* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure of the Atom
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
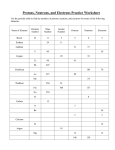
9/29/2008 Structure of the Atom Nucleus • Center of atom • Positively charged • Contains the “mass” of the atom • Contains subatomic particles Subatomic Particles in Nucleus • Protons - positive charge • Neutron - neutral charge (no charge) • Protons + Neutrons = Mass Number Element Identity • Elements are made up of only one type of atom • The number of protons an element has determines the type of atom it is. • Number of protons = atomic number Electron Cloud • Surrounds Nucleus • Subatomic particle in electron cloud electrons • Electrons - negative charge For example: • Carbon’s atomic number is 6; therefore Carbon has 6 protons. • How many protons does hydrogen have? • How many protons does Oxygen have? 1 9/29/2008 Atomic Mass • Measured in atomic mass unit (amu) • Mass number - atomic mass rounded. • For example: Average atomic mass of Potassium is 39.098 Mass number = 39 • What is the mass number of Boron? Practice • How many neutrons does Calcium have? Mass number = ___ Protons = ____ Mass number minus protons = _____ How many neutrons does Xenon have? Practice • How many electrons does Neon have? • Remember atomic number tells you how many protons the atom has. Neon’s atomic number is 10; therefore it has 10 protons and 10 electrons. Calculating Neutrons • IF protons + neutrons = Mass Number • THEN Mass Number minus protons = neutrons • For example: 11 + n = 23 or • 23 - 11 = n n = 12, • sodium has 12 neutrons Calculating Electrons • Atoms that are stable have no electrical charge; therefore, protons must equal electrons. • For example: Sodium has 11 protons and 11 electrons. (The positives must equal the negatives. ) Atomic Model • Diagram representing the subatomic particles in an atom. • Begin by filling in protons and neutrons in the nucleus (the center) • Place electrons around the nucleus • Electrons are distributed in the electron cloud in levels 2 9/29/2008 Electron Cloud Levels • 1st Level can only hold 2 electrons • 2nd Level can only hold 8 electrons • 3rd Level can hold up to 18 electrons Electron Cloud Levels Sulfur has ___ electrons. 2 will fill into the 1st energy level 8 will fill into the 2nd energy level 6 will fill into the 3rd energy level. 3