* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LIGHT, ATOMS, AND TELESCOPES
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Architectural lighting design wikipedia , lookup
Daylighting wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
Doctor Light (Arthur Light) wikipedia , lookup
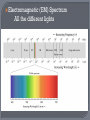
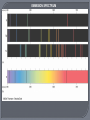
CH. 4 Energy that can travel through space from one point to another without any physical link We can see stars explode, but why can’t we hear them? Model A • Light is a wave that is a mix of electric and magnetic energy Model B • Stream of particles called photons Photons - packets of energy • Electrons & protons move in straight line that can act like waves Wave – Particle Duality • Scientists use which ever model the best fits a particular situation • Ex. Light reflecting off mirror (model B - photons) • Ex. Light focusing through a lens (model A - waves) Brightness • Measures the amount of energy carried by the light Height of wave (wave model) Number of photons (particle model) Color • Visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum • Determine light’s wavelength () Red = long , Blue = short • White light: Mix of all colors discovered by Newton with a prism and lens Electromagnetic (EM) Spectrum All the different lights Electromagnetic Spectrum • Spectrum of all different types of electromagnetic waves Use different waves to see what’s going on in space besides just visible light. • Radio Waves – longest Use every day – radio telescopes • Infrared – longer than visible light Can’t see it, but feel as heat • UV Light – shorter than visible light Infrared light is the Light that we perceive as heat. Almost everything Gives off Radio light. Including you. Very low Energy light. A slightly higher energy light that can interact with different substances and give them, different visible colors. Visible Light UV - Saturn UV - Rings E = hc/ • E = energy • h = constant • c = speed of light (constant) • = wavelength Means: • Shorter the wavelength, the higher the energy As object’s temp. increases: • Radiates light more strongly at shorter • Color changes: Red (long ), Yellow (medium ), Blue (short ) • Allows astronomers to predict temp. of stars Black Bodies • Objects that absorb all radiation • Reflect no light and looks black when cold See colors due to excited electrons • Absorption Atoms gain energy exciting electrons to higher energy levels • Emission Atoms lose that energy and emit a specific color of light Astronomers use spectrums to study star composition • Absorption Spectrum – shows λ of light absorbed • Emission Spectrum – shows λ of light emitted • Each λ of light that is absorbed or emitted can be match to a specific element EMMISION SPECTRUM ABSORPTION SPECTRUM Change from us in caused by motion towards or away Used to find/measure speed and direction of objects • Ex. Sirens Red Shift Blue Shift • appears to increase - Object is moving away • appears to shorten - Object is moving closer