* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The role of intra-specific trait variability in plankton biodiversity: a
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
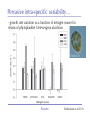
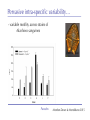
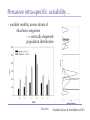
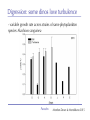
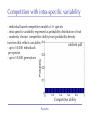
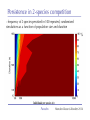
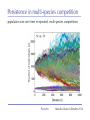
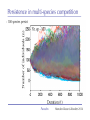
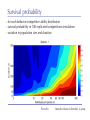
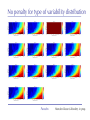
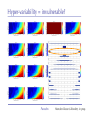
The role of intra-specific trait variability in plankton biodiversity: a game theoretic and model examination Susanne Menden-Deuer & Julie Rowlett Graduate School of Oceanography University of Rhode Island [email protected] Paradox Mathematical Sciences Chalmers University [email protected] Paradox Courtesy of John Delaney - with modifications Paradox DEAN JACOBSON ILLUSTRATION 2 Goals: 1. pervasive intra-specific trait variability in physiology, morphology and behavior in unicellular plankton 2. intra-specific variability matters and is adaptive Paradox DEAN JACOBSON ILLUSTRATION Pervasive intra-specific variability… - growth rate variation as a function of nitrogen source for strains of phytoplankter Heterosigma akashiwo ifemer.fr Paradox Fredrickson et al 2011 Pervasive intra-specific variability… - variable motility across strains of same phytoplankton species Heterosigma akashiwo ifemer.fr Paradox Harvey et al, in review Pervasive intra-specific variability… - variable motility across strains of Akashiwo sanguinea Hwan So Yoon Paradox Menden-Deuer & Montalbano 2015 Pervasive intra-specific variability… - variable motility across strains of Akashiwo sanguinea --> vertically dispersed population distribution Paradox Menden-Deuer & Montalbano 2015 Digression: some dinos love turbulence - variable growth rate across strains of same phytoplankton species Akashiwo sanguinea Paradox Menden-Deuer & Montalbano 2015 Pervasive intra-specific variability… - chemical composition (Moal et al. 1987) - thermal adaptation (Thomas et al. 2012) - growth optima (Boyd et al. 2013) - salinity tolerance (Brand 1984) - nitrogen fixation (Hutchins et al. 2013) - ocean acid response (Schaum et al. 2013) - genetics (Rynearson & Armbrust 2004,Whittaker et al. 2012) Empirical investigations of intra-specific variability in plankton physiology, genetics or behavior are rare but discoveries are frequent Paradox Paradox of the Plankton “How is it possible for a number of species to coexist in a relatively isotropic or unstructured environment all competing for the same sorts of materials?” G. Evelyn Hutchinson 1961 Paradox DEAN JACOBSON ILLUSTRATION Paradox of the Plankton “How is it possible for a number of species - with high intra-specific variability - to coexist in a relatively isotropic or unstructured environment all competing for the same sorts of materials?” G. Evelyn Hutchinson 1961 Paradox DEAN JACOBSON ILLUSTRATION Environmental Heterogeneity - Environmental & observational drivers - Problems of pattern and scale of observation (Levin 1992) Paradox Rynearson & Armbrust 2005 Many hypotheses advanced - resource ratio hypothesis (Tilman 1977, 1994) - chaotic oscillations (Huisman Weissing 1999) - chaotic fluid motion (Pentek et al. 2000) - localized competition (Kerr et al. 2002) - predation/competition (Record et al. 2013, Cropp and Norbury 2012) - latitudinal/seasonal gradients (Barton et al. 2010) Paradox Barton et al. 2010 Game theory - examines outcomes of competitions based on individual interactions - outcomes depend on behavior of individual players Paradox Game theory - examines outcomes of competitions based on individual interactions - outcomes depend on behavior of individual players - Prisoner’s dilemma famous example: Paradox Species interactions are cell-cell interactions - outcomes of ecological interactions are measured at the population level: abundance, growth rate, distribution - the processes that result in population dynamics occur at the individual level: feeding, motility, resource uptake, sex Paradox Species interactions are cell-cell interactions - outcomes of ecological interactions are measured at the population level: abundance, growth rate, distribution - the processes that result in population dynamics occur at the individual level: feeding, motility, resource uptake, sex Paradox Incorporating intra-specific variability - variability in traits results in species having some ‘stronger’ and some ‘weaker’ competitors Paradox Competition with intra-specific variability - individual based competition model of 2+ species - intra-specific variability expressed as probability distribution of trait - randomly choose: competitive ability from probability density function that reflects variability uniform pdf - up to 10,000 individuals per species - up to 10,000 generations Competitive ability Paradox Competition with intra-specific variability Probability - variability results in species having ‘stronger’ and ‘weaker’ than average competitors - all identical mean Competitive ability Paradox Persistence in 2-species competition - frequency of 2 species persisted in 100 repeated, randomized simulations as a function of population size and duration % Paradox Menden-Deuer & Rowlett 2014 Persistence in multi-species competition - population size over time in repeated, multi species competitions Paradox Menden-Deuer & Rowlett 2014 Persistence in multi-species competition - population size over time in repeated, multi species competitions Paradox Menden-Deuer & Rowlett 2014 Persistence in multi-species competition - 100 species persist Paradox Menden-Deuer & Rowlett 2014 Probing the role of intra-specific variability - 14 behavior distributions - identical mean - increased variance - bimodal distributions Paradox Menden-Deuer & Rowlett, in prep. Probing the role of intra-specific variability - 14 behavior distributions - identical mean - increased variance - bimodal distributions Paradox Menden-Deuer & Rowlett, in prep. Survival probability - for each behavior/competitive ability distribution - survival probability in 100 replicated competitions simulations - variation in population size and duration Paradox Menden-Deuer & Rowlett, in prep. No penalty for type of variability distribution Paradox Menden-Deuer & Rowlett, in prep. Probing the role of intra-specific variability - 14 behavior distributions - identical mean - increased variance - bimodal distributions Paradox Menden-Deuer & Rowlett, in prep. Hyper-variability = invulnerable? Paradox Menden-Deuer & Rowlett, in prep. Conclusions/Implications - incorporation of intra-specific variability enhances biodiversity - diverse variability distributions support survival - intra-specific variability has adaptive value, independent of specific formulations: heterogeneity, no. of nutrients - intra-specific variability may be a mechanism for marine microbes to acclimate and ultimately adapt to changing ocean Paradox D. Jacobsen, 1999 Variability an integral trait? Paradox Illustration Josh Wood Rynearson & Menden-Deuer, in press Dennis Hlynsky Rhode Island School of Design