* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Engaging the non-meteorology students
Project Stormfury wikipedia , lookup
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Precipitation wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
Severe weather wikipedia , lookup
Marine weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Weather Prediction Center wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
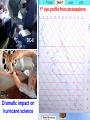
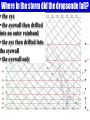
Engaging the non-meteorology student Arlene Laing COMET/MMM Let’s start with a quiz! Oh No! Don’t worry, it’s not graded What is Weather? • The condition of the atmosphere at a particular time and place "If you don't like the weather, wait a minute.” Mark Twain What am I? “The Cloud” Percy Shelly I am the daughter of Earth and Water And the nursing of the Sky I pass through the pores of the ocean and shores; I change, but I cannot die For after the rain when with never a stain The pavilion of Heaven is bare, And the winds and sunbeams with their convex gleams Build up the blue dome of air, I silently laugh at my own cenopath, And out of the caverns of rain, Like a child from the womb, like a ghost from the tomb, I arise and unbuild it again According to children * Water vapor gets together in a cloud. When it is big enough to be called a drop, it does. Elementary Meteorology Quiz USED WITH PERMISSION OF DR. ALISTAIR FRASER http://www.ems.psu.edu/~fraser/Quizzes/Met1Quiz/Met-quiz.cgi Water draining from a bathtub or sink rotates a) clockwise in the northern and counterclockwise in the southern hemisphere. b) counter-clockwise in the northern and clockwise in the southern hemisphere. c) cyclonically in both hemispheres. d) in a direction unrelated to the hemisphere. Elementary Meteorology Quiz The air flowing around the low pressure center of a large storm rotates a) cyclonically in both hemispheres. b) anti-cyclonically in both hemispheres. c) cyclonically in the northern hemispheres and anti-cyclonically in the southern hemisphere. d) anti-cyclonically in the northern hemisphere and cyclonically in the southern hemisphere. A LOW PRESSURE STORM SYSTEM IS A CYCLONE. FLOW IN A LOW PRESSURE IS BY DEFINITION CYCLONIC. What I have used • Online course material (own site, WebCT, Blackboard) • Real-time images, animations, graphs • Conceptual models – CD-ROMS supplied with text, COMET, UIUC, WISC, Alistair Fraser, CALMET, Texas A&M, … • Lab exercises – custom-made, text supplement, online sources • Videos – Discovery, TLC, Weather Channel, National Geographic, DailyShow, Library collection • Student web pages – graduate course) Where I have used Multimedia • • • • • Small class lecture (< 25 students) Large class lecture (> 150 students) Lab exercises (in & outside of class) Extra credit (students contribute websites) Connecting from the field Sample Topics & Tools Used • Interpreting Satellite Images • Hurricane tracking & intensity • Atmospheric Stability & Clouds • Precipitation Types • Finding Fronts • Thunderstorms & Tornadoes • General Circulation • Surface fluxes (air–sea temp, winds • Forecast contest UNIDATA TOOLS (McGUI, IDV), Web Browser, Gnumeric • Power Point • Video • CD-ROMs • Web Modules • Diary Webpage • Video Clips/Photos What we had before the lab What we had before the lab WORK WITH THE STORM YOU HAVE Review: http://www.comet.ucar.edu/nsflab/web/explore/o1ir.htm Review: http://www.meted.ucar.edu/hurrican/movncane/ Gabrielle: Rooftop Weather on the Web Review: http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml Resources for the Course Power point (Outline before. More slides few days after class) Text info & Websites Module started in class. Students encouraged to review Iowa’s Virtual Tornado Big hit with students & visitors Make new questions • • • For Africa, describe the changes in climate (temperature and precipitation) north from Cape Town to Cairo. Compare the climates of Kisagani and Mogadishu Describe the variation in climates of Timbouctou, Ouogadougou, and Mamou Using the Unidata IDV • Unidata IDV used to relate changing pressure and precipitation over the U.S. Mean sea level pressure and total precipitation were used. A ten-frame animation showed the Rossby wave progression and related changes in pressure and precipitation. • Students then used the data probe to measure mean sea level pressure and precipitation at a given latitude/longitude. After collecting these data, students plotted a simple time series graph of mean sea level pressure, identified the mean sea level pressure at the time of highest precipitation, and identified the trends over time of the two data sets. Graduate seminar course Presentations, Discussions (In class and Online), Videos, Student web pages, Final Conference Style Presentation & Term Paper Student Webpage Connecting from the field • Dropsonde team on NASA DC-8, CAMEX-4, 2001 • CAMEX Diary (images, video clips, graphs) • Students - CAMEX scientists emails • Writing exercise during lull in convection. Students played scientists. Used images from CAMEX-3 to give daily scientific briefing for their team. 1st eye profile from stratosphere DC-8 ER-2 Dramatic impact on hurricane science Where in the storm did the dropsonde fall? • the eye • the eyewall then drifted into an outer rainband • the eye then drifted into the eyewall • the eyewall only Other Exercises: In class and lab • Tracks and Observations Satellite, surface, and upper air data to track Erin and Gabrielle • Will there be a Gabrielle? Examined sea surface temperatures, 850-300mb wind shear, 300mb heights and wind vectors, and Hurricane Heat Potential derived by NOAA AOML. • Intensification Using COMET Remote Sensing laboratory exercise, students learnt to identify mesoscale convective development, eyewall structure, and relate those features to tropical cyclone intensification. Used technique to compare intensity changes in Hurricanes Erin and Felix More than Hurricanes Western seabreeze thunderstorm line advances eastward Eastern sea breeze (quasistationary) Western Seabreeze Eastern Seabreeze Seabreezes converge Weak Tornado forms where sea breezes converge Wakimoto and Wilson 1989 Some favorite resources • • • • • • • WW2010, Atmospheric Science, UIUC WXWISE, SSEC, U of Wisconsin DLESE Virtual Tornado - Iowa State (Doug Yarger, Bill Gallus) Radiation & Adiabatic Simulation – PALS, Doug Yarger Sea Breeze – John Nielsen Gammon, Texas A&M, COMET Coriolis, Forces – CD-ROM, Understanding Weather and Climate by Aguado & Burt, UIUC • Blue Skies (Perry Samson, Ahrens) • Remote Sensing – WXWise, COMET • Data archives – FSU, Weather Unisys, Plymouth State, Recent past - Texas A&M, RAL/NCAR