* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Levels of Biological Organization
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering in science fiction wikipedia , lookup
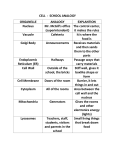
VE #___ Levels of Biological Organization Integrated Science 4 12/14 Name: Per. Macroscopic to Microscopic The following terms reflect various levels of organization that pertain to all vertebrates. These randomly assorted levels of organization represent both macroscopic and microscopic views of vertebrates. atoms, macromolecules, cells, organs, populations, organisms, organ systems, tissues, molecules. 1. Organize and list the levels of organization by size. 2. Draw a line between the levels that separate the macroscopic and microscopic views of vertebrates. 3. Label the levels as largest, smallest, macroscopic and microscopic. Genentic Organization All vertebrates are eukaryotic (organisms with enclosed nucleus), therefore their genetic material is located within the nucleus and is further organized in heretible units passed from generation to generation. 1. Define the following terms. nucleus – DNA – chromosome – gene – cell – 2. Organize the terms above to accurately represent the organization of genetic material within eukaryotic cells. Understanding the organization and relationship among these levels is crucial to the understanding of genetics and evolution. However, one obstacle to this understanding is the extremely small size of the nuclei, chromosomes, genes and DNA. The use of analogies is a valuable technique to help visualize these complex, hard-to-observe relationships. An analogy creates a relationship between two things that are otherwise not connected. 3. Read the following analogy. Circle the terms within the analogy that correlate to each of the genetic terms defined above. Match each set of correlated terms in the space below based example provided. GENETIC ORGANIZATION ANALOGY – HARRY POTTER SERIES Imagine a set of books, perhaps the Harry Potter series. The individual books are contained within a box on a shelf. Each book contains a distinct portion of the overall story. Within each book are chapters. The combinations of 26 letters of the alphabet are arranged to make the variation of words that tell the story of a young wizard’s life – Harry Potter. Example: - box – nucleus Your turn! Record your circled terms and their corresponding genetic terms below: 4. In the space provided below create an analogy of your own that explains the organization of genetic material. Circle the terms analogous to the levels of genetic organization and create a key for the correlated terms.