* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Into the Darkness
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Violence in the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
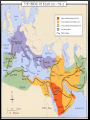
INTO THE DARKNESS 476- 800 RALLY ROBIN (PARTNER) Going back and forth with your Shoulder Partner, name as many things as possible that you saw the monks doing in the video. QUICK REVIEW • Rome falls in 476 A.D. • The lack of a substantial and stable emperor leaves a power vacuum in the Roman Empire. • The Church steps up. • Well structured and organized • God – given authority • Stability THE BENEDICTINE ORDER • St. Benedict (480-547) – Father of Western Monasticism • Wrote “The Rule of St. Benedict” a book of precepts for living the monastic life style. • The Rule can be summed up “Ora et labora” which means prayer and work. • 1500 year old tradition. MONTE CASSINO – BENEDICT’S MAIN MONASTERY BUILT IN 529. MONKS TODAY – BELMONT ABBEY MONKS SAVED THE (WESTERN) WORLD Monasteries become pockets of knowledge, culture, and prayer 3 Main Effects on Europe 1. Recovery and Evangelization of rural society - Boosted agriculture, acted as small towns for places not near cities. 2. Chief centers of learning and knowledge -Preserved important items and texts 3. Civilizing the Barbarians POPE ST. GREGORY THE GREAT “THE SERVANT OF THE SERVANTS OF GOD” • 540-604 • Originally the prefect of Rome – civilian leader (mayor/police chief/treasurer) • Lived as a monk & established 6 monasteries • Served as Papal Ambassador to Constantinople under Pope Pelagius II • Elected as the 64 th Pope in 590 1st monk to become pope • Responsible for the conversion of much of Europe especially England • Motivated by having watched a young English boy being sold as a slave FIVE LEGACIES OF POPE GREGORY THE GREAT 1. Friend of the Poor: used Church wealth to feed the poor and build churches and city walls 2. Church Leader and Reformer: Standardized seminary education, wrote guidelines for Bishops and standards for the moral life of clergy 3. Diplomat: Sent negotiators and missionaries to barbarians 4. Musician: Organized and wrote Christian music Gregorian Chant 5. Establishment of Christendom especially though the mission to Britain EARLY MISSION ACTIVITY IN EUROPE • Monks were pivotal in the converting of pagan tribes. • Violence and cruelty common among the barbarian tribes. • Many lands and people converted when their King or leader converted. • Europe totally Catholic (nominally) by 1330. MISSIONARY ACTIVITY CONTINUED Conversion of Franks • Clovis: King of the Franks (late 400’s) converted after winning battle. • Married to St. Coltilda • Merovingian Dynasty- Begins with Clovis. • Clovis unites Gaul (modern day France) Spain Spain is Christian due to the missionary efforts of the Apostle James the Greater and St. Paul Controlled by Visogoths in late 6th c. St. Hermengild (Visogoth prince) marries a Merovingian princess and eventually converts. Civil war with his father, captured and then killed. His brother converts to Catholicism and all of Spain soon follows. “The queen did not cease to urge him to recognize the true God and cease worshipping idols. But he could not be influenced in any way to this belief, until at last a war arose with the Alamanni, in which he was driven by necessity to confess what before he had of his free will denied. It came about that as the two armies were fighting fiercely, there was much slaughter, and Clovis's army began to be in danger of destruction. He saw it and raised his eyes to heaven, and with remorse in his heart he burst into tears and cried: "Jesus Christ, whom Clotilda asserts to be the son of the 1iving God, who art said to give aid to those in distress, and to bestow victory on those who hope in thee, I beseech the glory of thy aid, with the vow that if thou wilt grant me victory over these enemies, and I shall know that power which she says that people dedicated in thy name have had from thee, I will believe in thee and be baptized in thy name. For I have invoked my own gods but, as I find, they have withdrawn from aiding me; and therefore I believe that they possess no power, since they do not help those who obey them. I now call upon thee, I desire to believe thee only let me be rescued from my adversaries." And when he said thus, the Alamanni turned their backs, and began to disperse in flight. And when they saw that their king was killed, they submitted to the dominion of Clovis, saying: "Let not the people perish further, we pray; we are yours now." And he stopped the fighting, and after encouraging his men, retired in peace and told the queen how he had had merit to win the victory by calling on the name of Christ. This happened in the fifteenth year of his reign.” - St. Gregory of Tours, “History of the Frank” CONVERSION OF THE CELTS St. Patrick St. Columba • Roman Briton born near the beginning of the 5th c. • Important saints who helped Irish Monasticism. • Captured by pirates and became a slave, worked in NW Ireland. • Converted the Scots. • His spirituality and spreading of the faith led to the use of private, frequent penance. • Eventually he escaped and became a priest and Bishop of Ireland. • Preached and converted thousands in Ireland. CONVERSION OF ENGLAND St. Augustine of Canterbury • Sent to evangelize in Britain in 596. • Great example of obedience, upon hearing of the terrible violence of the Anglos/Saxons Augustine turns around and heads back to Rome. Gregory the Great then urges them and insists there is nothing to fear. • Missionary efforts were not always successful. St. Augustine had to work very hard. St. Bede • Father of English History, known as “Venerable” Bede. • First one to use “B.C.” and “A.D.” • Sets standard of historical scholasticism, leads to how history ought to be written. CONVERSION OF GERMANY St. Boniface – Born Winfrid in England • Apostle of Germany • Plagued by despair and discouraged by his suffering and the difficulty of evangelizing to the Germans • Felled the Oak of Thor- Not just cutting down a tree but a symbol of false gods and paganism. • Martyred by pagans • His work was pivotal in the expansion of Christianity within Germany. His establishment of monasteries, leadership, reform of the Church helped Catholicism take root and grow within the heart of Europe. CONVERSION OF THE SLAVS • St. Vladimir – Apostle of the Russians • Began as a Pagan Chieftain, multiple wives, many children worshipped idols and a feirce ruler • Wanted to use religion to solidify his rule. “Christianity was more edifying than Islam or Christianity” • Made a deal with Byzantine emperor Basil II Either I attack or I marry your sister Anna. • St. Vladimir was baptized then marred Anna. • Grace of God seemed to convert Vladimir. Reformed his ruling and focused on being a good follower of Christ. CONVERSION OF SLAVS CONTINUED • St. Cyril and St. Methodius • Helped convert the area of what is today Slovakia. • Feast Day February 14! • Did the liturgy in Slavic language • What was the common language of the Church at that time? • JPII “Patrons of Europe” CONVERSION OF SCANDINAVIA • St. Ansgar (801-865) Apostle of the North • Important figure with in Denmark and Sweden. • Worked to undo the slave trade, example of the Church’s social progressiveness. SO WHAT? • Evangelization is a necessary part of the Catholic faith. Jesus commands that we spread the word of God, “Go and make disciples of all nations.” • Christendom has now been established but a new religion begins and history shall unfold… • Example of the Church being “Apostolic” MISSIONARY REVIEW • Clovis & St. Clotilda • Franks, Gaul (France) • St. Patrick • Ireland • St. Columba • Scotland • St. Augustine of Canterbury • England • St. Bede • Father of English History • St. Boniface • Apostle of Germany • St. Cyril and St. Methodius • “Patron’s of Europe” , Slavic People • St. Vladimir • Apostle of Russia • St. Ansgar • Apostle of the North RISE OF ISLAM • Began in Mecca (Arabia) by Muhammad in 610 • Based on revelations by an angel of the one true God (Allah) • A mix of Judaism, Nestorian Christianity and Arabian Paganism. • Became very popular among tribal groups eventually led to jealousies that forced Muhammad and his followers (Muslims) to leave Mecca on the hijrah in 622 (year 1 on the Muslim Calendar) for the city of Medina • Muslim: submission to God • Islam: religion and way of life of Muslims ORIGINS OF ISLAM • The “prophet” Muhammad preaches monotheism in Mecca. • Forced to flee Mecca for his life. His teaching has caused problems with the Arabic elite. • This flight is known as the hejira or “flight” in Arabic. • Muhammad goes to Medina and is hailed as a religious leader. Becomes political and military leader of Medina. • (While in Medina Muhammad slaughters the Jewish population of men and sells the women and children into slavery). • 630 A.D. Muhammad conquers the city of Mecca. The Kaaba was spared destruction. SCRIPTURE BIBLE • Written by many authors over time = historical validity • Multiple recordings of same event(s). i.e. 4 Gospel accounts all telling the same story. • Divinely inspired – Holy Spirit works directly the free will of individuals to produce Christian scripture. • The Canon (list of Biblical books) decided by authority of the Magisterium. • The Bible is both prescriptive and descriptive. KORAN • Written by one man in a cave– Mohammed. Claimed that the angel Gabriel dictated the exact words of the Koran. • Koran means “recitation” in Arabic. • Written in the form of poetry, meant to be memorized. • Koran is prescriptive. COMPARISON OF LEADERS JESUS • • Miraculous birth. Part of the Holy Family. Heals many, controls nature, casts out demons, raises others from the dead. MOHAMMED • Raised as an orphan. • Adopts monotheism and begins preaching. • Political and Military leader. • Teaches about love, provides a perfect example • Has multiples wives, some very, very young. • Suffers the passion and dies on the cross. Resurrects. • Teaches submission to the one god Allah. • Ascends into heaven, promises to come again. Also provides help and grace in the mean time. • Dies of a fever at age of 63. JEWISH-CHRISTIAN-MUSLIM RELATIONS • Muslims consider Christians and Jews “people of the Book” • Muslims also call of conversion or death of all non-believers. • Jews and Christians have the same God, but Muslims think we corrupted the message of the prophets • Many converted because of religious enthusiasm or tax breaks • Muslim empire spread rapidly: Spain by 700’s • Failed sieges on Constantinople and France • defeated by Charles Martel@ Battle of Tours, 732 – if Muslims had been victorious all of Europe would have been conquered • In conquests: Jewish and Christian houses of worship were protected because God was worshipped there. ISLAMIC BELIEFS/IDEOLOGY • Jihad – “struggle” • Greater Jihad- personal spiritual battle to follow religious duties • Lesser Jihad – physical struggle against the enemies of Islam. • House of Islam/House of War • Theocracy – no separation of religion and government, both are one in the same. • Allah is the same God of the Jews. • Borrows from Judaism and Christianity – claims those two Religions have “misinterpreted” God’s will. EXCERPTS FROM THE QURAN And if you fear that you will not deal justly with the orphan girls, then marry those that please you of [other] women, two or three or four. But if you fear that you will not be just, then [marry only] one or those your right hand possesses. That is more suitable that you may not incline [to injustice]. Quran 4:3 Fight them until there is no [more] fitnah and [until] worship is [acknowledged to be] for Allah . But if they cease, then there is to be no aggression except against the oppressors. Fighting in] the sacred month is for [aggression committed in] the sacred month, and for [all] violations is legal retribution. So whoever has assaulted you, then assault him in the same way that he has assaulted you. And fear Allah and know that Allah is with those who fear Him. Quran 2:193-194 Indeed, the penalty for those who wage war against Allah and His Messenger and strive upon earth [to cause] corruption is none but that they be killed or crucified or that their hands and feet be cut off from opposite sides or that they be exiled from the land. That is for them a disgrace in this world; and for them in the Hereafter is a great punishment. Quran 5:33 Obey Allah and His Apostle": But if they turn back, Allah loveth [hubb] not those who reject Faith Quran 3:32 CONSIDER THIS…. ““You have heard that it was said, ‘AN EYE FOR AN EYE, AND A TOOTH FOR A TOOTH.’ 39 But I say to you, do not resist an evil person; but whoever slaps you on your right cheek, turn the other to him also. 40 If anyone wants to sue you and take your [am]shirt, let him have your [an]coat also. 41 Whoever [ao]forces you to go one mile, go with him two. 42 Give to him who asks of you, and do not turn away from him who wants to borrow from you. 43 “You have heard that it was said, ‘YOU SHALL LOVE YOUR NEIGHBOR and hate your enemy.’ 44 But I say to you, love your enemies and pray for those who persecute you, 45 so that you may [ap]be sons of your Father who is in heaven; for He causes His sun to rise on the evil and the good, and sends rain on the righteous and the unrighteous. 46 For if you love those who love you, what reward do you have? Do not even the tax collectors do the same? 47 If you greet only your brothers, what more are you doing than others? Do not even the Gentiles do the same? 48 Therefore [aq]you are to be perfect, as your heavenly Father is perfect. Matthew 5:38-48 QUESTIONS TO CONSIDER 1. According to these scriptures do Christians and Muslims have the same God or are they essentially different? 2. How do the views of marriage differ? 3. How are “enemies” dealt with in Islam? In Christianity? 4. Where did the Bible come from? Where did the Quran come from? 5. As Christians we called to obey God. Why should we obey God? Why do Muslims obey Allah? WHAT ABOUT VIOLENT BIBLE VERSES FROM THE OT? 1. We must understand the bible as a whole, both OT and NT. OT violence must be understood in the light of Jesus Christ and his saving action. 2. The Bible has a certain degree of interpretation guided by the authority of the magisterium. 3. OT violence is described within a story, it is not proclaimed as a decree which Christians must follow. This is different from the Koran (prescriptive vs descriptive). SPREADING OF ISLAM • Islam quickly spreads its empire after the death of Muhammad in 632. • The spread of territory and religion go hand in hand. The Islamic faith seeks converts and wages war on non-believers. • 638- Jerusalem falls • 643 – Alexandria falls • 698 – All of North Africa is under Muslim rule. • 711 – Spain falls • 732 – Muslim expansion into France is halted by Charles Martel in the Battle of Tours. • Muslims also attempted to take over Constantinople twice in 717 and 740. WHY DOES IS SPREAD SO QUICKLY? 1. Muslims gave newly conquered civilians two options: Conversion or the sword. Many chose to convert. 2. Islam appealed to the uncivilized, poor and ignorant. • It requires blind faith, intellectually easy, satisfies religious instincts without forbidding the baser pleasures of human life. MISC. • Islam claims is origins in the OT with Ishmael (Abraham’s son) but denies the Messianic theme of the OT. • Recognizes Jesus as a profit but wholly denies the NT accounts of Jesus life. • Rejects the divinity of Jesus • Mohammed picked and chose what he liked and did not like from Christianity and Judaism. • Preaches tolerance and peace but also the annihilation of non-believers. BATTLE OF TOURS 732 A.D. • Muslim conquest is quelled by Charles Martel (The Hammer) • Prevented from attacking Europe. • Defining moment of Christendom – Christian failure at the Battle of Tours would have led to full Muslim invasion of Europe and a very different story of history. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=otCpCn0l4Wo HTTP://WWW.YOUTUBE.COM/WATCH?V=OTCPCN 0L4WO CAROLINGIAN DYNASTY • Merovingian Dynasty corrupted and incompetent has nominal power over the Franks. • Carolingian Dynasty (named for Charles Martel) maintains the actual power over the Franks. • Charles Martel Pepin the Short Charlemagne Pepin the Short • Short, built, physically strong stature (namesake), yet extremely smart and clever = ambitious leader. • Asked Pope St. Zachary to name him King of the Franks because it was him who actually held the power. • The Pope officially recognized Pepin as the King bringing in the Carolingian Dynasty. Other members of the Carolingian Dynasty Charles the Fat, Charles the Bald, Charles the Simple, Pepin the Hunchback, Odo the Insane, Louis the Stammerer FRANKS AND THE PAPACY • November 11, 751 Pepin is crowned King of the Franks by St. Boniface. • Pope has shown that it has the Authority to appoint secular Kings. • Pepin becomes protector the Papacy • Threatened by the Lombards (Italian barbarians) Rome (the Papcy) looks to the Franks for help. • Pepin defeats the Lombards, preventing them from attacking Rome. • Secures Ravenna and Perugia thus creating the Papal States. THE PAPAL STATES • Donation of Pepin • The Papacy is now a sovereign political leader as well as a spiritual leader. ++++++ • Papacy gains independence from Byzantine influences. • Provided set boundaries to protect against Lombards and other belligerents. ----- Graying of Spiritual and Political power of the Pope/Church. - Temptation to abuse power can lead to the Church not always make the best decisions. CHARLEMAGNE –CHARLES THE GREAT • Son of Pepin the Short. • Reigned for almost half a century (769-814) • Extremely effective and good leader • Talented military strategist • Very intelligent, knew Latin and Greek, memorized portions of “City of God” • Brought about many reforms in his Frankish Kingdom; political, religious, cultural. • Devoted Catholic, adored the Church, created dioceses, gave to the poor protected the papacy, CHARLEMAGNE – UNITING AND RESCUING • July of 773 the Lombards (Barbarian tribe in Italy) threatened Rome. Charlemagne protects the papacy by defeating the Lombards. • Makes himself King of the Lombards thus uniting the Germanic tribes under one ruler. • Pope Leo III is attacked due to charges of corruption. Charlemagne comes to the rescue and helps the Pope regain his office. HOLY ROMAN EMPEROR • Christmas Day Mass in 800 Charlemagne is crowned by the Pope. • Reaffirms Charlemagne as King of the Franks and Lombards but also gives him the imperial title of Holy Roman Emperor. • This effectively includes the Germanic tribes into the Roman Empire. • Byzantine (Eastern) Empire is not pleased with the coronation but soon accept Charlemagne as the Emperor. CHARLEMAGNE AND THE SAXONS • Charlemagne forced the Saxons to become Christians! • How do we reconcile this? • Keep in mind Saxons practiced human sacrifice and ritualistic cannibalism. • Charlemagne struggles with the Saxons for 30 years, they continuously broke treaties, looted and terrorized Frankish villages. • 785 around 4,500 Saxons were tried in a military court and found guilty. They were all executed in one day. (Massacre of Verden) • Strict laws were passed to prevent Saxons from reverting back into heathenism.