* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Do you know about blood pressure (BP)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
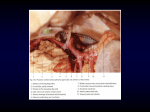
Effects of drugs on Rabbit blood pressure Pharmacological Department Z.G.Song Questions: 1. Do you know about blood pressure (BP) ? BP is the product output and peripheral vascular resistance. It can be decreased and increased by actions of drugs on either the peripheral resistance of the cardiac output, or both. 2. Do you know about the normal BP? normal BP is defined as a diastolic BP between 80-90 mmHg (mercury) and systolic BP between 120-130 mmHg. Abnormal BP include: hypertension (High BP) and hypotension (Lower BP) Hypertension: diastolic BP is greater than 90 mmHg and/or systolic BP is greater than 140 mmHg. Hypotension: diastolic BP is lower than 60 mmHg and/or systolic BP is lower than 90 mmHg. Hypertension: Elevated blood pressure is an extremely common disorder, affecting approximately 20% of the population. Although many of these individuals have no symptoms: 1. Persistent throbbing Headaches 2. Blurred vision 3. Nausea and vomiting 4. Ringing in your ears 5. Right side chest pain 6. Swollen feet chronic hypertension-either systolic or diastolic can lead to heart failure, myocardial infarction, renal damage, and cerebrovascular accidents. The incidence of morbidity and mortality significantly decreases when hypertension is diagnosed early and is properly treated. 3. How to do if someone have high BP? Six Ways to Lower Blood Pressure 4. Hypotension: Hypotension is caused by some reason, e.g. drugs and cardiac. Most severe consequence is shock . (One)Experimental drugs: 1. 0.01% Noradrenaline. 2. 0.01% Adrenaline Hydrochloride. 3. 0.1% Isoproterenol Sulfate. 4. 1% Phentolamine. 5. 0.01% Propranolol Hydrochloride. 6. 1% Heparin. 6. 5% Sodium Citrate. 7. 20% Urethane. Let us recall the drugs (effects on BP): 1. a, β-receptor agonist Adrenaline (a 1, a 2,β 1, β2), 2. a, -receptor agonist Noradrenaline (a 1, a 2) can activate β 1 -receptor 3.β -receptor agonist Isoproterenol (β 1, β2). 4. Phentolamine: a-receptor antagonist (a 1, a 2) Adrenaline reversal: The vasoconstrictive action of adrenaline is interrupted,but vasodilation of othervascular beds caused by stimulation of β–receptors is not blocked. 5. Propranolol β -receptor antagonist (Two) Objectives ? 1. To learn method of recording blood pressure via carotid artery cannula. 2. To observe effects and analyze interactions of adrenaline, noradrenaline, isoproterenol, propranolol, phentolamine on the rabbit blood pressure. (Two)Experimental drugs: 5. 2N Hydrochloric Acid 6. 30mg% Sodium Sulfadiazine 7. 1% Heparine 8. 20% Urethane (Three) Experimental animal domestic rabbit , 2.5~3.0kg. (Four) Experimental equipments: 1. Rabbit operating table 2. Mammal surgical instruments (Four) Experimental equipments: 3. Arterial cannula, Blood pressure transducer, RM6240 signal acquisition and processing system. (Five) Steps and methods 1. Debuggment and connection of device: . Connect the head of blood pressure transducer with a three-way, one opening of three-way connecting arterial cannula. Rotate rotary handle of three-way to make the cavity of transducer link with air through arterial cannula. Sodium citrate is slowly injected into transducer and artery cannula by syringe through another opening of three-way, clear the air in transducer and artery cannula, then rotate rotary handle, and close three-way. connect blood pressure transducer with the RM6240 signal acquisition and processing system. Operate the computer and enter blood pressure recording interface in RM6240 signal acquisition and processing system, adjust baseline, sensitivity and paperspeed. (Five) Steps and methods 2. Take a rabbit, weighten, anesthetized with 20% urethane (5ml/kg) by intravenous injection. When do we begin to operate? paying attention to: 1. muscle tension degrade 2. respiratory rate from fast to slow 3. corneal reflex disappear (Five) Steps and methods 3. Fixing rabbit and operation: the rabbit was fixed to the operating table on the back and the neck should be fixed straightly. Shearing hair in the neck, a incision should be cut about 5-7 cm long with a scalpel, and subcutaneous tissue and muscle should be separated bluntly to find out trachea,then carotid sheath in which there were carotid artery, vagus nerve, decompression nerve and sympathetic nerve could be found on both sides under the trachea. 4.Arterial intubation the right carotid artery was separated about 3cm long, two reserve threads should be made across the artery. Then 1% heparin was injected by intravenous injection which dose was 1ml/kg. Finally, the artery proximal heart is clamped with artery occlusion, and the artery distal heart is ligated. Then at the proximal of ligation a bevel should be cut, arterial cannula should be insert in the direction of towards heart, and arterial cannula should be enclosed tightly with thread to avoid slippage. 5. Depiction of normal blood pressure curve: 6. Observe and analyze effects of drugs on blood pressure: Nor(0.5ml/kg)–Adr( 0.5ml/kg)– Phe (0.5ml/kg)– Adr (0.5ml/kg)–Iso (0.5ml/kg)–Prop (0.5ml/kg)–Iso (0.5ml/kg) ※ Pay attention to: 1. After every administration, wash remain drug in the head of syringe with a small amount of saline (0.3ml) quickly. 2. The next drug should be administered after the disappearance of action on drugs .