* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Chain of Infection
Toxoplasmosis wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Toxocariasis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
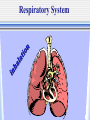
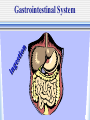
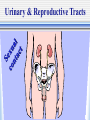
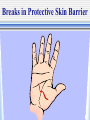
The Chain of Infection As healthcare professionals, it is important to understand two things about infection: 1.the various ways infection can be transmitted 2. the ways the infection chain can be broken There are six links in the chain of infection : 1st - The Infectious Agent -any disease-causing microorganism (pathogen) 2nd - The Reservoir Host -the organism in which the infectious microbes reside What are “Carrier Hosts” Hosts that do not show any outward signs or symptoms of a disease but are still capable of transmitting the disease are known as carriers. 3rd - The Portal of Exit -route of escape of the pathogen from the reservoir. Examples: respiratory secretions, blood exposure, breaks in skin 4th - The Route of Transmission -method by which the pathogen gets from the reservoir to the new host Transmission may occur through: direct contact air insects 5th - The Portal of Entry -route through which the pathogen enters its new host Respiratory System Gastrointestinal System Urinary & Reproductive Tracts Breaks in Protective Skin Barrier 6th - The Susceptible Host -the organism that accepts the pathogen The support of pathogen life & its reproduction depend on the degree of the host’s resistance. Organisms with strong immune systems are better able to fend off pathogens. Organisms with weakened immune systems are more vulnerable to the support & reproduction of pathogens. How to interrupt the chain of infection: -The essential part of patient care & self-protection. 1. Pathogen Identification -identification of infectious agent & appropriate treatment 2. Asepsis & Hygiene -potential hosts & carriers must practice asepsis & maintain proper personal hygiene 3. Control Portals of Exit -healthcare personnel must practice standard precautions: (Control body secretions & wash hands according to protocol.) 4. Prevent a Route of Transmission -prevent direct or indirect contact by: 1. Proper handwashing 2. Disinfection & sterilization techniques 3. Isolation of infected patients 4. Not working when contagious 5. Protect Portal of Entry -Health professionals must make sure that ports of entry are not subjected to pathogens. (nose, mouth, eyes, urinary tract, open wounds, etc.) 6. Recognition of Susceptible Host -health professionals must recognize & protect high-risk patients •Cancer Patients •AIDS Patients •Transplant Patients •Infant & Elderly Patients Remember--breaking the chain of infection is the responsibility of each health professional.