* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ANXIETY DISORDERS - Wikispaces
Eating disorder wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Psychological trauma wikipedia , lookup
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive behavioral therapy wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Munchausen by Internet wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral theories of depression wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Drug rehabilitation wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Treatment of bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Treatments for combat-related PTSD wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
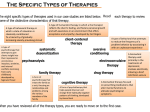
Psychological Disorders (7-9%) DEFINING ABNORMALITY Psychological Disorders: UMAD behavior that is Unjustifiable (irrational- does not make sense to most people) Maladaptive (harmful), Atypical (not shared by many others, unusual), Disturbing (to others-EX pedophilias sexual attraction to children). DSM IV TR: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual – Identifies Psychological Disorders. The DSM does not suggest causes or treatments. Clients are assessed at various AXIS levels, .Axis I is a clinical disorder, II is personality disorder, III is medical condition (physical related to mental) and IV psychosocial (stressful life events). Causes of Psychological Disorders Perspective Psychoanalytic / Psychodynamic Humanistic Behavioral Causes Internal, Unconscious childhood conflicts and/or repressed thoughts/ memories Failure to strive towards one potential (self-actualize), low self-esteem, lack of unconditional positive regard in one’s environment Behavior is learned through modeling or reinforcements of behavior, people are conditioned (through association) into behavior, the environment affects behavior Self-defeating, irrational and/or negative thinking, maladaptive thinking or interpretation of events. Biochemical imbalances (neurotransmitters), genetic predisposition for illness Cognitive Biomedical / Biological ANXIETY DISORDERS Phobias: irrational fears of specific object or situation (EX agoraphobia- open spaces) Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD): constant low-level anxieties Obsessive-Compulsive disorder (OCD): unwanted thoughts (obsessions) cause the need to engage in particular action or ritual (compulsions) to reduce the anxiety. Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD): flashbacks, nightmares because of involvement in war or natural disaster. Panic attacks: episodes of intense anxiety without any apparent provocation SOMATOFORM DISORDERS Hypochondriasis: complains of physical illness to doctor but cannot find cause Conversion disorder: people will complain of severe physical problem such as paralysis or blindness. They will be unable to move their arms or see but no biological cause can be identified. DISSOCIATIVE DISORDERS Dissociative Fugue or amnesia (not biologically caused) causes someone to suddenly be in unfamiliar environment after their brain dissociative from their real self. Dissociative Identity disorder: (aka multiple personalities) dissociate themselves from their true identity. Do not remember dissociation occurring. Caused by intense childhood physical/sexual abuse. Some claim the subject is role playing the disorder from the therapist’s questions’ MOOD OR AFFECTIVE DISORDERS Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) - experience depression when there is less sunlight. Treatment is light therapy Major Depressive disorder (unipolar depression)- the common cold of psychology. DSM criteria is more than 2 weeks of hopelessness, worthlessness, fatigue, and/or change of appetite, sleeping pattern. Women are 2 times more likely to get. Dysthymic Disorder mild depression 2 years or more Bipolar disorder (manic depressive): extreme highs (mania- characterized by high energy, confidence, creativity) and extreme lows (depression) SCHIZOPHRENIA Symptoms of schizophrenia: delusions (unrealistic beliefs) of persecution (people are out to get me), delusions of grandeur (belief that you have greater power/influence than you do. EX “I am the President” Hallucinations- hearing voices, seeing things that aren’t present, disorganized thinking. Positive symptoms – added unusual behaviors. Negative symptoms- absence of appropriate behavior. - Paranoid (delusions of persecution), Disorganized (word salad, neologisms), Catatonic (strange body postures, motionless), Undifferentiated (no particular category) Causes of Schizophreniastrong genetic influences through twin studies and the fact that 1% of population in almost all cultures has it excess of neurotransmitter dopamine. Parkinson’s Patients who take dopamine increasing meds often have hallucinations Correlates to Schizophrenia enlarged brain ventricles prenatal viruses PERSONALITY DISORDERS (PD’s) (least debilitating of all disorders but negatively affects people’s ability to function) Most PD’s can be deuced about it’s symptoms from the name EXCEPT antisocial Paranoid (mild persecution) Obsessive-Compulsive- OCD but not debilitated Dependent- need attention and help from others Narcissistic: seeing oneself as the center of the universe, self-absorbed, self-love Antisocial: little regard for other people’s feelings, no sense of guilt, often law breakers. Histrionic: overly dramatic behavior Other Psychological disorders include: philias (unusual sexual attractions to objects or persons), eating disorders, substance abuse, autism, ADHD David-Rosenhan Study: Faked a mental illness (said he heard voices) once labeled, every behavior within hospital was interpreted as a sign of schizophrenia. One of his confederates remained hospitalized for 58 days. (even acting normal). This showed the powerful influence of labeling someone with a disorder; it also questioned the care for the mentally ill. 1 Treatments of Psychological Disorders (5-7 %) HISTORYTrephining - holes placed in peoples heads might let the evil spirits out Dix, Pinel - movement to reform treatment of mentally ill, no longer caging/treating as criminals. Medical model- looked at mental illness as curable like physical illnesses. Deinstitutionalization (1950s) - emptying of institutions because of new attitudes and advent of drug therapy pros- save $, helped patients cons- led to increase of homeless. Preventive Psychology – focuses on preventing people from getting a disorder (reduces suffering for client and costs for society) Primary prevention – Reduce joblessness, homelessness, poverty, or prejudice Secondary prevention – includes getting treatment for those at risk. EX. grief counseling – the govt. offers counseling to war veterans Tertiary prevention – is stopping the manifested symptoms from becoming too severe. TYPES OF THERAPY Biological (Biomedical) Therapy - Psycho Surgery- destruction of part of the brain to change behavior o Prefrontal lobotomy- cuts the main neurons leading to the frontal lobe. Rarely done because of risks Electro Convulsive Therapy (ECT) - Electric current passed through both hemispheres of the brain. This is often used for severe depression. Side effects include memory loss. Drug therapy o antianxiety- Ex. Xanax, Valium (Tranquilzers- barbiturates) o antidepressants- Ex. Prozac, Zoloft, MAO inhibitors, SSRI’s (increase activity of serotonin) o anti-psychotic- Ex. Thorazine, Haldol (block receptors sites for Dopamine). Excessive use of these can lead to Tardiv Dyskenesia- muscle tremor associated with Parkinson’s o mood stabilizers- Ex. Lithium (Bi-Polar Disorder) Psychoanalytic Therapy Insight Therapies – revealing the repressed problems in the unconscious Hypnosis- people are less likely to repress troubling thoughts Free Association- to say whatever comes to mind without thinking (reveals clues and provides insight about what is really bothering us in our unconscious. Dream Analysis- through symbols reveal the latent (underlying) content of dream. Dreams are a window into the unconscious Resistance- patient disagrees with therapist’s analysis because painful thoughts are surfacing into the ego (denial is much easier), barrier to bringing out the unconscious Transference- patients sometimes transfer strong threatening feelings (of love or anger) they have toward parents or partners (or siblings) onto the therapist. (Resembles displacement) Behavioral Therapy Counter Conditioning- Reversing the present conditioned response. Systematic Desensitization- teaching client to gradually replace anxious feelings with relaxed ones. This is effective with phobias.(EX.- using anxiety hierarchy such as seeing a spider from 25 ft. away then seeing a spider crawl up your leg until the fear is extinguished) Exposure Therapy – exposure to what you normally avoid (virtual reality) Flooding therapy- exposure to fear but start with most frieghtening fear first. EX. Throw boy in room with dog. Aversive Conditioning- pairing unwanted behavior with an unpleasant stimulus (Ex. a nauseous pill is given to an alcoholic in his/her drink.) Alcohol is associated with sickness. Bed wetters can be shocked out of unwanted behavior. Modeling- watch people behave in a calm manner. Token economy- rewarded for every wanted behavior. Cognitive Therapy (Beck) Changing/Challenging thought patterns or beliefs about themselves or events. Emphasis on more positive thinking. Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT. Ellis) replaces irrational beliefs with rational ones aka cognitive restructuring. Humanistic Therapy (Rogers, Maslow, Perls - Gestalt) Client or person- centered therapy (Rogers) in which the therapist accepts the client no matter what he says/does (unconditional positive regard), shows empathy, uses active listening (EX. paraphrasing feelings/statements by client). Therapist helps client to self-actualize and grow as a person. Gestalt Therapy (Perls) – get in touch with the “whole” self. Existential Therapy – finding meaning within life Group Therapy- family therapy or AA where one sees that they are not alone with problems. 2