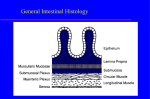
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM drg. ANIS A. MAKKY, MKes ORAL BIOLOGY DEPARTEMENT AIRLANGGA UNIVERSITY SURABAYA, APRIL 16, 2007 SMALL INTESTINE major organ of both : digestion and absorption this convoluted tube extends : from the pyloric sphincter to the ileocecal valve 20 feet long ? 3 regions: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. DUODENUM 10" long much of it is retroperitoneal the common bile duct : delivering bile from the liver and gallbladder main pancreatic duct : delivering pancreatic juice from the pancreas JEJUNUM it’s about 8' long extends between the duodenum and the ileum ILEUM it’s extends from the jejunum to the ileocecal valve it’s about 12' long. HISTOLOGY mucosa has intestinal glands (cavities) : for secretion of intestinal juice mucosa also has circular folds, villi & microvilli : for increased surface area “brush border” has many enzymes “brush border” has many enzymes (embedded in plasma membranes) : 1. several carbohydrate-digesting enzymes 2. peptidases 3. nucleosidases 4. enterokinase epithelial cell “shedding” important enzyme activator. PLICAE CIRCULARES large deep permanent folds of the mucosa and submucosa they slow the movement of chyme (more time for digestion/absorption) they increase the surface VILLI fingerlike projections of the mucosa they also increase the surface area within the core of each villus is a capillary bed and a lacteal : for transport of the absorbed nutrients. • between the villi exist pits : intestinal glands or ‘crypts of Lieberkuhn’ • the cells lining these pits secrete : intestinal juice (mucus, enzymes, etc.), lysozyme-secreting cells, and stem cells. in the proximal duodenum : the submucosa houses Brunner's glands secrete an alkaline mucus to help neutralize the acidic chyme (coming from the stomach) INTESTINAL PHASE OF REGULATING DIGESTION 1. chyme enters duodenum 2. three hormones secreted from SI mucosa 3. receptors in SI mucosa sense food or chemical presence in duodenum 4. neuronal activation of sympathetic NS or inhibiton of parasympathetic NS REGULATING of ABSORPTION C L P, Ca2+, Fe2+ : duodenum & jejunum bile salt, vit.B12,H2O,electrolite : ileum monosacharide & amino acid : secreted into cappilar lipid : secreted into central lacteal absorption of H2O : passive (osmotic gradient) mucosa epithelial cell of intestine : collect to form tubulus is like kidney : * functions as Na+/K+ pump within basolateral membrane * can stimulates absorption of NaCl & H2O within ileum 3 HORMONES from SMALL INTESTINE 1. gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) : * fatty acids in chyme : induce GIP secretion * inhibits gastric secretion * inhibits gastric “churning” * activates insulin secretion 2. secretin : inhibits gastric secretion 3. cholecystokinin (CCK) : * fatty acids in chyme : induce CCK secretion * CCK slows gastric emptying LARGE INTESTINE function : * absorb water * then eliminate them as feces compared to the small intestine : diameter is bigger but its length is far shorter (only about 5') their tone causes the LI wall to pucker into pocketlike sacs called ‘haustra’ LI : significant numbers of bacterial colonies they enter via both the anal canal and the oral cavity and colonize the LI in the LI, they metabolize and ferment indigestible carbohydrates they also synthesize B vitamins as well as vitamin K. haustral contractions move material from one haustrum to another and aid in mixing mass movements : slow waves of peristalsis one stimulus of colonic mass movements is the presence of food within the stomach this is known as the gastrocolic reflex. feces enter and stretch the rectal wall : initiate the defecation reflex this results in : * the contr. of the sigmoid colon and rectum muscularis * the relaxation of the internal anal sphincter * contr. diafragma higher input determines whether the external sphincter remains : contracted or relaxes. prolonged diarrhea may result in : * dehydration * acidosis * and other electrolyte imbalances if water absorption >> than normal : due to waste moving too slowly through the colon constipation !!! BREAK DOWN OF LIPID fats are not digested until the small intestine there they are first emulsified by bile and then acted upon by pancreatic lipase most ingested fats are broken down into glycerol, monoglycerides, and fatty acids fatty acids & monoglycerides : passively enter intestinal epithelial cells they're combined with cholesterol & proteins form chylomicrons BREAK DOWN OF PROTEIN protein digestion begins in the stomach : pepsin in the SI, protein digestion continues with trypsin and many other proteases the end result : free amino acids amino acids enter the intestinal epithelial cells via cotransport with sodium DEFECATION after absorption of electrolite & H2O : colon forming of feces : in the colon feces in the rectum : pressure of rectum reflex of defecation problems : constipation (absorption >>) diarrhea (absorption <<) DEFECATION MECHANISM pressure of rectum contraction of m.longitudinal of rectal support by parasimpathetic stimulation (n. pelvic) feces enter canal anal sphincter anal internal & external relaxation feces exit from anal DIARE fast movement of fecal matter through colon excretion of excess fluid together feces etio : enteritis, psychogenic, colitis ulcerative Tx : change fluid & electrolite that lost (saline iv & glucose) 1. cholera : * enterotoxin released by bacteria of cholera * enterotoxin stimulates active transport of NaCl followed by H2O into lumen * iritation of mucosa * secretion , motility * electrolite & fluid secretion from crypts Lieberkuhn 10-12 L/hr * reabsorp colon 6-8 L/hr 2. celiac sprue : * intestinal mucosa rupture * disturb of absorption by consumption of gluten 3. lactose intolerance COLITIS ULCERATIVE etiology : idiophatic, alergy destructive immune secretion motility colon wall : inflamation & ulcer MORNING SICKNESS • nausea , vomitus • prevalence : * 51.4 % : nausea; 9.2 % : vomitus *1: 500 gravid hiperemesis gravidarum • prolonged :12-22 weeks • etio : * HCG * estrogen * deficiency B6 * gastric emptying : time >> NAUSEA – VOMITING MECHANISM • stimulasi pusat muntah di medula, yang mengendalikan zona pemicu kemoreseptor (Chemoreceptor Trigger Zone – CTZ) di otak • Peristaltik lambung menurun • Tonus duodenum & jejunum meningkat • Reflux lambung • Kontraksi lambung, kontraksi diafragma, kontraksi otot abdomen • Isi lambung keluar PENATALAKSANAAN • Kasus yang berat : – Obat-obatan : • Sedatif : fenobarbital • Vitamin : B1 dan B6 • Antiemetik (bila diperlukan) – Terapi psikologik dan isolasi – Cairan parenteral Pusat muntah (batang otak) Aferen Eferen GIT/vestibular, korteks serebri, CTZ (chemoreceptor Trigger Zone) otak (korteks) impuls ke diafragma, otot abdomen, lambung serta esofagus. Pusat muntah Saluran lambung-usus, Jantung, testis organ keseimbangan Chemoreceptor Trigger Zone (CTZ) Metoklopramid Domperidone neuroleptika Anti histamin LIVER THANK YOU