* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 16 Evolution of Populations and Speciation
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
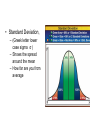
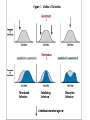
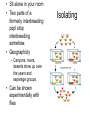
16 Evolution of Populations and Speciation Genetic Equilibrium • Combining Mendel’s work on genetics with Darwins ideas of evolution • Population Genetics: studying evolution from a genetic point of view Variation of Traits in a pop. • Evolution is the change in the genetics of a group of organisms. • A population is the smallest grouping that can evolve. – What would be a larger grouping? Bell Curve • If you measure an observable trait, there is often a large average group, with a few with more, and a few with less. • Standard Deviation, – (Greek letter lower case sigma σ ) – Shows the spread around the mean – How far are you from average Causes of Variation • Envi. Factors: food variability • Genetics: Even two brothers will look dif. – Mutations cause some of this – Recombination: when genes get mixed around during meiosis – The random pairing of sperm and eggs (gametes) Coen Brothers Allele Frequencies and the Gene Pool • Gene Pool: Total genetic information available. – If there’s no gene for feathers, then nobody has feathers. – If you know what’s there, you can predict what will be there in the next generation – Like Punnet squares for groups instead of just a mom and dad • Allele frequency: divide the number of a certain allele by the total number of alleles of all types in the population. – Expressed as a percent – If it’s 20%, then 1 in 5 chromosomes has it – Shows the amount of diversity in a group – Bloodtypes, eye colors Phenotype Frequency • Number of individuals with a particular phenotype divided by the total number of individuals in the population. • Remember lots of phenotypes are inner (proteins, enzymes) • Is behavior a phenotype? Is it inheritable? Variability in mollusc species, (bean clams) Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium • A population that doesn’t change its frequencies… – Has no mutation – Has no immigration or emigration – Is very large – Mates are chose randomly – There is no natural selection • This population doesn’t evolve or change • It is hypothetical Disruption of Genetic Equilibrium • How does evolution happen when the HardyWeinberg equilibrium is broken? Mutation • Doesn’t happen too often • Mutagens: mutation causing things – Latin: Origin of change – Gamma rays, UV light, • Mostly mutations are harmful, gimp you up. – Often carcinogens: Cancer causing – Teratogen: Birth defect causing • But a good mutation influences evolution Migration • Immigration/emigration • Behavior affects this • Gene Flow: Process of genes moving from one population to another. • Baboons: Since only a few alpha males reproduce in a group young males often leave and find their own group. If humans have humanity do baboons have baboonity? Genetic Drift • Phenomenon by which allele freq. in a population change as a result of random events or chance • how important it is for everyone to reproduce depends on the size of your group disasters change the genetics of a population Non-random mating • Who’s close by? • Assortive mating: Mate with someone who looks like you. – Tall girls & tall guys Natural selection • The most important factor that disrupts a genetic stability • Stabilizing selection: The average individual is best suited for the environment and has the most kids • Everyone becomes more average Directional Selection • One of the extremes of a trait is more successful and has more kids. Disruptive selection • Opposite extremes are more fit than the average • Could lead to two species Sexual Selection • If you are healthy enough to have some weird plumage you’ll make a good dad, and your kids will have even weirder plumage. Tommy Lee, peacocking Formation of Species • New species show up, old species go extinct • Speciation: Forming new species • Well how do you know if you have a new species? Morphological concept • What shape is it? • If it’s shaped like a grizzly bear, then it’s a grizzly bear. • Except sometimes one species will have different shapes. – They look dif, but they’ll breed together. • Pheidole barbata Ants look dif, but that’s because they have dif roles in the colony Biological species concept • If a group can breed together, but not with other groups, then it’s a species • Can’t see this for extinct animals The Western meadowlark (left) and the Eastern meadowlark (right) appear to be identical, and their ranges overlap, but their distinct songs prevent interbreeding. Problems • What about asexual organism? • What about potential breeding, like they can’t breed now, but they could if things were dif? • Ring species:species with a geographic distribution that forms a ring and overlaps at the ends. • subspecies of Ensatina salamanders – subtle morphological and genetic differences – They all interbreed with their neighbors, but not subspecies across the ring – So where do we mark the point of speciation? • Really matters for endangered species laws and where you can build on habitat • Sit alone in your room • Two parts of a formerly interbreeding popl stop interbreeding somehow. • Geographicly – Canyons, rivers, deserts show up over the years and seperage groups. • Can be shown experimentally with flies Isolating Reproductive isolation • Same area, but suddenly there are barriers to breeding – Prezygotic barriers: Happen before fertilization • Mating dance isn’t right • Mating season isn’t right • These damselfly penises illustrate just how complex insect genitalia may be. – Postzygotic barrier: happens after fertilization • Weak offspring How long does this take? • Depends, • Bananas reached the Hawaiian islands about a thousand years ago. – Now the moths that eat bananas have several distinct species – Punctuated equilibrium: sometimes change comes fast – The fossil record doesn’t show gradual change – The one hopeful monster that starts a whole new branch. • What does a bell curve look like? • What is meant by the term gene pool? • What is genetic equilibrium? • What is genetic drift? • How does mutation disrupt genetic equilibrium? How does immigration? • What is sexual selection? • What are shortcomings of biological species concept? • How can isolation lead to speciation? • What is punctuated equilibrium? Review