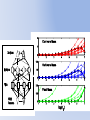
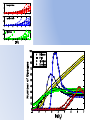
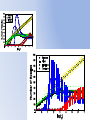
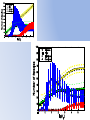
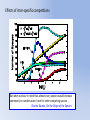
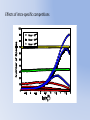
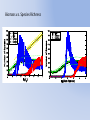
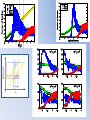
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download from random mutation to
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup