* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download History of Lisp
Closure (computer programming) wikipedia , lookup
Lambda calculus wikipedia , lookup
Scala (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Lambda calculus definition wikipedia , lookup
Standard ML wikipedia , lookup
Combinatory logic wikipedia , lookup
Falcon (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
C Sharp (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
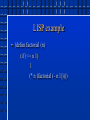
History of Lisp And Functional Programming Languages Scotty Smith Overview • • • • • Lambda Calculus History of Lisp Key Features of Functional Languages Haskell Why no one uses functional languages Lambda Calculus • Developed by Alonzo Church in the 1930’s • Type Free • Deals with recursion, higher-order functions, and currying λx.x+1 ≡ fun x => x+1 The Beginnings of LISP • John McCarthy -1956 • Dartmouth summer research project on Artificial Intelligence. • IBM 704 FLPL: FORTRAN List Processing Language • Implemented at IBM by Herbert Gelernter and Carl Gerberich • Written as an extension of FORTRAN Conditional Expressions • Developed in 1957 – 1958 at MIT. • XIF(M,N1,N2). • Developed a true conditional that evaluated only one of its parameters. Innovations Beyond FLPL • Recursive functions using conditional expressions • Maplist Implementation of LISP • Fall of 1958 • MIT • Started by hand compiling functions written in M-expressions • Prefix notation • Contains side effects Turing Machines and LISP • The universal LISP function • eval[e,a] • e – The LISP expression • a – a list of assignments of values to variables The Interpreter • Written by S.R. Russell • Froze the development of the form of the language. Moving On • Lisp 1.5 • Insertion of elements into lists and deletion • Lexical scoping • FUNARG device • A compiler Other contributions of LISP • Garbage collection LISP example • (defun factorial (n) (if (<= n 1) 1 (* n (factorial (- n 1))))) Key Features of Functional Languages • Higher Order functions • Curried functions • Lazy Evaluation (Non-strict Evaluation) • Static typing • Pattern Matching • Guards • fac 0 = 1 fac n|n>0 = n*fac(n-1) Haskell • Purely functional language • Attempt at a standard functional language • Features • • • • • • Higher order functions Lazy evaluation Static polymorphic typing User-defined datatypes Pattern matching List comprehensions • New to Haskell • I/O system • Overloading • Array comprehensions Why no one uses functional languages • Portability/Availability • Training • Popularity References • • • Hudak, P. 1989. Conception, evolution, and application of functional programming languages. ACM Comput. Surv. 21, 3 (Sep. 1989), 359-411. DOI= http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/72551.72554 McCarthy, J. 1978. History of Lisp. In Preprints of Proceedings of ACM SIGPLAN History of Programming Languages Conference. SIGPLAN Notices, Vol. 13, pp. 217223 Wadler, Phillip. “Functional Programming: Why no one uses functional languages” SIGPLAN Notices 33(8):23-27, August 1998.