* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
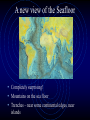
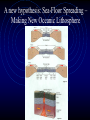
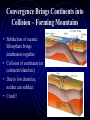
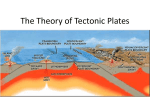
Plate Tectonics Living with a Dynamic Planet Alfred Wegener: a man before his time • Meteorologist • Research on arctic climates • • • • – Greenland Evidence for past climates preserved in rocks A super-continent: Pangea Pangea broke apart 200 million years ago Continents drifted to their present locations Wegener’s Continental Drift Evidence for Pangea: glaciation Evidence for Pangea: paleontology (fossils) How Science Works: Continental Drift Disputed • Lack of Mechanism – what makes • • • • continents move? Alternate explanations possible Anti-German sentiments in the U.S. What are the credentials of Wegener? Continental Drift largely dismissed until 1960’s Oceanography: a new science and new evidence • Following WW II – a convergence of • • • • questions, technology, manpower and money Defense needs – mapping the seafloor Anti-submarine technology GI Bill – a wave of scientists and engineers Booming postwar economy and support for science A new view of the Seafloor • Completely surprising! • Mountains on the sea floor • Trenches – near some continental edges, near islands More puzzles: Magnetic stripes near the Mid-Ocean Ridges A new hypothesis: Sea-Floor Spreading – Making New Oceanic Lithosphere Continental Drift Revised: the New Global Tectonics • Earth’s lithosphere is made of crust and • • • • uppermost mantle Lithosphere is broken into plates Plates float on moving asthenosphere (upper mantle) Plate motion driven by heat in mantle Plates interact – especially at edges Lithosphere and Asthenosphere Plates • Made of Continental and Oceanic Crust – attached to uppermost part of mantle • Plates move • Plate interactions produce specific features (e.g., mountains, etc.) and processes (e.g., earthquakes) • Motion is also related to heat dissipation and density differentiation Balancing the System • Sea Floor (oceanic lithosphere) is created at MOR (divergence) • Either Earth is expanding (no evidence!) or • Sea Floor must be destroyed somewhere – where plates converge Subduction – destroying sea floor The sinking of cold, dense, oceanic lithosphere into the asthenoshere, beneath an over-riding plate. • Associated: Trenches, Volcanoes, Mountains, Earthquakes Convergence Brings Continents into Collision – Forming Mountains • Subduction of oceanic lithosphere brings landmasses together • Collision of continents (or continent/island arc) • Due to low densities, neither can subduct • Crash!! TRANSFORM BOUNDARIES – Two Plates Passing • Transform boundaries link other types of plate boundaries: • Transform boundaries allow a single plate edge to have multiple types of interactions w/other plates • Transforms are major Faults – Earthquakes! The Big Picture of Plate Interactions Plate Tectonics Explains: • • • • Formation of Oceans Formation of Mid-ocean Ridges Formation of Trenches Formation of Mountains • Formation of Metamorphic Rocks • Formation of Sedimentary Rocks as mountains erode • Earthquakes: cause and distribution • Volcanos: cause, types and distribution • Formation of Igneous Rocks