* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Self test (final version) (NEW)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
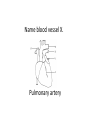
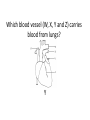
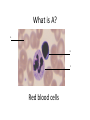
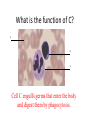
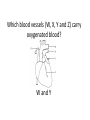
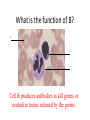
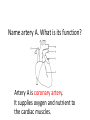
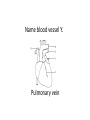
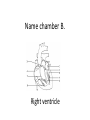
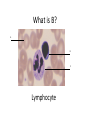
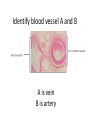
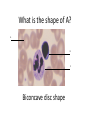
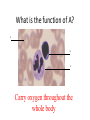
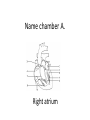
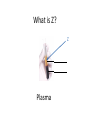
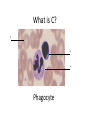
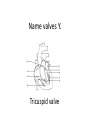
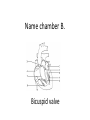
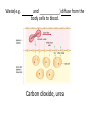
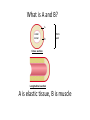
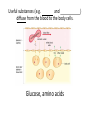
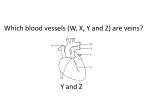
Name blood vessel X. Pulmonary artery Three types of blood vessels are Artery, vein and capillary Artery carry blood ________ heart away from Which blood vessel (W, X, Y and Z) carries blood from lungs? Y What is X? X Blood cells State two differences between A and B The wall of A is thinner than B. The lumen of A is larger than B. Name blood vessel W. aorta What is A? A B C Red blood cells Name valves X. Semilunar valve What is the function of C? A B C Cell C engulfs germs that enter the body and digest them by phagocytosis. Red blood cells Made in Red bone marrow Name chamber C. Left atrium Which blood vessels (W, X, Y and Z) are veins? Y and Z Which blood vessels (W, X, Y and Z) carry oxygenated blood? W and Y What is the function of B? A B C Cell B produces antibodies to kill germs or neutralize toxins released by the germs. Explain why blood pressure changes periodically in aorta. The heart contracts and relax periodically. Old red blood cell will broken down in Liver The circulatory system includes Blood Blood vessels Heart Explain two ways how blood cell A is structurally adapted to its function. A B C It does not contain nucleus so it has more space to carry more haemoglobin. It is biconcave disc shape so it has a large surface area to volume ratio. Oxygen can diffuse rapidly across the cell membrane. Name blood vessel Z. Vena cava Main substance in plasma is water Name artery A. What is its function? Artery A is coronary artery. It supplies oxygen and nutrient to the cardiac muscles. A DNA moleculeconsists of 2 polynucleotide chains. The chains run in opposite directions and twist to form a Double helix Name valves X. Semilunar valve Compare the thickness of the wall of right and left ventricles. What is the significance of the difference? Left ventricle has thicker wall than right ventricle. Left ventricle can provide greater force to pump blood to all parts of the body except lungs whereas right ventricle pumps blood only for a short distance to the lungs. Name chamber D. Left ventricle Name blood vessel Y. Pulmonary vein Name Q. Septum Vein carry blood ________ heart towards What is the function of septum? Septum prevents the mixing of oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood. Name chamber B. Right ventricle What is B? A B C Lymphocyte The _______ of capillary is one cell thick. wall Blood pressure in venae cavae is very low. Explain how a continuous blood flow is maintained. • Valves in the venae cavae prevent backflow of blood. • When the muscles lying next to the veins contract, they press against the veins. The veins are squeezed so blood flows forwards. What is the function of valves in vein? Prevent the backflow of blood Blood platelet can help in Blood clotting to stop bleeding and prevent entry of germs Identify blood vessel A and B A is vein B is artery Explain why the capillary wall is only one-cell thick. It provides a short distance for rapid exchange of materials between the blood and the body cells by diffusion. Which blood vessels (W, X, Y and Z) are arteries W and X The red pigment in red blood cell is haemoglobin What is the shape of A? A B C Biconcave disc shape Blood platelet Made in Red bone marrow What is the function of A? A B C Carry oxygen throughout the whole body Name chamber A. Right atrium What is Z? Z Plasma Which of the following cannot found in plasma? a. b. c. d. Water Glucose Starch Protein What is C? A B C Phagocyte Identify blood vessels P, R and T? P: artery, R: capillary, T: vein Name valves Y. Tricuspid valve Name chamber B. Bicuspid valve White blood cells Made in Red bone marrow Explain why blood pressure is very low in venae cavae. The blood has overcome great friction of the blood vessel walls after travelling a long distance. Waste(e.g. and ) diffuse from the body cells to blood. Carbon dioxide, urea What is A and B? A small lumen B thick wall Cross section Longitudinal section A is elastic tissue, B is muscle Useful substances (e.g. and diffuse from the blood to the body cells. Glucose, amino acids ) Explain why the carpillaries are highly branched to form a network.. It provides a large surface area for rapid exchange of materials between the blood and the body cellsby diffusion.