* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ferrites - Home | accelerators.org.au
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Multidimensional empirical mode decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum analyzer wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Sound level meter wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
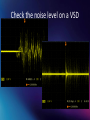
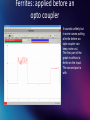
Ferrites What they are What they do How to apply What Ferrites are 5750nH 1520nH 10700nH 12340nH Ferrites are made of magnetic material to create an inductance in a current path 708nH Ferrites: What can they do? Keep noise at bay. Noise from: • • • • Switched mode power supplies Variable speed drives Stepper motors drivers Ground currents They can be applied to keep noise out of your signals: signals you monitor And they can be applied to keep noise in your device: driving signals How do we get ground currents? Generator Receiver ground currents magnetic field • By any changing magnetic field in a loop (nearby currents) • By capacitive coupling (nearby changing voltages) How do ground currents generate voltage in cables? Generator Receiver resistance ground currents • Resistance in the shield/return lead • Inductive coupling one lead to another (coax is much better but not perfect) Ferrites: What they do How to keep noise out. RF goes through without any obstruction. Ground currents see the ferrite. Ferrites: Test on network analyzer Ferrites: Test on network analyzer Ferrites: Test on network analyzer Ferrites: Test on network analyzer Ferrites: Test on network analyzer Ferrites: What they do How to keep noise in Variable speed drive Motor Ferrite How to apply ferrites Ferrites inside or outside the shield? Ferrites how to apply them Difference between in and outside shield You are outside of the shield small device Computer Ferrite You are here Ferrites how to apply them Difference between in and outside shield You are inside of the shield BIG DEVICE Variable speed drive Ferrite You are here Ferrites how to apply them Difference between in and outside shield Ferrites: how to apply them How many turns? Be creative with ferrites! How to determine noise sources A simple coil of a few turns, will do the job. Check the noise level on a VSD Check the noise level on a VSD Check the noise level on a VSD Ferrites: some examples Ferrites: applied before an opto coupler It sounds unlikely but in some cases putting a ferrite before an opto-coupler can keep noise out. The first part of the graph is without a ferrite on the input. The second part is with. Ferrites: typical noise Coax cable connected to a sensor, but what we see here is typical noise from a switched mode power supply. Because there is ground current through the coax shield through the protective earth of the scope. A few turns of the coax through a ferrite did significantly reduce the noise. Ferrites: applied to kill 50Hz Ferrites: how to interrupt common mode currents Example: a patch panel at the Australian synchrotron coax cables patch panel booster vacuum chamber Booster ring common mode current Ferrites: how to apply them. Patch panel metal patch panel N conn SMA conn Equip ment noise plastic patch panel Equip ment What ferrites cannot do. Kind of noise the ferrite cannot eliminate. • A ferrite is meant to isolate currents, it does not filter! • Once the common mode current created a differential mode voltage, the ferrite can do nothing about this. •In the case below there will be common mode current through the cable shield regardless the ferrites. • The main reason why ferrites work in a network of cables, is because you work in a low impedance network, and you apply a higher impedance in one cable. Currents through the shield, due to capacitive and/or inductive coupling Noisy cable