* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download An Introduction to Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry What are
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
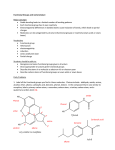
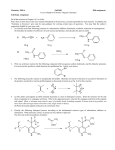
What are Functional Groups An Introduction to Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry Functional groups are common bonding patterns found in organic molecules Examples O O C H C CH3 HO Reactivity of Functional Groups CH3 a carboxylic acid an aldehyde Reactivity of Functional Groups O O 2 Li + 2 H2O → 2 LiOH + H2 + Tollen's Reagent C H + silver mirror C HO CH3 CH3 2 Na + 2 H2O → 2 NaOH + H2 O 2 K + 2 H2O → 2 KOH + H2 O + Tollen's Reagent C H CH2CH3 + silver mirror C HO CH2CH3 1 Functional Groups Containing Carbon and Hydrogen Only Reactivity of Functional Groups O O + Tollen's Reagent C H atoms, and therefore possess only single bonds. + silver mirror C HO R R O HO no silver mirror produced + Tollen's Reagent C R Alkanes contain only sp3 hybridized carbon A compound is only called an alkane if it contains none of the other functional groups. Alkenes contain at least one carbon-carbon Alkynes contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. O O CH2 C C H OH + Tollen's Reagent ??? triple bond. Cyclic Hydrocarbons CH2CH3 CH3 C CH3 CH3 an alkane CH3 H H C C CH3 an alkene H C C CH3 an alkyne An alkane which contains a ring made up of three or more atoms is called a cycloalkane. Likewise, a cycloalkene contains a carbon-carbon double bond somewhere in a ring of carbon atoms. Cycloalkynes are relatively rare, for reasons we will see later (think bond angles). We will not consider these as distinct functional groups We still classify a cycloalkene as an alkene a cycloalkane a cycloalkene 2 Aromatics Alkyl Halides The term aromatic has a rather detailed meaning which we will discuss next semester. For now, when we describe a compound as containing an aromatic group, we mean to say that it contains a benzene ring. Three equivalent ways of representing the benzene molecule Note that the benzene ring is not considered either an alkene or a cycloalkene; the special term aromatic makes the presence of the ring and double bonds understood. As we shall see, aromatic compounds react in distinctly different ways than do alkenes, owing to delocalization of electrons within the ring. Alcohols H H Technically, the carbon should be sp hybridized. OH H C C CH3 alcohols. H3C a halogen atom bonded to a carbon atom somewhere in the molecule. We are sometimes more specific, calling a compound an alkyl chloride, alkyl bromide, etc. H Cl H C Br CH3 Thiols and Amines Compounds which contain the hydroxyl group -OH bonded to carbon (R–OH) make up the class of compounds called Alkyl halides are compounds which have CH3 3 Thiols are similar to alcohols in structure, with a sulfur atom replacing the oxygen atom: R–SH Amines have a nitrogen atom bonded to at least one carbon atom; the remainder of its bonds may be to carbon or hydrogen. OH 3 Thiols and Amines H3C C Ethers OH H CH3 alcohols thiols OH SH H H3C C CH3 The ether functional group is described as an sp3 oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms, and may be symbolized as R-O-R'. R and R' may be the same groups or different. SH CH3 CH3 H amines N H3C C CH3CH2 CH3 CH3 O CH3 CH2CH3 O Carbonyl-Containing Functional Groups C CH3 NH2 A carbonyl group is made up of a carbon atom double bonded to an oxygen atom. The carbon atom is not bonded to any other heteroatom. O CH3 O Ketones The ketone functional group contains a carbonyl group, with the carbon of that group bonded to two other carbon atoms. R and R' may or may not be the same. C O C the carbonyl group We will not consider the carbonyl group to be a functional group in-and-of itself; rather, it is the essential portion of two functional groups: aldehydes and ketones. R R' a ketone 4 Aldehydes Carboxylic Acids The aldehyde functional group contains a carbonyl group, with the carbon of that group bonded to at least one hydrogen atom. The other bond is either to a carbon atom or another hydrogen atom. R is an alkyl group or another hydrogen atom in the case of formaldehyde. C C OH O carboxylic acid the carboxyl group C O O O R A carboxyl group looks similar to a carbonyl group, but at least one of its sigma bonds is to a second oxygen atom. H The carboxylic acid functional group has a hydrogen atom bonded to this oxygen atom. It is generally acidic, for reasons we discussed in Chapter One. The other bond need not be specified; it may be an alkyl group, a hydrogen atom, or another –OH. an aldehyde Carboxylic Acid Derivatives There are several functional groups which are structurally similar to carboxylic acids. The ester functional group has an alkyl group in place of the hydrogen bonded to the carboxylic oxygen atom. O Carboxylic Acid Derivatives C R C O R' an anhydride OR' an ester O O C R The anhydride functional group is a two-sided carboxyl group: R and R' may or may not be the same. R and R' may or may not be the same. 5 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives The acid chloride (or acyl chloride) functional group has a chlorine atom in place of the carboxylic oxygen Carboxylic Acid Derivatives An amide has an sp3 hybridized nitrogen atom in place of the carboxylic oxygen atom. O O C R N C R Cl an amide an acid chloride Practice The nitrogen atom is bonded to 0-2 alkyl groups. The remaining bonds are to hydrogen. Do not confuse amides with amines! Practice—Solutions Circle and label all the functional groups in the molecules below. OH CH2 CH3 CH O C Cl CH3 alcohol O C CH3 ether CH2 CH ester O O OH O C Cl CH3 CH3 O C F alkyne C N SH CH3 CH O H3C CH3 ether O C CH3 O SH alkyl halide aldehyde O alkyl halide O H O ketone CH3 H alkene CH N thiol H3C CH3 amine F 6