* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download India - assinihonors09
Gautama Buddha wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Silk Road transmission of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Women in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in India wikipedia , lookup
Enlightenment in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Pre-sectarian Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Decline of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent wikipedia , lookup
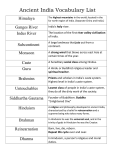
India Kacey Brown Christina Barbaro Alexa Elliot Dakota Brovero Vocabulary Section One A subcontinent is a large landmass that is part of a continent but is separate from it. Sanskrit is the written language developed by the Aryans in India. A prince who led an Aryan tribe in India is a raja. A caste is a social group that a person is born into and cannot alter. A guru is a religious teacher and spiritual guide in the religion of Hinduism. Vocabulary Section Two The system of religion that grew out of the religion of the Aryans was Hinduism. In Hinduism, the universal spirit of which all gods and goddesses are different parts is Brahman. Reincarnation is the rebirth of the soul or spirit in a different body. Dharma is the divine law that requires people to perform the duties of their caste in Hinduism. Vocabulary Section Two (continued) Karma is the good or bad energy a person builds up based upon whether he or she lives a good or bad life, in the religion of Hinduism. Buddhism is a religion founded by Siddhartha Gautama the Buddha which taught the way to find truth was to give up all desires. In Buddhism, a state a wisdom and freedom from the cycle of rebirth is nirvana. A government headed by religious leaders is theocracy. Vocabulary Section Three A line of rulers from the same family is a dynasty. A stupa is a Buddhist shrine that is shaped like a dome. A person who travels to go to a religious shrine or site is a pilgrim. Social Classes There are 5 levels to the Indian social class. This is a caste, basically meaning when you’re alive, you cannot move up or down. Your reincarnated person will move up or down on the classes from the action you did in your life. 1. Brahmans 2. Kshatriyas 3. Vaisyas 4. Sudras 5. Pariahs Priests Warriors, Rulers Common People Servants Untouchables India History • • • • • • • • • • 3000 B.C.: The Harappan Civilization Began 1500 B.C.: The Aryans Invade India 563 B.C.: The Buddha was born the Himalayan 518 B.C.: The Persians invade India 483 B.C.: The Buddha died at age 80 327 B.C.: Alexander the Great invaded India 321 B.C.: The Mauryan dynasty began 273 B.C.: The Asoka began to rule India 183 B.C.: The last Mauryan ruler was killed 320 A.D.: The Gupta empire began Major achievements with most enduring legacies. • Farming. Learning to use soil to grow crops is when farming started and still with us today. •Hinduism. One of the oldest religions in the world and is still practiced today and is the third largest religion •Algebra. One of the first mathematicians of the empire used algebra and it is still being learned and taught in our society today. •Astronomy. Ancient Indians followed mapped movements of planets and stars. They understood many things like gravity and that the Earth was round. Geography Cause To Settlement • Mountains provide great protection from Invasions. • There were many different rivers for a wide range to trade with. • This was good because Trade was very Great in India. • So important People brought a couple of wagons or boats to carry all their things to trade and what they traded for. • India was able to sustain because of the High lands and the walls that stopped floods. They also had longer growing seasons since there weren’t as long winters than in other places. Technology Advancements • People learned to use Iron. Which gave them more deadly weapons and better tools. • This helped the economic system because more people wanted to buy the iron tools and weapons which gave more jobs to people. It also made more trade and more money was being made. • The caste was created, but each level was made at different times. Written Language • Globally, ancient carving in rocks can inform us about civilizations that began them, but also unravel a need for early people to show permanence to their views. • Throughout time, India has benefitted from language by being able to pass on knowledge and tell traditions in writing and stories. • Ancient Indians also wrote down science and mathematics, not just literature. • In Ancient India, the earliest findings of writing are on rocks and pillars. They displayed the era of the Emperor Ashoka and his time being ruler after he embraced Buddhisim and worked on non-violence of the people. This with writings such as the Vedas and the Upanishads gave a lot of information and solved many mysteries for today's time. • All over the world, people realize that ancient Indian texts include the business of living, not just religion. Many people are beginning to view spirituality too. Geography Key Points • The most important of them was River Saraswati, which is not traceable now. • There was encompassing desert, mountains, forest, and jungle all over ancient India. All of these types of places were susceptible to unpredictable periods of flood, drought, and monsoon. • The Himalayas provided a great deal of protection from nomadic and military invasions from the north. • The water ways of the Indus valley provided an excellent source for trade and commerce all through India's history. Siddhartha Gautama or The Buddha Born around 563 BC in a small kingdom. (Nearby present-day Nepal) In the beginning, he was wealthy, handsome, happily married, and had a family. One day, he traveled outside of the palace and saw for the first time, suffering. Beggars, the sick, the homeless, and other low people. Siddhartha Gautama (continued) Siddhartha then thought to himself, Why did people suffer and how could their suffering be cured? With that, Siddhartha left his family and kingdom to find his answer. For days, he could not eat and was forced to sleep on the cold, hard dirt. Once he began meditating (after 45 days) he found his answer. Siddhartha Gautama (continued) Basically, the lessons he taught to people all over the countryside were about life and the nature of suffering. This is known as Buddhism. What’s Buddhism? If you wish to understand his ideas and thoughts, you must first see the world in his eyes. Buddhism The Buddha did not think anything in the everyday life was real, like any other good Hindu. He believed the only way to find the truth about the world was to give up all desires. If did so, all pain and sorrow would vanish. If someone gave up all desires, they would reach nirvana. Nirvana is not a place, but a state of wisdom. Buddhism The heart of his teachings were the 4 Noble Truths. 1. Life is full of suffering. 2. People suffer because they desire worldly things and self-satisfaction. 3. The way to stop suffering is to end desiring things. 4. The only way to stop desiring things is to follow the Eightfold Path. Buddhism The Eightfold Path 1. Know and understand the four Noble Truths. 2. Give up worldly things and do not harm others. 3. Tell the truth, and don’t gossip or speak badly of others. 4. Don’t commit evil acts, like killing, stealing, or living an unclean life. 5. Do rewarding work. 6. Work for good and oppose evil. 7. Make sure your mind keeps your senses under control. 8. Practice meditation as a way of understanding reality.