* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name: KEY Class Period: GTT (7th) – SCIENCE OF TECHNOLOGY
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
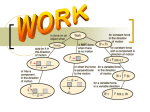
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Name: KEY Class Period: GTT (7th) – SCIENCE OF TECHNOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW 1. Define a chemical reaction: A chemical change where one or more substances are changed into new substances. 2. Define a compound: Substances made up of two or more elements such as water (H20), and carbon dioxide (CO2). 3. Define an adhesive: Any man made product that is used to join materials together; sticky 4. Define Environmental Engineering: A branch of engineering dealing with the treatment of waste, and purification of water and air 5. Define Petroleum Engineering: A branch of engineering dealing with the drilling for and production of oil, and gas. 6. What is Chemistry? A branch of science concerned with the properties and interactions of substances. 7. What are the parts of an atom and how do you define them? Protons – positively charged particles in the nucleus Neutrons – atomic particles with no charge in the nucleus Electrons – negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus 8. Define the parts of a circle (radius, diameter, circumference, area). Radius – the distance from the center of a circle to the edge Diameter – the distance across a circle through the center Circumference – the distance around the perimeter of a circle 9. What are the six different simple machines and the classes of simple machines (ex. Different classes of levers, pulleys, etc). What are examples of each? SIMPLE MACHINE EXAMPLES Screw Screw, Spiral slide Wedge Knife, Ax, Door Jam Inclined Plane Ramp Wheel & Axle Car wheels, bike wheels First Class Lever See Saw, Scissors Second Class Lever Wheel Barrel, Nut cracker Third Class Lever Tweezers Fixed Pulley Blinds on a window, water well Movable Pulley Pulley moves Block and Tackle Both fixed and movable 10. Define a compound machine. Two or more simple machines working together 11. What are the different types of energy (Kinetic, Gravitational Potential, Elastic Potential)? How do you calculate them? Where are they at their highest? Lowest? Kinetic Energy – energy of a moving object. At its highest when an object is traveling faster, and at it’s lowest when an object is stopped. 1 Formula: 𝐾𝐸 = 2 × 𝑚 × 𝑣 2 Potential Energy – stored energy due to an object’s position or condition Gravitational Potential Energy - stored energy due to gravity. At its highest when the object’s height is at its highest. At its lowest when the object is on the ground. Formula: 𝑃𝐸 = 𝑚 × 𝑔 × ℎ (g = 10) Elastic Potential Energy – stored energy due to the material 12. How do you calculate velocity? Velocity = the distance an object travels divided by the time it takes to travel 𝑣= 𝑑 𝑡 13. Define Work. Work is defined as the result of a force moving an object a distance 14. STEM stands for: Science Technology Engineering Mathematics 15. What did salt do in our ice cream experiment? Salt lowered the freezing point of water and made the ice colder than normal ice in order to freeze our ingredients 16. What did detergent do in our oil spill cleanup project? Detergents made the oil clump into smaller clumps in order to make it easier to clean up. 17. What does the law of conservation of energy state? Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only change forms. 18. List as many careers that use nanotechnology that you can think of. Military, Space programs, food, clothing, health, etc.