* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Digestive System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
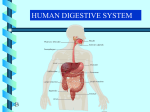
- Zachary Davis, Bobby Archambault, Kristin Cotatgis, Robert Scalisi, Dawson Clark, and Jacob Cohn Function The Digestive System breaks down food and absorbs nutrients that gives your body energy. The system begins with food taken in the mouth, going through the system (esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine). The liver and the pancreas are glands which provide chemicals needed for digestion, while the gallbladder is a storage organ. The Mouth The mouth is defined in front and at the sides by the lips, jawbone, teeth and gums. When a human body is dehydrated, it’s thirst mechanism shuts off. Your tongue is germ free only if it is pink. If it is white, there is a film of white bacteria. * The stomach is the main food storage tank of the body which is crescent shape. If it were not for the stomach’s storage capacity we would have to eat constantly instead of just a few times each day. The stomach has a mixture of acid, mucus, and digestive enzymes. The stomach also stretches when we eat large meals. The Gallbladder The Gallbladder is a small storage organ located next to the liver. The job of the gallbladder is to help digest food. The gallbladder holds bile which is needed to digest fatty foods. * All nutrients from the intestines go to the liver. The liver warms the blood and heats the entire body. The liver breaks down alcohol and drugs, bacteria, old blood cells, toxins and excess hormones. It is located on the right side of the abdomen and is the biggest gland in the body. THE SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine measures 18 to 23 feet long in the average adult and 1 ½ to 2 inches in diameter. The small intestine is divided into three sections; the duodenum, the jejunum and the ileum. First the large intestine (or bowel, colon) is the last part of the digestive system in vertebrate animals. The large intestine consists of the cecum, rectum and anal canal. The large intestine is about 4 feet (1.5m) long, which is about one fifth of the whole length of the intestinal canal. Dear Medulla Oblongata, The digestive system has many functions. To start with, there is the mouth. Without the mouth we wouldn’t be able to eat or drink. If you weren’t able to eat or drink then you could die of hunger and dehydration. Without food, our bodies would have no energy. Next, the stomach is the main food storage tank with digestive enzymes. The enzymes are important to break down our food. Then there is the gallbladder which holds bile needed to digest fatty foods. Without the gallbladder you would not be able to digest fatty foods. Subsequently, we have the liver which breaks down alcohol, drugs, bacteria, old blood cells, toxins, and excess hormones which can be harmful to the body. Equally important is the small intestine as ninety percent of what we eat is absorbed through the small intestine giving us all the nutrients we need to survive. Finally, the large intestine passes any unused waste from the body and absorbs vitamins and minerals. In conclusion, the digestive system has many important functions for our bodies so we all need our jobs. Sincerely, Kristin, Dawson, Robert, Zach, Bobby, and Jacob Bibliography Manolis Kay, The Digestive System. Minneapolis, MN, Bellwether Media, Inc., 2009 Royston Angela, Eating and Digestion. Chicago, Illinois, Rigby Interactive Library, 1997 Parker Steve, Digestion. Chicago, Illinois, Raintree, 2004