* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grammar Unit II: Pronouns
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sanskrit grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Literary Welsh morphology wikipedia , lookup
Bound variable pronoun wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Third-person pronoun wikipedia , lookup
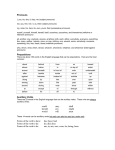
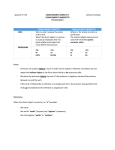
Grammar Unit II: Pronouns Lesson 1 Personal Pronouns (Pronouns that are friendly!) DEFINITIONs Pronoun: a word that is used to replace a noun Ex: Marcy went to the market, and she bought bread. Personal Pronoun: a word that is used to replace a noun that refers to a person or thing Ex: Marcy went to the market, and she bought bread. Personal pronouns Two cases of personal pronouns include SUBJECT OBJECT Subject pronouns are the subject of a verb. They generally appear BEFORE the verb. Object pronouns are the receiver of the action of the verb or for whom an action was performed. They generally appear AFTER the verb. She went to the store. Subject pronoun Jordan bought her roses. Object pronoun Personal pronouns Nominative (SUBJECT) PRONOUNS Singular Plural First Person I we Second Person you you Third Person she, he, it They Practice Directions: Identify the subjective pronoun in each sentence. On the line label is at S (singular) or P (plural) and 1st, 2nd, or 3rd person. rd P-3 ____ 1. They went to the basketball game. st P-1 ____ 2. In June, we will start summer vacation. rd S-3 ____ 3. He took French class in ninth grade. rd P-2 ____ 4. You all will have a quiz on pronouns. Personal pronouns OBJECT PRONOUNS Singular Plural First Person me Us Second Person you you Third Person her, him, it them Practice Directions: Identify the objective pronoun in each sentence. On the line label is at S (singular) or P (plural) and 1st, 2nd, or 3rd person. rd S-3 ____ 1. Skylar gave her roses. st P-1 ____ 2. The teacher gave us an assignment. rd P-3 ____ 3. The email was sent to them yesterday. rd P-2 ____ 4. I told you all about the quiz. !The exception! The exception to this is when the verb is a linking verb (and not an action verb). BASIC LINKING VERBS The exception? AM Subject pronouns are used AFTER these verbs. IS ARE WAS WERE BE SUBJECT PRONOUN The best player is she. BEING BEEN LINKING VERB Practice Directions: Underline the pronoun in each sentence. Above each pronoun write SUB (subjective) or OBJ (objective). On the line label S or P. Then 1st, 2nd, or 3rd person. SUB s-3rd ____ 1. She put on the mittens. SUB p-3rd ____ 2. They were black with white snowflakes. OBJ rd p-3 ____ 4. Marcy’s mother gave them to her. s-3rd SUB ____ 5. Marcy feels the best mother in the world is she. OBJ rd p-2 ____ 2. The teacher will give you all a quiz soon. TESTING YOUR KNOWLEDGE What is a pronoun? A word that takes the place of a noun What is a personal pronoun? A word that takes the place of a person or thing Give the seven subject pronouns: I, we, you, she, he, it, they When do you use subject pronouns? When it is the subject of the sentence or AFTER a linking verb List the basic linking verbs? am, is, are, was, were, be, being, been TESTING YOUR KNOWLEDGE cont. Give the seven object pronouns? me, us, you, her, him, it, them When do you use object pronouns? After action verbs—or to describe who is receiving the action of the verb or to describe for whom the action was performed. Grammar Unit II: Lesson 1.2 Using Subjective Personal Pronouns Correctly Personal pronouns SUBJECT PRONOUNS First Person Second Person Third Person Singular I you she, he, it Plural we you they Using Subjective Pronouns Subjective personal pronouns should always be used when they are the subject of the sentence or when they immediately follow a linking verb. This sounds easy, but things can get complicated. Why? Read this sentence. Then decide which pronoun is the correct choice. John and (I, me) went to the store. Many people will make the mistake of using me in the above sentence. However, cover up the words John and. Now, read the sentence using me. It sounds very incorrect. I becomes the obvious choice. Compound subjects A compound subject is made up of two or more subjects that are connect by AND, BUT, or OR and share the same verb. John and I went to the store. John and I are the compound subject John and I share the verb went It gets harder! Read this sentence. Then decide which pronoun is the correct choice. The best basketball players are (her and me, she and I). Many people will make the mistake of using her and me in the above sentence. However, the verb are is a linking verb; therefore, subjective pronouns needs to be used. She and I is the correct answer. Why use subjective pronouns after linking verbs? We use subjective pronouns after linking verbs because a linking verb shows that the subject is equal to what comes after the verb. The best basketball players = she and I If we compare this to math class: 2+2 = 4 Just like in math, both sides of the sentence or equation equal each other. Because they equal each other, we can reverse the equation (just like in math). 4=2+2 Subjective pronouns & Linking Verb The best basketball players = she and I Or we can reverse the sentence: She and I = best basketball players She and I are the best basketball players. Subjective pronouns & Linking Verb Because we can make the pronoun the subject, we need to always use subjective pronouns after linking verbs. My related arts teachers are she and he. teachers = she and he She and he = teachers She and he are my related art teachers. Guided Practice Read each sentence and make the correct pronoun choice. 1. Miles and (they, them) went to the basketball game. 2. (Casey and him, Casey and he) was injured. 3. The players that fouled them are (they, them). 4. (We, us) players were astonished. 5. The writer of this report is (him, he). Grammar Unit II: Lesson 1.3 Using Objective Personal Pronouns Correctly Personal pronouns OBJECT PRONOUNS First Person Second Person Third Person Singular me you her, him, it Plural us you them Using objective Pronouns Objective personal pronouns should always be used after 1. an ACTION verb AV Tyler hit it out of the park. 2. a PREPOSITION Larry gave the ball to him. preposition Common prepositions about after before behind beside between by for from like near of Suzy gave the paper to her. Linda sat between him and her. The story was written by them. to with without Guided Practice Read each sentence. Underline all verbs twice. Label them AV or LV. Place a box around prepositions. Circle the correct pronoun. LV 1. Between (you and me, you and I), this is easy stuff! AV 2. After class, Gabby gave (she, her) a note. AV 3. The book delighted (us, we) readers. AV 4. The teacher assigned (they, them) homework for Thursday. Subjective & Objective Practice Read each sentence. Underline all verbs twice. Label them AV or LV. Place a box around prepositions. Circle the correct pronoun. Label it Sub or Obj on the line. AV Sub ___1. (He, him) and Dana wrote the report. AV obj ___2. Larry told John and (me, I) about the assignment. LV sub ___3. The write of the report was (she, her). obj AV ___4. The report was challenging for (they, them). Possessive Pronouns A possessive pronoun is a pronoun that shows who or what has something. A possessive pronoun may take the place of a possessive noun. Read the following sentences. Notice the possessive nouns and the possessive pronouns Continue Possessive Pronouns Homer’s story is famous. His story is famous. This story is Homer’s. This story is his. Possessive nouns are in green. Possessive pronouns are in red. Continue Possessive Pronouns Possessive pronouns have two forms. One form is used before a noun. The other form is used alone. Singular Plural my Used your before nouns his, her, its Used alone mine yours his, hers, its our your their ours yours theirs Possessive Pronouns Possessive pronouns are not written with apostrophes. The pronoun its, for example, shows possession. The word it’s, on the other hand, is a contraction of it is. Read the following sentences. Notice the meaning of the words in red type. Its central character is Odysseus. (possessive pronoun) It’s about the adventures of Odysseus. (contraction of It is)