* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Generator and Transformer
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Aluminium-conductor steel-reinforced cable wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Loading coil wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
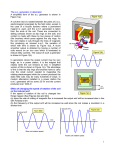
Generator and Transformer Moving Conductor If a straight conductor is moved in a path perpendicular to a magnetic field, a current is induced in the conductor Induced emf =Blv l – length of conductor v – velocity of conductor Example An airplane travels at 1000 km/hr in region where the Earth’s magnetic field in 5.0 x 10-5 T. What is the emf induced between the wing tips that are 70m apart? Generators (Dynamo) Transforms mechanical energy into electric energy Coil of wire spins in the presence of a permanent magnetic field Induces are current in the coil Current produced actually fluctuates as the coils position in the field changes Max current when perpendicular to B Min current when coil parallel to B (no current) Moving Electricity How does electric energy transmit over large distances? How much power is wasted when 10000W of power is transmitted along a cable with a resistance of 1 at 200V? What would be lost if transmitted at 2000V instead? Much less lost when travels at a higher V and lower I Transformer Device that changes voltages Two coils around an iron core Current supplied to the primary coil induces a current in the secondary coil By varying the number of windings in the coils you can vary the potentials Types Step-up – more windings on the secondary coil increases the voltage Step-down – less windings on the secondary coil decreases the voltage Transformers work only on AC current. Why? Transportation Electric energy is stepped up for transmission and then stepped down for household use Most transformers are close to ideal (100% efficient) - low resistance - very permeable rounded core