* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
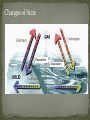
Matter is anything that has volume and mass. All matter is made of substances called elements. An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means. Elements are made up of atoms. All atoms consist of even smaller particles—protons, neutrons, and electrons. The center of an atom is called the nucleus, which is made up of protons and neutrons. A proton is a tiny particle that has mass and a positive electric charge. A neutron is a tiny particle with approximately the same mass as a proton, but it has no electrical charge Surrounding the nucleus of an atom are electrons, smaller particles that are in constant motion. An electron has little mass, but it has a negative electric charge that is exactly the same magnitude as the positive charge of a proton. In this representation of an atom, the fuzzy area surrounding the nucleus is referred to as an electron cloud. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons. However, the number of neutrons of an element’s atoms can vary. Atoms of the same element that have different mass numbers are called isotopes. The atomic mass of an element is the average of the mass numbers of the isotopes of an element. Radioactive decay is the spontaneous process through which unstable nuclei emit radiation. In the process of radioactive decay, a nucleus can lose protons and neutrons, change a proton to a neutron, or change a neutron to a proton. Because the number of protons in a nucleus identifies an element, decay can change the identity of an element. An atom that gains or loses one or more electrons from its outermost energy level has a net electric charge and is called an ion. •Positive ions – atoms that lose electrons •Negative ions – atoms that gain electrons The two most abundant elements in the universe are hydrogen and helium. However, the two most abundant elements in Earth’s crust are oxygen and silicon. A compound is a substance that is composed of atoms of two or more different elements that are chemically combined. Compounds have different properties from the elements of which they are composed. Compounds are represented by chemical formulas that include the symbol for each element followed by a subscript number showing the number of atoms of that element in the compound. (ex. MgCl2) Making Compounds A state of stability is achieved by some elements by forming chemical bonds. A chemical bond is the force that holds together the elements in a compound. Three types of bonds covalent – share electrons ionic – transfer electrons metallic – sea of electrons The change of one or more compounds into other compounds is called a chemical reaction. Chemical reactions are described by chemical equations. Example Water is formed by the chemical reaction between hydrogen gas (H2) and oxygen gas (O2). 2H2 O2 2H2O A mixture is a combination of two or more components that retain their identities. When a mixture’s components are easily recognizable, it is called a heterogeneous mixture. In a homogeneous mixture, also called a solution, the component particles cannot be distinguished, even though they still retain their original properties. A solution can be liquid, gaseous, or solid Solids are substances with densely packed particles, which can be ions, atoms, or molecules. Most solids are crystalline structures because the particles of a solid are arranged in regular geometric patterns, giving solids definite shape and volume. An increase in temperature increases the thermal vibrations of atoms in a solid. When thermal vibrations become vigorous enough to break the forces holding the solid together, the particles can slide past each other, and the substance becomes liquid. Liquids take the shape of the container they are placed in, but they do have a definite volume. Some vibrating particles can gain sufficient thermal energy to escape a liquid. This process of change from a liquid to a gas at temperatures below the boiling point is called evaporation. Gases, like liquids, have no definite shape. Gases also have no definite volume unless they are restrained by a container or a force such as gravity. Deposition Evaporation The periodic table of the elements is arranged so that a great deal of information about all of the known elements is provided in a small space. Generally, each element is identified by a one-, two-, or three-letter abbreviation known as a chemical symbol. All elements are classified and arranged according to their chemical properties in the periodic table of the elements. The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus is its atomic number. The sum of the protons and the neutrons in an atom’s nucleus is its mass number. This diagram of the element chlorine explains how atomic numbers and atomic mass are listed in the periodic table of the elements.