* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Coding Focus Vol 4, Issue 3: Congestive Heart Failure
Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
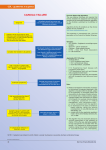
Volume 4, Issue 3, March 2017 Risk Adjustment Coding Academy- Coding Focus Congestive Heart Failure Symptoms Heart failure is a serious medical condition that occurs when the heart is no longer able to pump blood as it should. The body depends on the heart to pump oxygen and nutrients in the blood throughout the body. When the heart muscle becomes damaged or weakened, it is no longer able to sufficiently meet the body’s needs for blood and oxygen. According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), about 5.7 million adults in the United States have heart failure. Approximately half of those who develop heart failure die 1 within five years of the initial diagnosis . Congestive Heart Failure Congestive Heart Failure, or CHF, is a specific type of heart failure. In CHF, the blood that flows out from the heart is slowed, which causes the blood that is returning to the heart to become backed up in the veins, creating congestion within the body’s tissues. This congestion can produce swelling, known as edema, which is usually found in the ankles and legs. Excess fluid can also accumulate in other areas, such as the lungs, making it difficult to breathe and increasing the risk of respiratory 2 distress . There are a variety of symptoms that a person with heart failure may have which include: Feeling weak or tired Shortness of breath from daily activities Chronic coughing or wheezing Weight gain and swelling in the legs, ankles and feet or stomach diastolic or systolic failure or a combination of both.” ICD-10-CM contains specific codes for systolic, diastolic and combined congestive heart failure with additional detail to indicate acuity (acute, chronic, acute on 4 chronic) . Providers will need to document the specific type and acuity in order to code to the highest degree of specificity. Heart Failure (HCC 85) Causes and Treatment I50.1 – Left ventricular failure I50.2_*- Systolic (congestive) heart failure I50.3_*- Diastolic (congestive) heart failure I50.4_*- Combined systolic (congestive) and diastolic (congestive) heart failure I50.9 – Heart failure, unspecified There are multiple factors that can lead to CHF. It is more likely to occur in persons over the age of 65. Having certain medical conditions such as diabetes, coronary artery disease, having a previous heart attack and high blood pressure can also increase the risk. Certain behaviors may also be contributing factors, such as smoking tobacco, eating a diet high in cholesterol, fat and sodium, not getting enough exercise and being obese. While heart failure is considered to be a long-term (chronic) condition, there are a variety of treatments available to help manage symptoms. Medications like diuretics or blood vessel dilators may be prescribed as well as lifestyle changes that include a sodium reduced diet, increased exercise and smoking cessation. Additionally, there are surgical options, such as angioplasty or coronary artery bypass. In the most severe cases, a heart transplant may be the only 3 effective treatment option . Coding Guidance Per the AHA Coding Clinic, 2014, Volume One, “coders cannot assume either *Requires a fifth character: ._0 – Unspecified ._1 – Acute ._2 – Chronic ._3 – Acute on chronic Resources: 1 Centers for Disease Control. (n.d.) Heart Failure Fact Sheet. Retrieved February 15, 2017 from cdc.gov 2 U.S. National Library of Medicine. (n.d.). Heart Failure. Retrieved February 15, 2017 from medlineplus.gov 3 American Heart Association. (n.d.) Treatment Options for Heart Failure. Retrieved February 15, 2017 from heart.org 4 Schmidt, A., Kenney, A., Krawzik, K., & Willard, P. (2016). ICD-10-CM expert for physicians 2017: The complete official code set. Place of publication not identified: Optum360° This publication contains proprietary information of Anthem, Inc. It is intended to be used as informational by individuals participating in Anthem’s Medicare Advantage plans. Reference the ICD-10-CM codebook, CMS-HCC Risk Adjustment Model V22, and AHA Coding Clinic for complete code sets and official coding guidance. Anthem does not guarantee that the information supplied is without defect. Any redistribution or other use is strictly forbidden. © 2005-2017 Anthem, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Y0114_17_30782_I_03/03/2017 ANTHEM is a registered trademark of Anthem Insurance Companies, Inc .