* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter1-obrian11_Intro HumanGeog
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
Spatial analysis wikipedia , lookup
Scale (map) wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Cartography wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
History of longitude wikipedia , lookup
Cartographic propaganda wikipedia , lookup
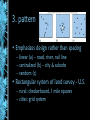
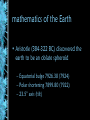
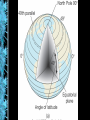
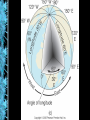
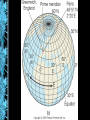
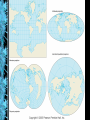
Human Geography Chapter 1 what is geography? • “description of the earth” • a study of spatial variation – the how and why of physical & cultural differences – location, location, location – observable patterns that have evolved through time -interaction of physical environment and human activity -cultural landscape can alter the natural environment evolution of the discipline - mapping/human interpretation • Aristotle (384-322 BC)-earth is spherical • Erathosthenes (276 BC)-Greek scholar”geo”=earth “graphy”=to write • Strabos (63BC-24AD)/Herodotus (484423BC) Ptolemy (2nd century AD) outside the western world • Chinese Scholars • Muslim Scholars • • • • Where are people? What are they like? What is their interaction over space? What kinds of landscapes do they erect? human geography physical geography • attention towards natural landscape – landforms and their distribution – atmospheric conditions and climatic patterns – soils / vegetation associations modern geography….. • 1. Climates, patterns, processes of physical environment • 2. Rapid development of natural sciences • 3. Accurate mapping • 4. Data collection / statistics academic geography • • • • Earth science Man-land relations Areal differentiation Spatial organization – – – – – location processes patterns interactions/relations distributions three concepts about space • Location • Direction • Distance absolute location • Mathematical location – Latitude & Longitude • degrees, minutes, seconds – Township & Range (1785 Land Ordinance) • Subdivision: parallels & meridians • Topographic quadrangle, US Geological Survey – Metes & Bounds latitude & longitude (22° 15' N, 114° 10‘ E) relative location • “place” in relationship to surroundings • Site – absolute location concept – physical & cultural characteristics • Topography, vegetation, water, physical characteristic • Situation – external relations of locale – relative location concept – dynamic absolute directions • Based on cardinal systems – north, south, east, west – from solar system relative directions • Based on cultural & local perceptions – no absolute boundaries or definitions – “down south”, “out west”, “up north”, “down south”, “Near East”, “Far East” absolute distance • Absolute mathematical mileage, or measurement of distance relative distance • Refers to a more regional spatial relationship – how distance is described $$$ & TIME MILES MINUTES psychological distance • Distance lengthened / shortened – first time traveled – night / day travel – safety / danger / excitement size & scale • Size of unit studied • Scale implies degree of generalization – broad or narrow – Varying sizes • local • regional • global landscapes • Natural • Cultural • Dynamic multi-varied landscapes process of change Before 1970 After development Long Island, New York spatial interaction • Accessibility – how easy/difficult to overcome time & space separation • Connectivity – how places are connected • Spatial diffusion – process of dispersion of ideas or items from a center of origin to more distant points • Globalization – Increasing interconnection of peoples and societies worldwide globalization • Standardization – $$$$, EU, time, United Nations • Containerization – movement of products – outsourcing • Intersection of the ‘haves’ & ‘have nots’ – cell phones, internet spatial distribution • Arrangement of items on Earth’s surface • Three concepts 1. density • Measure of the number/quantity within a defined unit of areas – proportion • arithmetic • physiological density 2. dispersion (concentration) • Amount of spread of phenomenon over an area – 1. clustered, agglomerated – 2. dispersed, scattered, random 3. pattern • Emphasizes design rather than spacing – linear (a) – road, river, rail line – centralized (b) – city & suburbs – random (c) • Rectangular system of land survey - U.S. – rural: checkerboard, 1 mile squares – cities: grid system regional concepts • 1. formal or uniform regions – Areas of essential uniformity • Physical or cultural • Sahara Desert, “Bible Belt” 2. functional region • spatial system defined by interactions/ connections Glendale Galleria Newspaper Route 3. perceptual regions • Less structured & more culturally based China Town The “Valley’ cartography – the science of making maps • Maps provide a visual tool • Maps are subjective • Map projections transfer locations on a round surface to a flat surface – some form of distortion always occurs – greater distortion results from larger areas depicted global grid system mathematics of the Earth • Aristotle (384-322 BC) discovered the earth to be an oblate spheroid – Equatorial bulge 7926.38 (7924) – Polar shortening 7899.80 (7922) – 23.5° axis (tilt) seasons and climate • Earth’s rotation & movement around the sun • Tilt of the earth’s axis (23.5°) • Receipt of solar radiation • Re-radiation of energy in the form of heat the Earth’s divisions • Latitude lines – Equal distance between lines – Lines become increasingly smaller descending from the equator to poles • Longitude lines – Each line is the same exact length – All lines become increasingly close together as they descend to the poles important lines of latitude • Equator: 0 degrees • Tropic of Cancer: 23.5 degrees North • Tropic of Capricorn: 23.5 degrees South • Arctic Circle: 66.5 degrees North • Antarctic Circle: 66.5 degrees South important lines of longitude • Prime Meridian: 0 degrees (runs through Greenwich, England) • International Dateline: 180 degrees • Time Zones: every 15 degrees of longitude equals one hour maps • Scale – the smaller the scale the greater the detail - for example one inch = one mile is more detailed than one inch = one hundred miles 1:1 or 1:100 • Legend – interprets map information map projections & distortion • • • • Shape Distance Relative size Direction Robinson map projection Fuller’s Dymaxion projection Topographical map Thematic maps Cartogram map Geographical Information Systems mental maps