* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Ions Atomos “uncuttable” Protons +
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
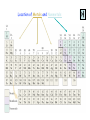
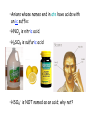
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Ions Atomos “uncuttable” Dalton’s Atomic Theory ~1805 (page 38) …Atoms are small, indivisible balls. Mid-1800s: scientists find that atoms consist of: Protons charge +1 Neutrons 0 Electrons -1 Modern View of Atomic Structure 1. Atoms in their elemental form are electrically Neutral 2. Mass of 1 proton ≈ Mass of 1 neutron 3. e- s are MUCH lighter than protons & neutrons 4. Nucleus consists of protons and neutrons only; nuclei contain all of the positive charge and almost all of the mass of the atom 5. Most of an atom’s volume is empty space http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5pZj0u_XMbc How big are atoms? 1Å = 10-10 m Atoms: Atomic Number Mass Number Atomic Symbols Isotopes: Atoms of a given element that differ only in the # of neutrons. Atomic Weight of an Element = Weighted average of all isotopes of the element AW = Σ (mass of each isotope) x (its % abundance) The Periodic Table • Elements are arranged by atomic number, and in groups with similar properties in vertical columns. Group names you must know: 1 - alkali metals 2 - alkaline earth metals 3 -12 Transition metals 17 - halogens 18 - noble gases (rare, or “inert” gases) Location of Metals and Nonmetals Ions Ions have UNEQUAL #s of protons and electrons ∴ ions are charged particles Ions form when a neutral atom loses or gains one or more electrons. • Metals form Positive ions • Nonmetals form Negative ions Metal Atoms lose e-s (oxidation) to form CATIONS Non-Metal Atoms gain e-s (reduction) to form ANIONS Cl Na Na+ e- Cl- When a nonmetal gains an e-, where does it come from? Predicting Ionic Charges; can we? sometimes…. how? • Find nearest noble gas • Use periodic table; count # of e-s a metal must lose or a nonmetal must gain • Note: Cannot predict for ALL atoms, but can often tell from formula. Ions combine to form Ionic Compounds, which are 1. Composed of ions ; with 2. Neutral overall; Amount of positive charge must equal amount of negative charge. 3. Formed by transfer of e-(s) from metal to nonmetal 4. Held together by electrostatic attraction Pg. 60 & 62 Group 1A Group 2A Group 3A Group 7A Group 6A Group 5A Can’t predict! Nomenclature =naming substances. 1.Ionic Compounds Cation name is unchanged Add anion name: Simple anions - names end in ide • if cation’s (metal’s) charge is variable use Roman numerals PbS HgS vs PbS2 vs Hg2S Fe2O3 vs FeO 2. Polyatomic Ions; many common ones end in –ide or -ate ex. OH- (hydroxide ion) CN- (cyanide ion) C2H3O2- (acetate ion) • Polyatomic cations have -ium ending Oxyanions Memorize these 5 common oxyanions: NO3- nitrate ClO3- chlorate CO32- carbonate SO42- sulfate PO43- phosphate All related forms are derived from these Green = Ba(NO3)2 Red = SrCO3, Li2CO3 Stars = KClO4 Black = PbO2 White= PbCO3 Blue = CuSO4 Reddish-yellow =PbO Green =FeSO4 Oxyanions Common form = ate ex: SO42- (sulfate ion) • one less O = ite ex: SO32- (sulfite ion) • One more or two fewer O s; Use Prefixes : perchlorate ion (ClO4-) chlorate ion (ClO3-) chlorite ion (ClO2-) hypochlorite ion (ClO-) Announcements 1. Office hours canceled today; Chapter 2 homework is now due Monday night instead of Sunday night… 2. If you are in lab section: 036 Monday 2- 5 pm TA: Awanthi 037/S37 Tuesday 1-4 pm TA: Lyndsay or You will take the exam upstairs in SEM 326 next Friday. Figure 2.26 (p. 61) Note: • Oxyanions with 2- and 3- charges can add H+ to form anions with less negative charge. Acids Neutral compounds that produce H+ ions in water • Acids formed by simple anions have a hydro prefix and an ic suffix: • ex. HCl is hydrochloric acid. HF is ? • Anions whose names end in ate have acids with an ic suffix: • HNO3 is nitric acid. • H2SO4 is sulfuric acid • HSO4- is NOT named as an acid; why not? Molecular Compounds 1. Made of neutral nonmetal atoms only 2. Neutral overall; no charges involved (no ions!) 3. Formed by sharing of e-s between atoms • Chemical formulas • Empirical formulas Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules: 7 exist in nature Binary Molecular Cmpds: • Contain two different nonmetals • Named like ionic compounds, except • Prefixes are used to indicate how many atoms of each element: • mono (1) • di (2) • tri (3) • tetra (4) • penta (5) • hexa (6) • hepta (7) • octa (8) NaCl SiO2 (table salt) sand CaCO3 limestone, shells quartz