* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intentional Introduction: biological control
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
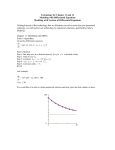
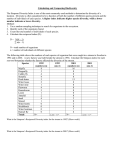
Questions DP Biology G3: Impact of Humans on Ecosystems 1. The ozone layer. a. State the chemical formula for ozone. O3 (1) b. State the role of ozone in the stratosphere. c. Distinguish between the ozone layer and the greenhouse layer, using a simple diagram. d. Outline the effects of CFC’s on the ozone layer. e. Outline the effects of UV radiation on living tissues and biological productivity. f. Describe the consequences of ozone layer damage due to CFC use in terms of long-term environmental and human health impacts. 2. Monitoring ecological systems. a. State the function of Simpson’s Diversity Index. b. List some of the uses of Simpson’s Diversity Index data in environmental decision making: c. Describe how Simpson’s Index could be used to compare two locations. d. Calculate Simpson’s Diversity Index for these two grassland areas: Grassland Site 1 Species A B C D E F G H Present y y y x x x x x N= number 65 12 8 0 0 0 0 O Σn= B C D E F G H 3 N-1= 2 n-1= Simpson’s Index: Grassland Site 2 Species A Present y X y y y y y y N= number 12 o 32 21 08 6 07 4 Σn= 7 N-1= n-1= Simpson’s Index: e. Deduce which site was a farmed area and which was wild. Explain your answer. 6 3. Read the article “Aborigines improve biodiversity by starting fires” and then work through this example of Simpson’s Diversity Index. The data have been simplified. (http://scienceblogs.com/notrocketscience/2008/09/aborigines_improve_biodiversity_by_starting_fires.php ) a. Species populations were recorded before and 5-years after fire. Calculate D for before and after the fires. Immediately prior to burning species count n(n-1) Five years post-burning species n(n-1) count A 125 A 16 B 21 B 45 C 14 C 34 D 8 D 95 E 7 E 25 F 5 F 36 G 5 G 80 H 5 H 101 ΣN ΣN ΣN(N-1) ΣN(N-1) Σn(n-1) D= ΣN(N-1) Σn(n-1) D= Σn(n-1) D= ΣN(N-1) Σn(n-1) D= b. Compare the diversity before and after the fires. c. Deduce which species in the table represents Spinifex. Explain your answer. d. Identify the type of ecological succession taking place in this situation. 4. Discuss the following reasons for conservation of biodiversity in rainforests: Ethical/moral Economical Economical Aesthetic 5. Introduction of non-native species. a. Define alien species. b. Outline the impacts of three examples of introduction of alien species: Intentional Introduction: food source Intentional Introduction: biological control Accidental Introduction: shipping or globalization c. Explain the effects of invasive alien species on native species, with examples: Predation Interspecific competition & competitive exclusion Habitat destruction Biological control Extinction d. Use the Global Invasive Species database to complete this information for a an invasive species found in your local area or home country (http://www.issg.org/database/welcome/) i. Binomial and common names and taxonomy ii. Native and introduced geographical ranges iii. Introduction pathways or vectors iv. Local dispersal methods v. Impacts vi. Management strategies e. Outline how Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus (RHDV) has been used for biological control in Australia. Problem: Solution: Effectiveness: 6. Pollution & the food chain a. Define biomagnification. b. Distinguish between bioaccumulation and biomagnification. c. Using a diagram or flow-chart, describe the cause and consequences of one named example of biomagnification.