* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7 – Our Planetary System 7.1 Studying the Solar System
Exploration of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Jumping-Jupiter scenario wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Space: 1889 wikipedia , lookup
Naming of moons wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
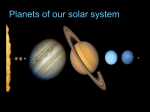
Chapter 7 – Our Planetary System 7.1 Studying the Solar System What does the solar system look like? • There are ___________ major planets with nearly circular orbits. • Pluto and Eris are smaller than the major planets and have more elliptical orbits – these are called _______________ _________________. • Planets mostly orbit in same _______________ (counterclockwise) and nearly in same __________________. What can we learn by comparing the planets to one another? • Comparing the planets reveals patterns among them. • Those patterns provide insights that help us understand our own planet. Similarities/Differences Terrestrial Planets - Gas Giants What are the major features of the Sun and planets? Planets are very tiny compared to distances between them. • Over 99.9% of solar system’s ___________________ • Made mostly of ____________________________ gas (plasma) • Converts 4 million tons of mass into ________________________ each second Sun Mercury • Made of _____________________________; large iron core • Desolate, _________________________; long, tall, steep cliffs; no _______________________ • Very hot and very cold: 425C or 800 F(day), –170C or -275 F (night) Venus • Nearly identical in __________________ to Earth; surface hidden by clouds • Hellish conditions due to an extreme ______________________________________________ • Even __________________ than Mercury: 470C or 880 F, day and night Earth • Only planet with ___________________ (so far) • The only surface ____________________________ water in the solar system • A surprisingly __________________________ moon Mars • A thin atmosphere but you can’t breathe it – no ________________________ • Giant volcanoes, a huge canyon, polar caps, more • Liquid water flowed in distant past; could there have been life? Jupiter • Much _____________________ from Sun than inner planets • Mostly _____________________________; no solid surface • 300 times more _____________________ than Earth • Many _______________, ______________________ • Jupiter’s 4 largest moons are called ____________________moons • Io: active ________________________all over • Europa: possible subsurface _______________________ • Ganymede: ________________________moon in solar system • Callisto: a large, cratered “_________________________________” Saturn • _____________________ and _________________ like Jupiter • Many moons, including cloudy _____________________, the only moon with an atmosphere • Spectacular __________________ • • Rings are ________________________; they are made of countless small chunks of ice and rock, each orbiting like a tiny moon. The Cassini probe has been orbiting and studying Saturn since 2004 Uranus • Smaller than Jupiter/Saturn; much larger than Earth • Made of H/He gas and hydrogen compounds (H2O, NH3, CH4) • Extreme axis _______________ • Also has ___________ and _________________ Neptune • Similar to Uranus (except for axis tilt) • Many moons (including Triton) Pluto and other dwarf planets • Much __________________ than major planets • Icy, comet-like composition • Orbit the sun but on a ________________________________ than the “regular” planets