* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Brain Anatomy - Seattle Central College
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
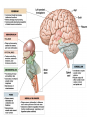
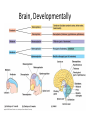
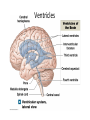
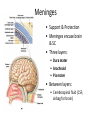
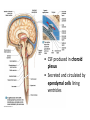
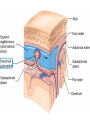
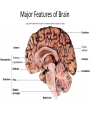
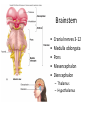
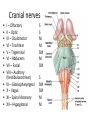
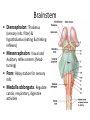
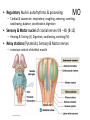
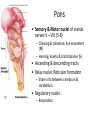
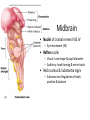
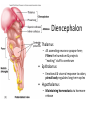
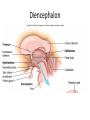
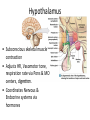
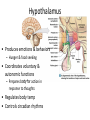
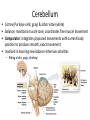
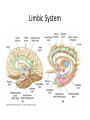
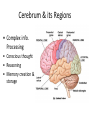
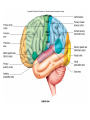
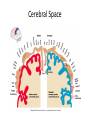
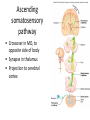
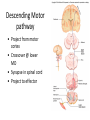
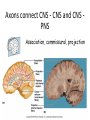
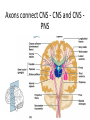
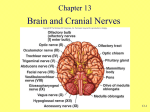
CNS Anatomy of the Brain & Cranial Nerves Major Structures & their function Meninges Major Regions Brain, Developmentally Ventricles Meninges • Support & Protection • Meninges encase brain & SC • Three layers: • Dura mater • Arachnoid • Pia mater • Between layers: • Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF; airbag for brain) • CSF produced in choroid plexus • Secreted and circulated by ependymal cells lining ventricles Figure 8.37b Major Features of Brain Brainstem • • • • • Cranial nerves 3-12 Medulla oblongata Pons Mesencephalon Diencephalon – Thalamus – Hypothalamus Cranial nerves • • • • • • • • • • • • I – Olfactory II – Optic III – Oculomotor VI – Trochlear V – Trigeminal VI – Abducens VII – Facial VIII – Auditory (Vestibulocochlear) IX – Glossopharyngeal X – Vagus XI – Spinal Accesory XII – Hypoglossal S S M M SM M SM S SM SM M M Brainstem • Diencephalon: Thalamus (sensory info. filter) & hypothalamus (eating & drinking reflexes) • Mesencephalon: Visual and Auditory reflex centers (headturning) • Pons: Relay station for sensory info. • Medulla oblongata: Regulate cardio, respiratory, digestive activities MO – Cardiac & vasomotor; respiratory; coughing, sneezing, vomiting, • Regulatory Nuclei: autorhythmic & processing swallowing, balance, coordination, digestion • Sensory & Motor nuclei of cranial nerves VIII – XII (8-12) – Hearing & Tasting (S), Digestion, swallowing, vomiting (M) • Relay stations (Pyramids): Sensory & Motor nerves – conscious control of skeletal muscle Pons • Sensory & Motor nuclei of cranial nerves V – VIII (5-8) – Chewing & salivation; Eye movement (M) – Hearing; kinetic & static balance (S) • Ascending & descending tracts • Relay nuclei: Reticular formation – Share info between cerebrum & cerebellum • Regulatory nuclei: – Respiration Midbrain • Nuclei of cranial nerves III & IV – Eye movement (M) • Reflex nuclei – Visual: Lens shape & pupil diameter – Auditory: head turning & nerve tracts • Red nucleus & Substantia nigra – Subconscious Regulation of body position & balance Diencephalon • Thalamus – All ascending neurons synapse here; Filters the humdrum & projects “exciting” stuff to cerebrum • Epithalamus – Emotional & visceral response to odors; pineal body regulates long-term cycles • Hypothalamus – Maintaining homeostasis via hormone release Diencephalon Hypothalamus • Subconscious skeletal muscle contraction • Adjusts HR, Vasomotor tone, respiration rate via Pons & MO centers, digestion. • Coordinates Nervous & Endocrine systems via hormones Hypothalamus • Produces emotions & behaviors – Hunger & food seeking • Coordinates voluntary & autonomic functions – Prepares body for action in response to thoughts • Regulates body temp • Controls circadian rhythms Cerebellum • Cortex (Purkinje cells; gray) & arbor vitae (white) • Balance; maintains muscle tone; coordinates fine muscle movement • Comparator: integrates proposed movements with current body position to produce smooth, exact movement • Involved in learning new balance-intensive activities – Riding a bike, yoga, climbing Movement & Body position Limbic System • Facilitates memory storage & retrieval • Establishes & drives emotional states • Links conscious with unconscious and autonomic functions of the brain stem Limbic System Cerebrum & its Regions • Complex info. Processing • Conscious thought • Reasoning • Memory creation & storage Cerebral Space Ascending somatosensory pathway • Crossover in MO, to opposite side of body • Synapse in thalamus • Projection to cerebral cortex Descending Motor pathway • Project from motor cortex • Crossover @ lower MO • Synapse in spinal cord • Project to effector Axons connect CNS - CNS and CNS PNS Association, commissural, projection Axons connect CNS - CNS and CNS PNS