* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Soviet Union in World War II, Part III
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Propaganda in the Soviet Union wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Pursuit of Nazi collaborators wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Budapest wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Ursula Kuczynski wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
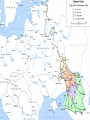
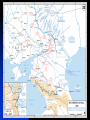
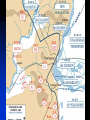
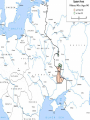
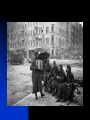
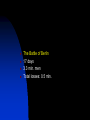
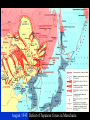
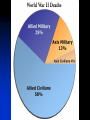
The Soviet Union in World War II, Part III Compare US and Soviet wartime posters: http://slon.ru/russia/photo/voennye_plaka ty_vtoroy_mirovoy_nayti_10_otlichiy145.xhtml July 1942: Massive German offensive in southern Russia The city of Stalingrad is besieged The turning point of World War II August 23: Massive German bombing destroys 80% of the city’s residential buildings Fighting in the city: average life expectancy of the Soviet soldier – 24 hours Stalingrad before the war Stalingrad, September 1942 Women volunteers signing Oath of Allegiance Red Army infantry counterattack at Stalingrad Stalingrad worker militia Soviet “Katyusha” rocket attack Stalingrad: street fighting Stalingrad: surrender of German Field Marshal von Paulus The Battle of Stalingrad claimed over two million casualties, more than any other battle in human history, and was also one of the longest: it raged for 199 days. Killed, wounded or captured at Stalingrad: Germans and allies: 850,000 Soviets: 1,130,000 (incl. 40,000 civilians) General Georgiy Zhukov General Aleksandr Vasilevsky General Konstantin Rokossovsky General Ivan Konev July-August 1943: The Battle of Kursk Casualties: 50 days 2.7 mln. men 8,000 tanks 5,000 aircraft German – 260,000 Soviet – over 1 mln. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=awRhSozctvs The Soviet Steamroller, documentary: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uONX 3xzfJkM&feature=related Vitya Zhaivoronok, Soviet Army scout, Yugoslavia, 1945 Ruins of Peterhof German POWs in Russia German POWs outside Moscow Diplomacy in the Grand Alliance The main issues: Helping USSR Opening the 2nd front Postwar settlement The Big Three: Churchill, Roosevelt and Stalin at Yalta, Feb.1945 Churchill: Stalin is a "devil"-like tyrant leading a vile system”. (it didn’t prevent him from making a territorial deal w. Stalin, however) Roosevelt: “ I just have a hunch that Stalin is not that kind of a man. . . . I think that if I give him everything I possibly can and ask for nothing from him in return, noblesse oblige, he won't try to annex anything and will work with me for a world of democracy and peace.” James Byrnes, member of US delegation: “It was not a question of what we would let the Russians do, but what we could get the Russians to do." Major decisions of the Yalta Conference 1. Unconditional surrender of Germany 2. Division of Germany into 4 occupied zones 3. Demilitarization and denazification of Germany 4. Germany’s reparations, including by forced labour of its soldiers 5. A new govt in Poland, including non-Communists 6. Changes of Poland’s borders 7. Return of citizens to USSR and Yugoslavia 8. Soviet Union will participate in the creation of the UNO 9. Stalin agreed to attack Japan within 90 days of Germany’s surrender. 10. Nazi war criminals were to be hunted down and brought to justice. 11. A "Committee on Dismemberment of Germany" was to be set up. Hitler’s last public speech: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HRSn qLFPQ2A&feature=related US and British aid to the Soviet ally, 1941-45: Food - $1.5 bln. in Automobiles – 427,000 Warplanes – 22,000 Tanks – 13,000 Warships – over 500 Explosives – 350,000 tons Other supplies Total estimated cost of Allied aid to USSR in contemporary prices – $100 bln. The Battle of Berlin: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eDxCMuQhe gs Hitler phones Stalin (a satire): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9pbIrMtmU9 8&feature=related The Battle of Berlin 17 days 3.3 mln. men Total losses: 0.5 mln. Red flag over Berlin, May 1945 Checking out Hitler’s headquarters, May 1945 Berlin, 1945: surrender of German High Command Ovens in Buchenwald concentration camp Survivors of a Nazi concentration camp June 24, 1945: Marshal Zhukov leads Victory Parade in Red Square Victory Parade in Red Square, June 24, 1945: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QDQ2 gQttPBs&NR=1 July 1945: Stalin, Truman and Churchill at Potsdam, Germany Marshal Zhukov and General Eisenhower August 1945: Defeat of Japanese forces in Manchuria Japanese-American historian T. Hasegawa: Soviet war on Japan was the decisive factor for Japanese surrender – not the atom bomb http://books.google.ca/books?id=iPju1MrqgU4C&pri ntsec=frontcover&dq=racing+the+enemy&hl=en&sa =X&ei=BM_GT_73B8fJ6gGV7KTMCw&ved=0CDgQ 6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=racing%20the%20enemy& f=false The war took all nine of her sons Nazi war criminals on trial at Nuremberg Soviet losses in World War II Over 27 mln. killed (13.6% of the population) Of those who survived, 29 mln. took part in the fighting (including 0.8 mln. women) Battlefield losses – 11.5 mln. (Germany lost 8.6 mln.) 5.8 mln. POWs (of them 3 mln. died in concentration camps) 1,710 cities and 70,000 villages completely or partially destroyed 40,000 hospitals, 84,000 schools, 43,000 libraries destroyed Historically unprecedented level of damage suffered by a country