* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forms of Energy - Muskingum Valley Educational Service Center
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
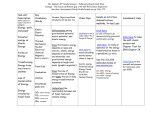
Center for Performance Assessment Unwrapped, Standards-Based Performance Assessment Template Grade Level: 7 Science Targeted Content Area(s): Physical Science 2, 3, and 5 Authors: Debbie Hardesty, Lori Cabot, Jill Fry School, District, and State: River View and Ridgewood Middle Schools Ohio Phone and E-mail (Preferred, But Optional) Assessment Title: How to Become an Energized Bunny Overview of Performance Assessment: (Summary of the assessment with a brief synopsis of each task) Task 1 Use magazines or drawings to create a poster showing potential and kinetic energy. Task 2 Write a descriptive paragraph detailing one form of energy. Task 3 Trace the energy transformation in the closed system of a flashlight. Task 4 Produce and demonstrate a product that shows different forms of energy. Full Text of Standard(s) and Indicators(s) in Targeted Content Area: Physical Sciences Standard 2. Describe how an object can have potential energy due to its position or chemical composition and can have kinetic energy due to its motion. 3. Identify different forms of energy (e.g., electrical, mechanical, chemical, thermal, nuclear, radiant and acoustic). 5. Trace energy transformation in a simple closed system (e.g., a flashlight). Related Interdisciplinary Standard(s) and Indicators(s): Language Arts Acquisition of Vocabulary 1. Define the meaning of unknown words through context clues and the author’s use of comparison, contrast, definition, restatement and example. Reading Process 5. Select, create, and use graphic organizers to interpret textual information. Writing Applications 4. Write informational essays or reports, including research, that present a literal understanding of the topic, include specific facts, details and examples from multiple sources, and create an organizing structure appropriate to the purpose, audience, and context. Research 8. Use a variety of communication techniques, including oral, visual, written or multimedia reports, to present information that supports a clear position with organized and relevant evidence about the topic or research question. Technology Technology and Communications 2. Generate multimedia presentations that communicate information for specific purposes. Technology for Productivity Applications 8. Use content specific tools/software/simulations to support learning/research to create educational projects. Designed World 6. Design, develop, fabricate, and service a product. Art Connections, Relationships, Applications 3. Demonstrate understanding of the relationship between words and images by applying text to images and images to text. “Unwrapping” Content Standard(s) Grade Level and Content Area: 7 Science Standard(s) and Indicators by Number: Physical Science 2, 3, 5 Concepts: Need to Know About Different Forms of Energy 1. Potential --------Kinetic 2. Electrical, mechanical, chemical, thermal, nuclear, radiant, and acoustic Skills: Be Able to Do Describe (potential and kinetic energy) Identify (Forms of energy) Trace (Energy transformation, closed system) Topics or Context: (What you will use to teach concepts and skills—particular unit, lessons, activities) 1. Text 2. Demonstrations 3. Student Activities Identifying Big Ideas from Unwrapped Standard and Indicators 1. Potential energy comes from an object’s position or chemical composition. 2. Kinetic energy is due to motion. 3. There are many different forms of energy. 4. Energy changes forms which can be traced. Essential Questions from Big Ideas to Guide Instruction and Assessment 1. How and why do we store energy? 2. What is the difference between potential and kinetic energy? 3. Which forms of energy do you use? 4. Can you trace the energy transformations in a closed system? “Engaging Scenario” Planning Include elements of an effective Engaging Scenario: Presents students with a challenge Connects learning to real life – “Why do we need to learn this?” Conveys importance – “What does this mean to the student personally?” Acknowledges audience – “Can the student present the completed task to others?” Engaging Scenario (Full description): Our world today relies on energy. Each form of energy has its advantages and disadvantages.The big job is to track the energy we use to better understand where it came from and where it is going. As a scientist, you will investigate energy forms and how they change. At the end of your investigation, you will share important facts and uses of one energy form to your teacher and class. You will research energy forms and their transformations, then create visual representations to share with your classmates. Task 1 Planning Guide (“SQUARE” – Key Elements to Include in the Design of a Standards-Based Performance Task) Which STANDARD(s) and Indicators Will This Task Target? 2. Describe how an object can have potential energy due to its position or chemical composition and can have kinetic energy due to its motion. Which Essential QUESTION Will This Task Address? 2. What is the difference between potential and kinetic energy? Which UNWRAPPED Content Knowledge and Skills Will This Task Develop? Concepts: Need to Know About Different Forms of Energy 3. Potential --------Kinetic Skills: Be Able to Do Describe (potential and kinetic energy) What APPLICATION of Learning Will This Task Require? (What will the students actually do or produce in this task?) A poster showing potential and kinetic energy What Instruction, Information, and RESOURCES (including Technology Connections and Related URLs) Will Students Need First? Instruction: Define and demonstrate potential and kinetic energy. What Individual EVIDENCE of Learning Will This Task Provide? (How will you know by the work students produce what they have learned relative to this task?) The poster will accurately depict potential and kinetic energy. Task 1 Complete Description (The Full Details of What Students Will Do in This Task) Students will create a poster using 10 x 14 drawing paper, magazines, markers, scissors, glue, etc. The poster will show a change of energy from potential to kinetic using two pictures, one demonstrating potential energy and the other kinetic. They will label each picture. Task 1 – Scoring Guide Exemplary: All Proficient Criteria Met PLUS: an unusual or creative depiction of potential and kinetic energy (i.e. items not already discussed in class) Proficient: The poster has two pictures. Pictures are properly labeled and neatly displayed. Pictures accurately depict potential and kinetic energy. Progressing: Pictures represent both forms of energy but are labeled inaccurately or not labeled. Not Yet Meeting Standard(s) and Indicators(s): Pictures do not represent both forms of energy Peer Evaluation (Optional) _____ Self-Evaluation _____________ Teacher Evaluation __________ Comments__________________ Task 3 Planning Guide (“SQUARE” – Key Elements to Include in the Design of a Standards-Based Performance Task) Which STANDARD(s) and Indicators Will This Task Target? 5. Trace energy transformation in a simple closed system (e.g., a flashlight). Which Essential QUESTION Will This Task Address? 4. Can you trace the energy transformations in a closed system? Which UNWRAPPED Content Knowledge and Skills Will This Task Develop? Concepts: Need to Know About Different Forms of Energy 3. Tracing energy forms Skills: Be Able to Do Trace (Energy transformation, closed system) What APPLICATION of Learning Will This Task Require? (What will the students actually do or produce in this task?) Students will use a hand powered flashlight, compass and magnet to discover energy transformations and produce a flowchart to show the energy transformations. What Instruction, Information, and RESOURCES (including Technology Connections and Related URLs) Will Students Need First? Descriptions and examples of different types of energy What Individual EVIDENCE of Learning Will This Task Provide? (How will you know by the work students produce what they have learned relative to this task?) A flowchart will show the energy transformations in a hand powered flashlight. Task 3 Complete Description (The Full Details of What Students Will Do in This Task) Students have a flashlight, magnet, and compass. Working in groups of three, students investigate the inner workings of the flashlight. Students will discuss the energy transformation from the body to the lighting of the bulb: Chemical (food in body that allows body to function), to kinetic (hand squeezing the handle), to kinetic (gears in flashlight move) to kinetic (rotation of the magnet) to electrical (copper wire) to radiant (lighting of the bulb) Students use a flowchart template to label and describe each energy transformation. Task 3 – Scoring Guide Exemplary: All Proficient Criteria Met PLUS: Took on a leadership role in the group and helped lead others to conclusions. Descriptions include illustrations. Proficient: Students participate appropriately in group discussion Flowchart shows and describes all energy forms in the correct order of energy transformation using scientific vocabulary Flowchart is neatly completed. Progressing: Flowchart is missing one or more components Flowchart components are out of order. Peer Evaluation (Optional) _____ Self-Evaluation _____________ Teacher Evaluation __________ Comments__________________ Task 2 Planning Guide (“SQUARE” – Key Elements to Include in the Design of a Standards-Based Performance Task) Which STANDARD(s) and Indicators Will This Task Target? 3. Identify different forms of energy (e.g., electrical, mechanical, chemical, thermal, nuclear, radiant and acoustic). Which Essential QUESTION Will This Task Address? 3. How many different forms of energy do you use each day? Which UNWRAPPED Content Knowledge and Skills Will This Task Develop? Concepts: Need to Know About Different Forms of Energy Electrical, mechanical, chemical, thermal, nuclear, radiant, and acoustic Skills: Be Able to Do Identify (Forms of energy) What APPLICATION of Learning Will This Task Require? (What will the students actually do or produce in this task?) Students will research a form of energy in order to write a paragraph describing that form of energy without naming it. They will include clues in their paragraph which include examples and facts so that other students in the class can guess which form of energy about which the paragraph is written. What Instruction, Information, and RESOURCES (including Technology Connections and Related URLs) Will Students Need First? Students will need to know how to access different sources of information including the internet, reference books, textbooks, trade books, and local power suppliers. What Individual EVIDENCE of Learning Will This Task Provide? (How will you know by the work students produce what they have learned relative to this task?) The students’ paragraphs will accurately describe one energy form with examples of each. As students listen to their classmates’ paragraphs, they will accurately identify the forms of energy being described for any paragraph the teacher decides adequately represents each form. Task 2 Complete Description (The Full Details of What Students Will Do in This Task) Students will use at least one reference to research a given form of energy. They will collect four or five facts about that form of energy and at least three examples of how that form of energy is used. The students will use their notes to compile a paragraph to present to the class. The paragraph will not name their form of energy but will adequately describe it so that others in the class can accurately identify it. Students will listen as their classmates read their paragraphs aloud and will vote by ballot as to what form of energy the paragraph describes. They will write the presenter’s name, the form of energy, and their own name on a ballot. Task 2 – Scoring Guide Exemplary: All Proficient Criteria Met PLUS: Paragraphs exceed 5 facts and 3 examples Paragraphs follow all writing conventions with few or no errors. All votes cast accurately identify the form of energy being described. Proficient: Paragraphs include at least 4 facts and at least 3 examples of the given form of energy Paragraphs follow most conventions of writing (spelling, grammar, punctuation, legibility, etc.) Paragraphs accurately describe the energy form without identifying it. 80% of votes cast accurately identify the form of energy being described. Progressing: Paragraphs include no more than three facts and two examples. Paragraphs contain conventional writing errors that compromise the understanding of the content. Less than 80% of votes cast accurately identify the form of energy being described. Peer Evaluation (Optional) _____ Self-Evaluation _____________ Teacher Evaluation __________ Comments__________________ Task 4 Planning Guide (“SQUARE” – Key Elements to Include in the Design of a Standards-Based Performance Task) Which STANDARD(s) and Indicators Will This Task Target? 2. Describe how an object can have potential energy due to its position or chemical composition and can have kinetic energy due to its motion. 3. Identify different forms of energy (e.g., electrical, mechanical, chemical, thermal, nuclear, radiant and acoustic). 5.Trace energy transformation in a simple closed system (e.g., a flashlight). Which Essential QUESTION Will This Task Address? 1. How and why do we store energy? 3. Which forms of energy do you use? Which UNWRAPPED Content Knowledge and Skills Will This Task Develop? Concepts: Need to Know About Different Forms of Energy Potential --------Kinetic Electrical, mechanical, chemical, thermal, nuclear, radiant, and acoustic Skills: Be Able to Do Describe (potential and kinetic energy) Identify (Forms of energy) Trace (Energy transformation, closed system) What APPLICATION of Learning Will This Task Require? (What will the students actually do or produce in this task?) The students will design a presentation that shows energy transformations of a system. What Instruction, Information, and RESOURCES (including Technology Connections and Related URLs) Will Students Need First? Research resources such as the internet, trade books, reference books, resources from energy suppliers. Access to computers, video camera, or other equipment or supplies for presentation. What Individual EVIDENCE of Learning Will This Task Provide? (How will you know by the work students produce what they have learned relative to this task?) Students will demonstrate through a presentation a flow of energy through a system from beginning to end. The presentation will include a visual aid. Task 4 Complete Description (The Full Details of What Students Will Do in This Task) Students will write a plan for teacher approval telling what type of system they will demonstrate and what means they will use to present it. Upon plan approval, students will individually design a visual aid and oral presentation to present to the class. Visual aids could include but are not limited to transparencies, Power Point, poster, video, skit, photographs, or model. Task 4 – Scoring Guide Exemplary: Student has more than one visual aid. Student engages the audience in the presentation. Student demonstrates knowledge of the system by accurately answering questions from the audience. Proficient: Visual aid accurately shows an energy transformation. Student appropriately uses the visual aid as part of his/her presentation. Student accurately explains each energy transformation of their chosen system. Student shows knowledge of the system by telling the information without reading it. Progressing: Student reads information or information is incomplete or inaccurate. Visual aid is missing steps or does not correspond with oral information. Peer Evaluation (Optional) _____ Self-Evaluation _____________ Teacher Evaluation __________ Comments__________________ Teacher Reflections at Conclusion of Performance Assessment: 1. What Worked? What Didn’t? 2. What Will I Do Differently Next Time? 3. What Student Work Samples Do I Have for Each Task? What Scoring Guide Examples of Proficiency Do I Have for Each Task? 4. What Field Notes Can I Provide for Other Teachers Who May Use This Performance Assessment? Bloom’s Taxonomy Definitions Verbs that express varying levels of understanding Appropriate responses 1. Knowledge – Remembering facts Verbs: Know, define, memorize, record, name, recognize Describe ________________________________. Who? What? Where? When? How? 2. Comprehension – Understanding the meaning Verbs: Discuss, relate, clarify, explain, Retell in your own words ____________________. What is the main idea of ____________________? 3. Application – Using what you know in a new situation Verbs: Translate, interpret, demonstrate, dramatize, practice Why is __________ significant? 4. Analysis – Examining specific parts of information Verbs: Distinguish, analyze, differentiate, solve, examine Classify _______ according to ________________. Compare and contrast _____________ and _______________. 5. Synthesis – Combing ideas in a new way Verbs: Compose, plan, propose, formulate, arrange What could you predict from ______? What solutions would you suggest from _____________? 6. Evaluation – Developing opinions, judgments, or decisions Verbs: Judge, appraise, evaluate, estimate, select Do you agree with _____? Prioritize _________. What is the most important _______________? Advertising Applicant Architect Artist Athlete Journalist Judge Jury Member Lawyer Musician Autobiographer Biographer Business Person Campaign Worker Cartographer Cartoonist Character, Book/Movie Chef Citizen Coach Collector Consumer Consumer Advocate Contractor Curator Detective Editor Engineer Executive Famous Person Inventor Advertising Campaign Anthem Anthologies Autobiography Brochure Business Letter Business Plans Committee Board Members Consumer Newsletter Newscaster Parent Photographer Photojournalist Playwright Poet Police Officer Reporter Researcher Set Designer Software Developer Speech Writer Stock Broker Student Teacher Textbook Publisher Tour Guide Travel Agent Tutor Debate Designs for Experiments Diorama Ecosystem Eulogy Fable Fashion Show Film Review Food Critique Friendly Letter Graphs How-To Directions HyperStudio Inventions Journals Judge’s Decision Lab Report Lawyer’s Argument Maps Observation Logs Panel Discussion Personal Narrative Persuasive Letter Models Movie or short film Museum Exhibit Newspaper Prequel Proposal Puppet Show Quilt Reaction Paper Scrapbook Sculpture Short Story Slide Show Symphony Tall Tales Technical Manual Travel Journals Website