* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download atomic structure what are atoms?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
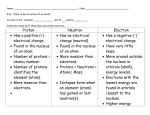
ATOMIC STRUCTURE WHAT ARE ATOMS? smallest part of an element that still has element’s properties. building blocks of molecules WHAT’S IN AN ATOM? NUCLEUS center of each atom small & dense has positive electric charge PROTONS subatomic particle that has positive charge (+1) found in nucleus NEUTRONS subatomic particle that has no charge no overall charge equal number of protons and electrons whose charges exactly cancel ELECTRONS subatomic particles with negative charges (-1). located in a cloud (orbit) moving around outside nucleus QUARKS particles of matter that make up protons and neutrons MODELS OF THE ATOM DEMOCRITUS Greek philosopher developed theory around 400 B.C. proposed that atoms make up all substances Atom — “unable to be divided” JOHN DALTON Developed atomic theory in 1808 first atomic theory with a scientific basis model was simple sphere thought the atom could not be split Atoms of same element exactly alike NIELS BOHR theory developed in 1913 suggested that electrons in an atom move in set paths around the nucleus much like planets orbit sun It is impossible to determine an electrons: exact location speed direction Best scientists can do is: calculate chance of finding an electron in a certain place within an atom J.J. Thomson (1897) Discovered negatively charged particles atom was divisible! Particles discovered are electrons Atom consists of positively charged material with negative charges spread evenly throughout Rutherford (1908) Gold Foil Experiment Positive particles shot at gold foil occasionally bounced back! Proposed dense, positively charged center called the nucleus ENERGY LEVELS path of a given electron's orbit around a nucleus, marked by a constant distance from the nucleus Closer to nucleus, lower energy level of electrons Further from nucleus, more energy electrons have Number of filled energy levels an atom has depends on number of electrons ORBITAL region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons VALENCE ELECTRONS found in outermost shell of an atom determines atom’s chemical properties participate in chemical bonding Every atom has between one and eight