* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A blast from the not so distant past*
Object relations theory wikipedia , lookup
Sabina Spielrein wikipedia , lookup
Collective unconscious wikipedia , lookup
Psychoanalysis wikipedia , lookup
Ego psychology wikipedia , lookup
Analytical psychology wikipedia , lookup
Id, ego and super-ego wikipedia , lookup
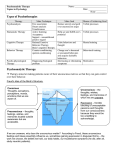
A blast from the not so distant past… • Psychologists who have studied personality have developed a number of theories to explain its nature • One of these psychologists who conducted such studies was Sigmund Freud, specifically through his use of psychoanalysis… • Many of his theories, while not in use today, have been used as a foundation of personality’s relationship with psychology • Freud’s most important contribution to the study of human personality is his view of the unconscious • Prior to Freud, psychologists mainly focused on the conscious • Freud felt that the unconscious contains desires, wishes, needs, and impulses that we are not aware of under normal circumstances Freud: “The Human Mind is an Iceberg” • Freud coined this phrase as a means to describe the conscious and the unconscious, aka “the visible and non-visible” • The conscious (visible) is the portion of the iceberg above water, with the unconscious (non-visible) being the portion below the water… • The portion below the water, much like our unconscious, is the biggest part of the iceberg • Hence Freud’s belief that the unconscious plays the largest role in our behaviour/development of personality… Freud had more to say… • Freud also felt that our personality is composed of three other systems • The Id, the ego, and the superego… Freud & Id.. • The Id is the system of our personality that is existent at birth; it becomes the energy source for the two other systems • It is the most basic part of the personality, and wants instant gratification for our wants and needs. • It is completely unconscious, and has no direct contact with the environment. It acts accordingly to the pleasure principle, meaning that it “seeks to keep the level of tension low by obtaining pleasure” Freud & Ego… • The Ego, unlike the Id is primarily conscious • It involves learned ways of behaviour • The Ego plays a middle role between the desires of the Id, and the realities of the outside world • Operating on the basis of the reality principle, it finds appropriate ways for the person to satisfy needs, i.e. drinking A LOT of H2O when your thirsty (Id) versus drinking a moderate amount to quench current and then cover future thirst • The ego is an accumulated phenomenon, a by-product of living with others. Ego is a need; it is a social need, it is a social by-product. • The ego allows us to see that certain responses would be socially unacceptable, but it also allows us to know that there are other more appropriate means of venting our frustration. Freud & Superego… • Finally, we come to the Superego, aka the moral aspects of someone’s personality • It represents those values and ideals that are established by society and learned by the individual • The Superego tells us what is “right” and “wrong” • It tries to prevent Id impulses from being expressed (most of these are socially unacceptable); it tries to persuade the Ego to adopt moralistic goals in place or realistic on; it strives for perfection rather than for pleasure or for realistic thinking • The Superego's criticisms, prohibitions, and inhibitions form a person's conscience, and its positive aspirations and ideals represent one's idealized self-image How do they work together? • Based on our internal energy, each one of these systems shares a common “power source” • Depending on what system is allowed to grow the most determines what uses more • i.e. if the Id gets the majority of the power, the person will act more based on impulse & rewards; if the Ego has more control then the person will be more realistic; and if the Superego is #1 then the individual is more moralistic The Anti-Freud… Carl Jung • Despite at one time being a close counterpart of Freud, Carl Jung branched off and explored his own version of psychoanalysis (Analytical Psychology) • Freud & Jung disagreed on what determines human behaviour – Freud was pro-childhood experience, Jung was pro-goal determined (strive to be something) and ancestral (interests, etc.) • Perhaps Jung’s biggest contribution to what shapes our personalities and behaviours was his understanding of two major attitudes – introversion and extraversion… An “inny” or an “outy”…? • Jung believed that our personalities include two distinct attitudes • Are we introverts or extraverts? • An introvert is someone who mainly responds to “internally oriented stimuli, such as their own ideas and inner thoughts • An extravert is someone who more often than not responds to external stimuli such as social situations and the ideas of others Classifying introverts and extraverts… Introverts most likely… • • • • • • Feel hurt easier Daydream frequently Blush often (embarrass easily) Stay in the Background in Social Settings Have Stage Fright Worry about potential misfortune & decision making ability • Care a lot about what others say of you • Care for personal property Extraverts most likely… • Don’t feel hurt as easy • Seldomly daydream • Make friends easily • Life of the party • Not big on worry • Laugh frequently and easily • Enjoy presenting • Accept orders from others • Are “good” losers Another vs. Freud on Personality… • As we know, Freud – and Jung somewhat as well – developed theories on personality that were pro-within in regards to what shapes all of us • Other psychologists emphasize outside forces – social and cultural – as shapers of our personalities… • Alfred Adler was one such psychologist… • He felt that people are “primarily social creatures… motivated by social interests” that are mainly conscious beings, meaning that conscious awareness was more important than the unconscious • Adler – people strive to be perfect, they develop feelings of inferiority due to any imperfections they may have; inferiority drives people to become superior = total completion of personality • Adler’s #1 concept = creative self; this is what causes people to strive towards complete fulfillment • Personal fulfillment is unique, so then each of us is unique, which then results in unique personalities